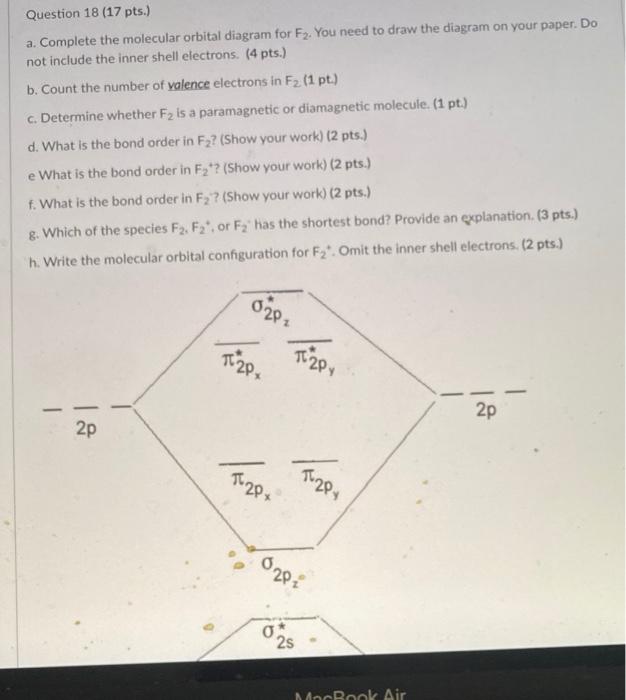
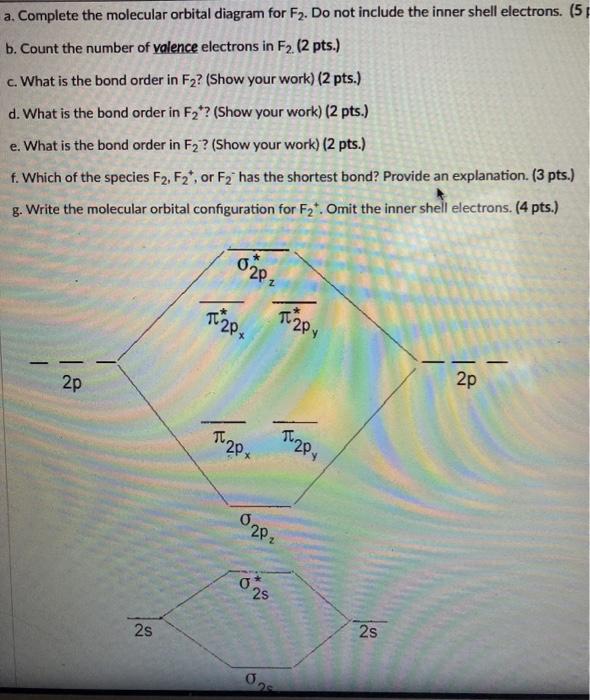
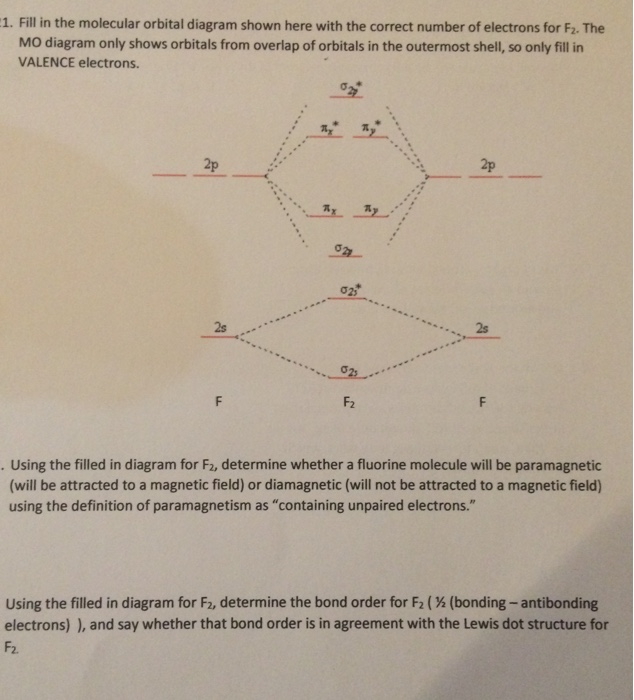
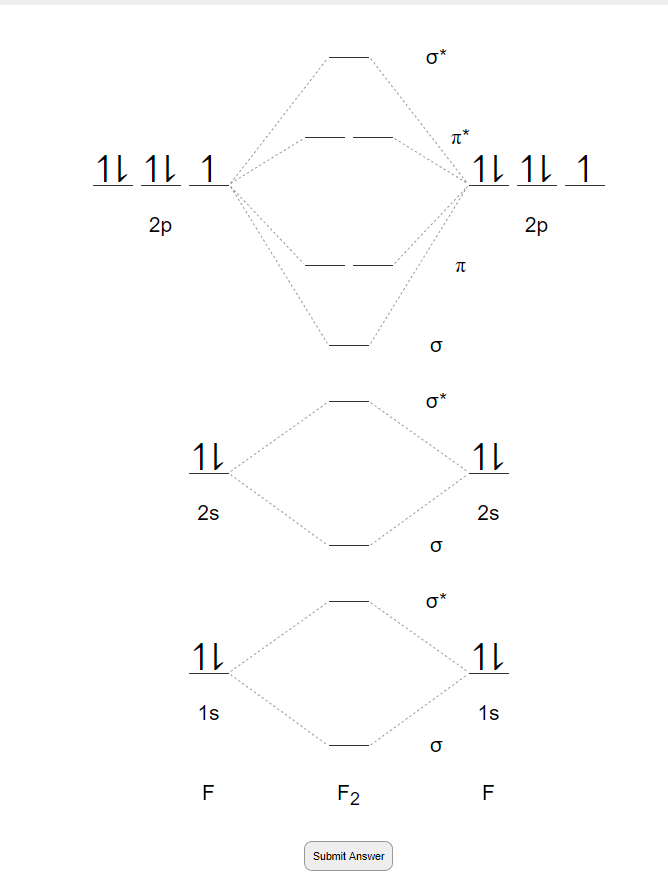
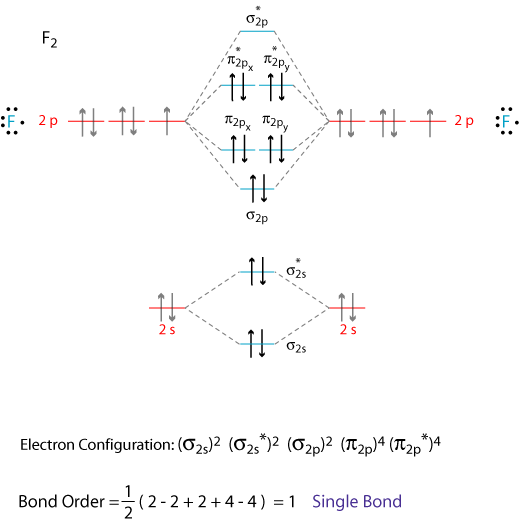
43 molecular orbital diagram of f2
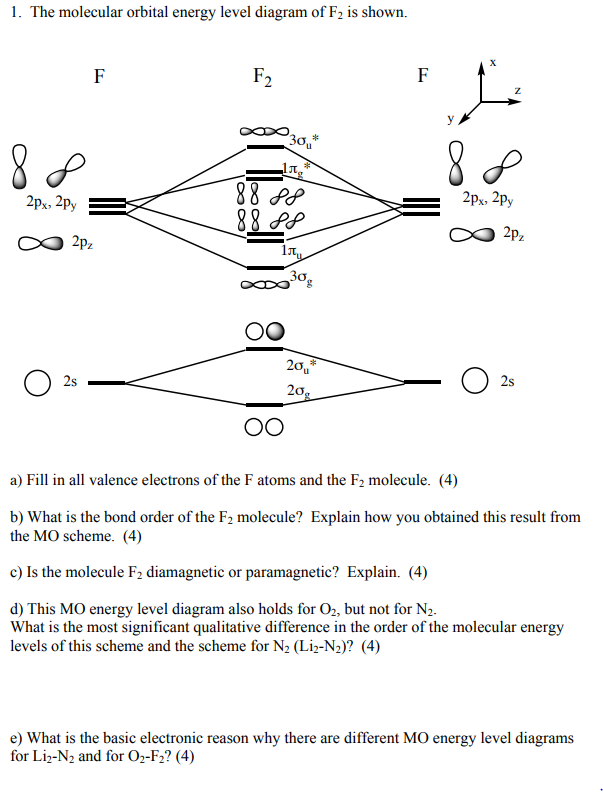
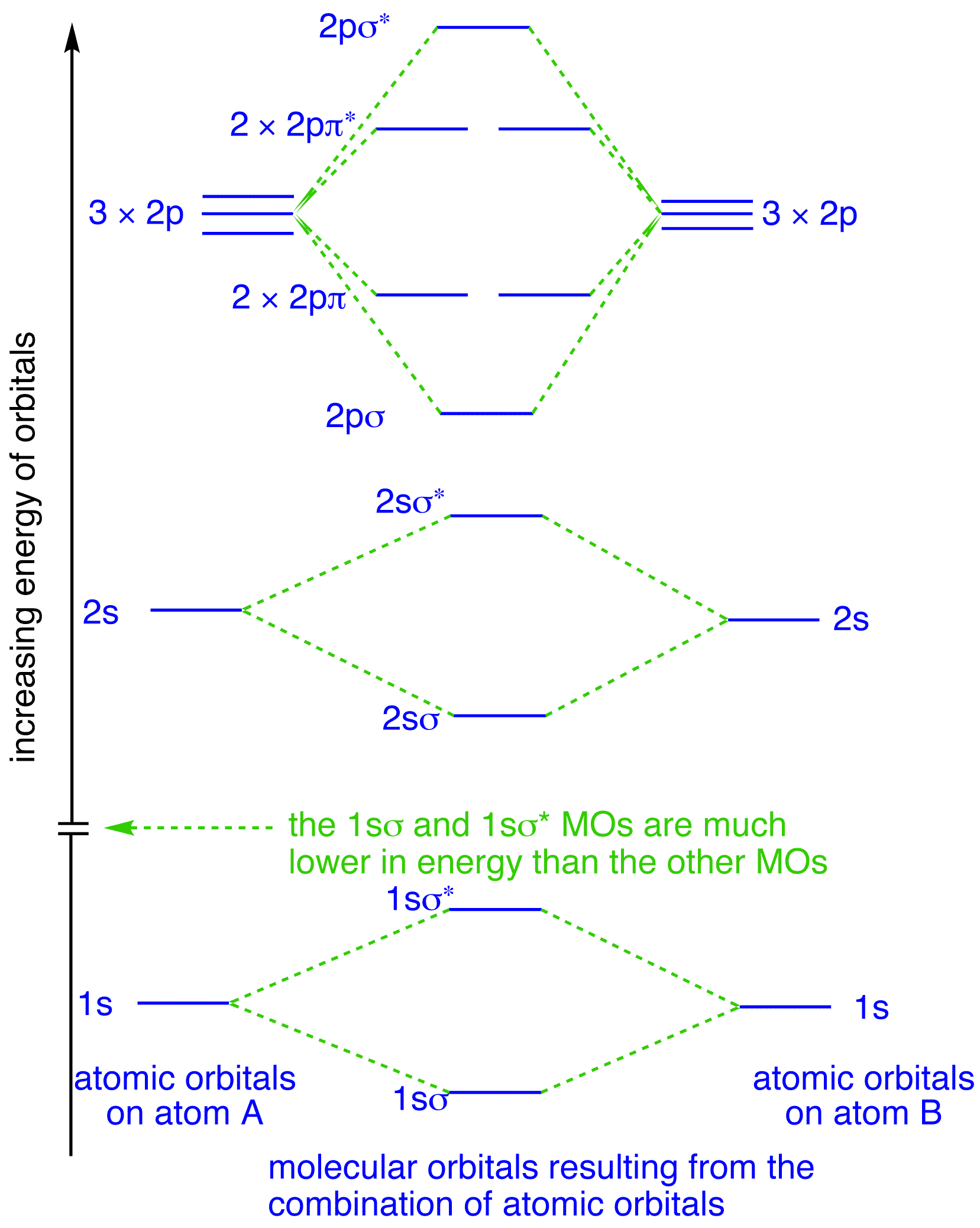
What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2? - Answers So, since oxygen has two unpaired electrons in the molecular orbital diagram it will have the strongest mass shift on a magnetic susceptibility balance. No, it is not correct to say that the bond energy always decreases when a diatomic molecule loses an electron. F2 and O2 are counterexamples to... Asked for: "skewed" molecular orbital energy-level diagram, bonding... Figure 4.10.1: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules.(a) For F2, with 14 valence electrons (7 from To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for O2, we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in...
MO Diagrams | Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
Molecular orbital diagram of f2
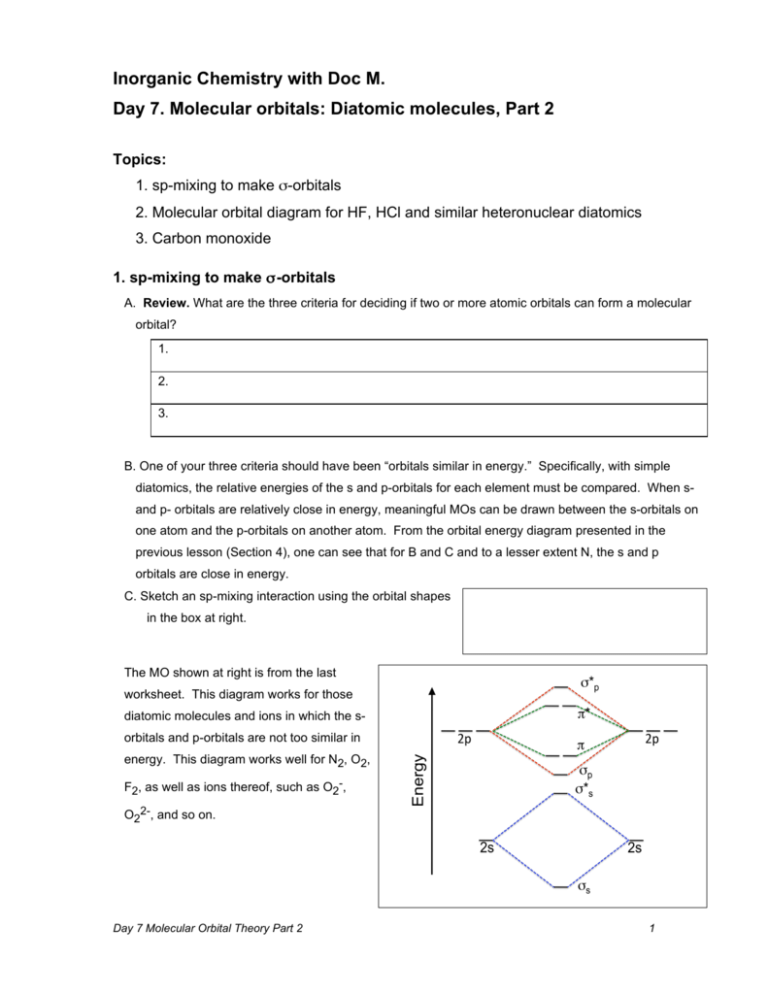
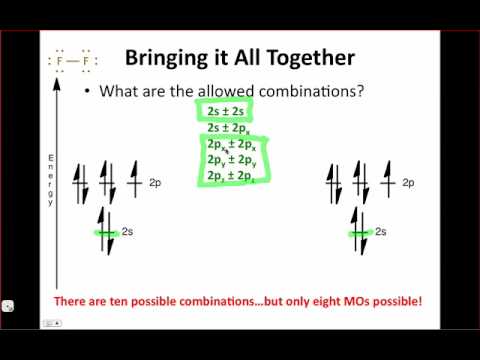
Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center. Atomic orbitals (AO) energy levels are shown for comparison. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels. Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals) The diagram shows how the molecular orbitals in lithium hydride can be related to the atomic orbitals of the parent atoms. Notice that the relative energies of the 2p-derived σ and π bonding molecular orbitals are reversed in O2 and F2. This is attributed to interactions between the 2s orbital each atom... AP Chemistry - Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Diatomic molecules: The bonding in F 2 2p xA + This produces an MO around both F atoms that has two nodes: one on the Diatomic molecules: MO diagrams for Li 2 to F 2 Molecular Orbital Theory In this diagram, the labels are for the valence shell only - they ignore the...
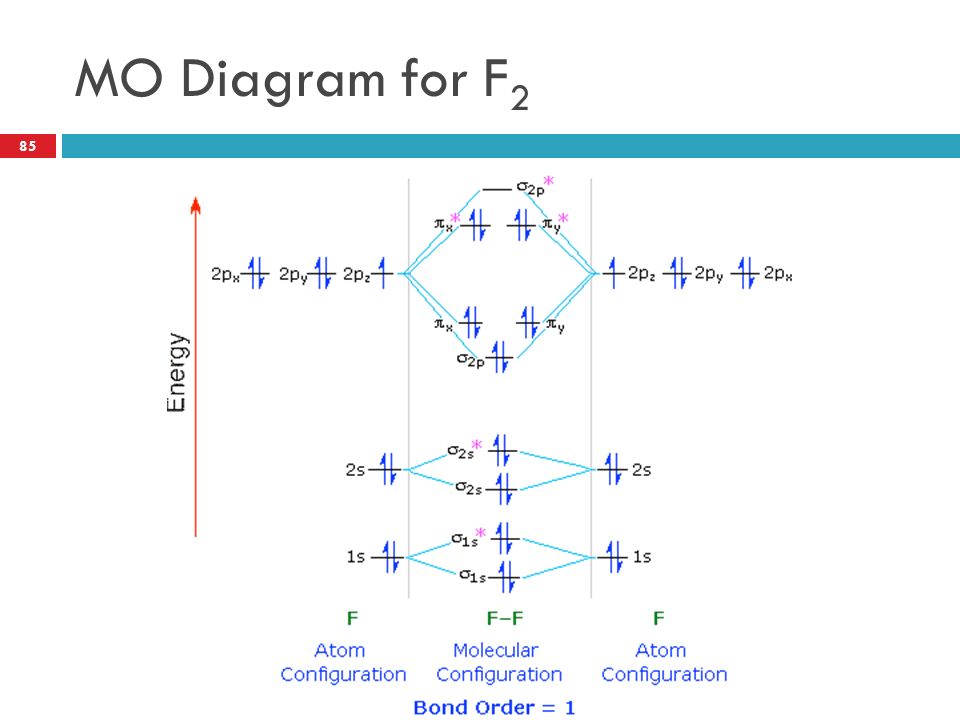
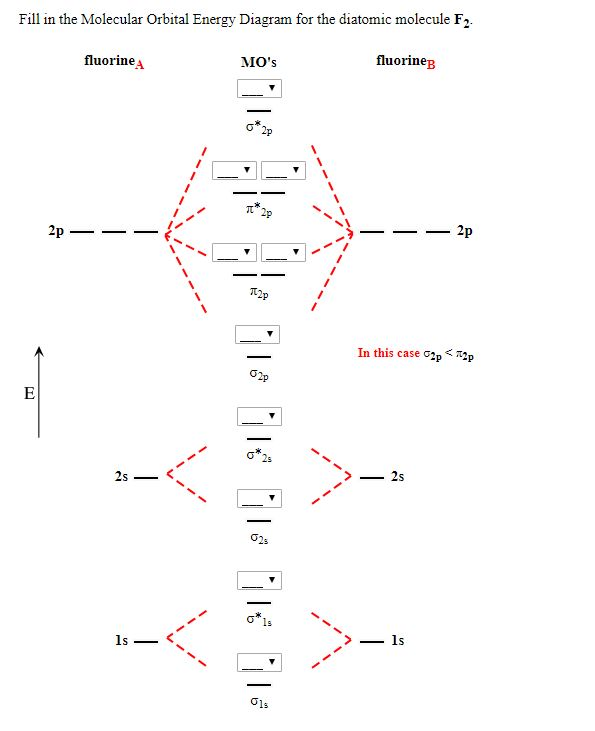
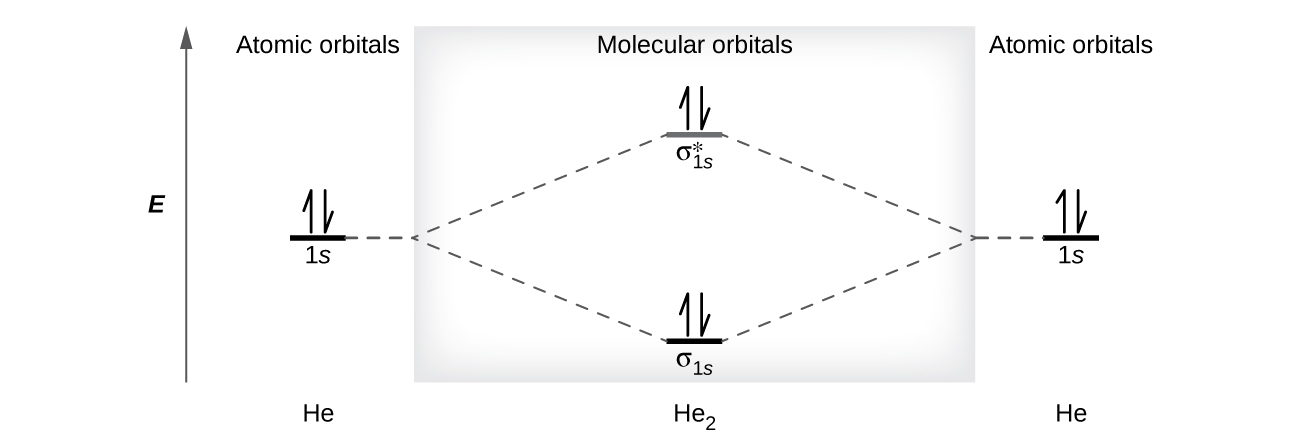
Molecular orbital diagram of f2. F2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram - Techiescientist As per molecular orbital (MO) theory, all the constituent atoms in a molecule contribute to the formation of molecular orbitals. Let us have a look at the MO diagram for F2. The 2s orbitals of both F atoms mix to form a low energy bonding orbital and a high energy antibonding orbital (as shown... PDF Chapter 5 | 5.2.2 Orbital Mixing Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules; it comple-ments and extends the introductory bonding models in Chapter 3 . In molecular in the schematic sketches on the left of the energy level diagram and in the calculated molecular orbital images on the right.* Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified | by Megan A. Lim | Medium Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories If you can understand the foundation and skeleton of the diagram specific to that molecule, then it will be easier and faster for you to draw it. PDF Molecular Orbitals in | 9-2 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Molecular orbital calculations indicate, however, that for O2, F2, and hypothetical Ne2 molecules, the 2p orbital is lower in energy The energy level diagram for He2 is similar to that for H2 except that it has two more electrons. These occupy the antibonding 1#s orbital (see Figures 9-5a and 9-6b and...
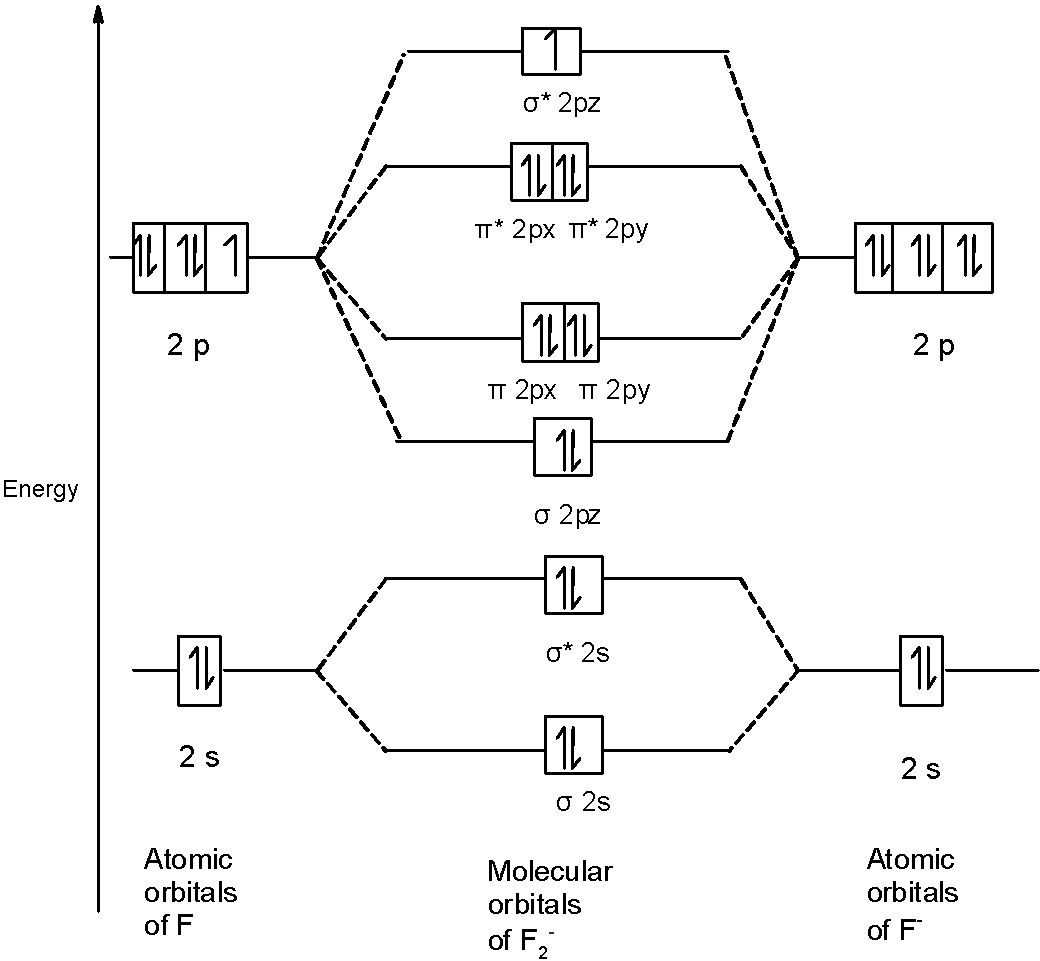
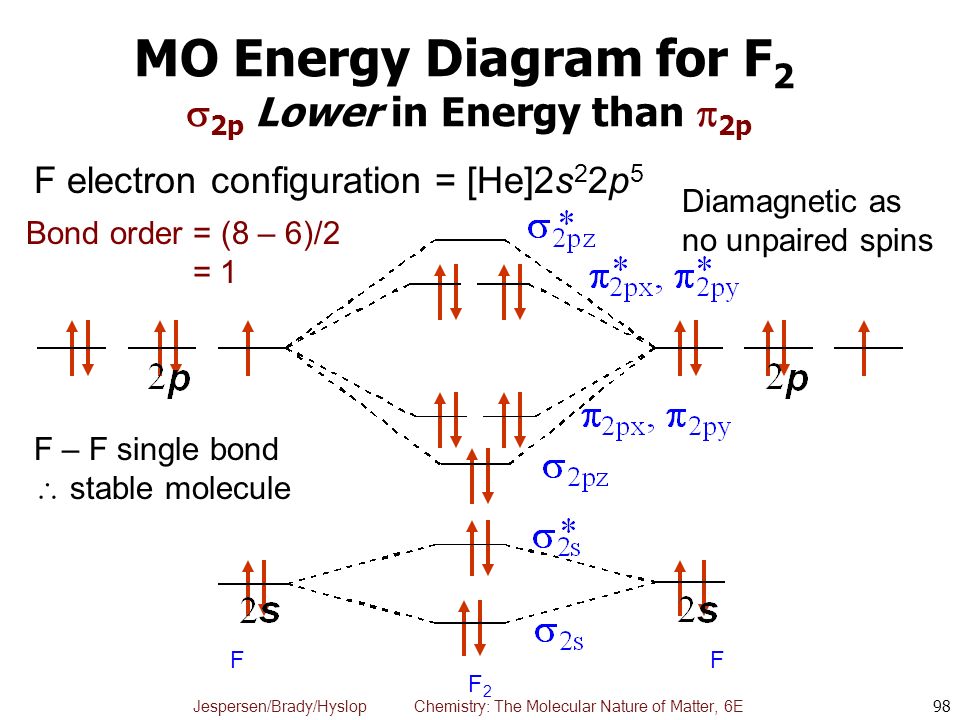
PDF Figure 9.32: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for • The following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the... Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), Chemistry Study... | eMedicalPrep The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. This kind of mixing of orbitals or symmetry interaction is not applicable for O2 and F2 molecule formation because of larger energy gap between 2s and 2p orbitals for these atoms. PDF Slide 1 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram for a Heteronuclear Diatomic. F2s non-bonding - too low in energy F2px,2py non-bonding because of wrong symmetry. Molecular Orbitals in Polyatomic Molecules. Molecular Orbital Theory The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions Experiments have shown that O2 and F2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but B2, C2, and N2 are best described by a model that...
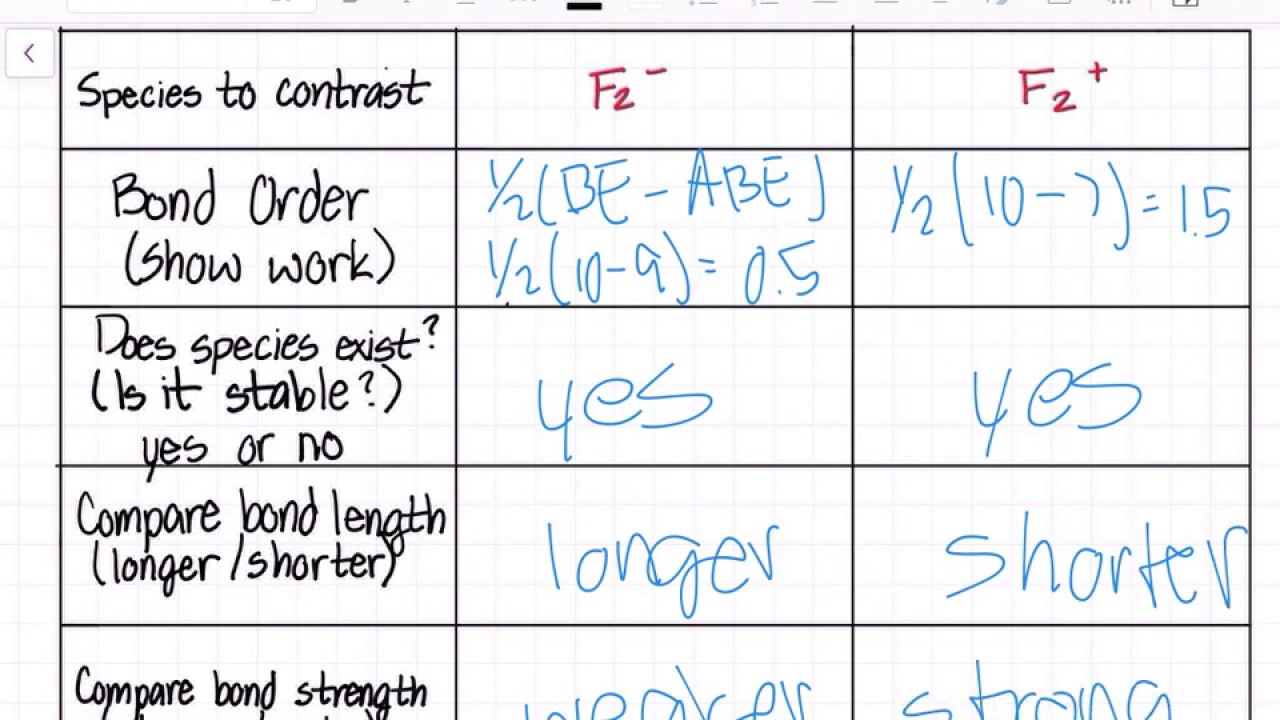
PDF PowerPoint Presentation | VB Theory and Orbital Hybridization Molecular Orbital Diagrams. An MO diagram, just like an atomic orbital diagram, shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each MO. molecule has opposite effects: N2+ has a weaker longer bond than N2, but O2+ has a stronger, shorter bond than O2. Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry/Molecular Orbital Theory... Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. Figure 2. Qualitative molecular orbital diagram of HF −. The 2σ... Download scientific diagram | Qualitative molecular orbital diagram of HF −. The 3σ orbital is a combination of the F 2p z and H 1 s orbitals and is bonding, whereas the F 2p x and 2p y orbitals cannot interact with the H 1 s orbital due to different symmetries and serve as non-bonding orbitals. 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 8). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right.
PDF lecture_6 Molecular orbital 'resembles' the atomic orbital to which it lies closest in energy. Always break MO diagrams down into components based on symmetry. Walsh diagrams summarise changes in MO diagram wrt structure note a combination of first and second order effects.
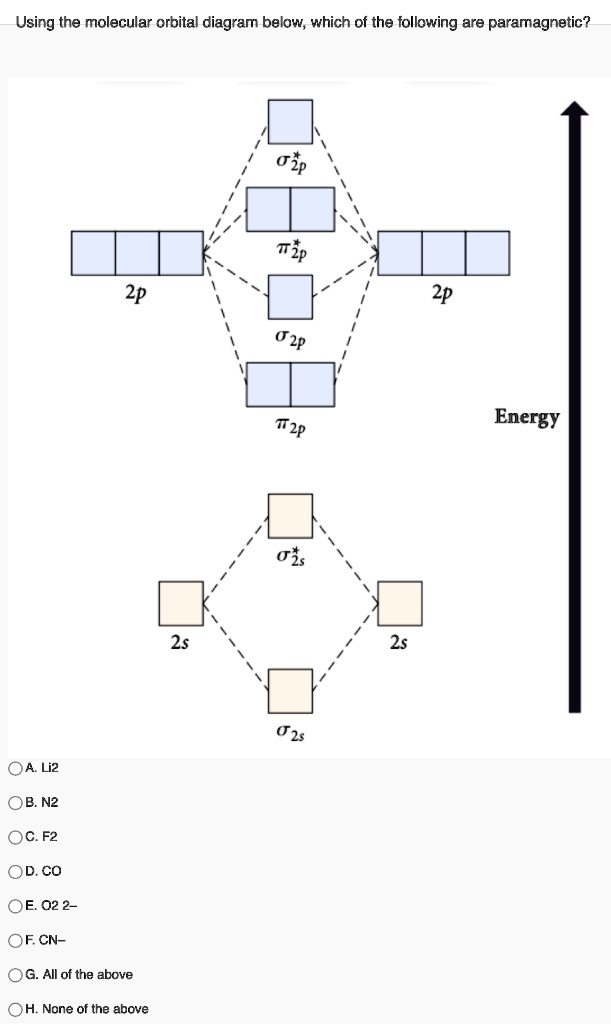
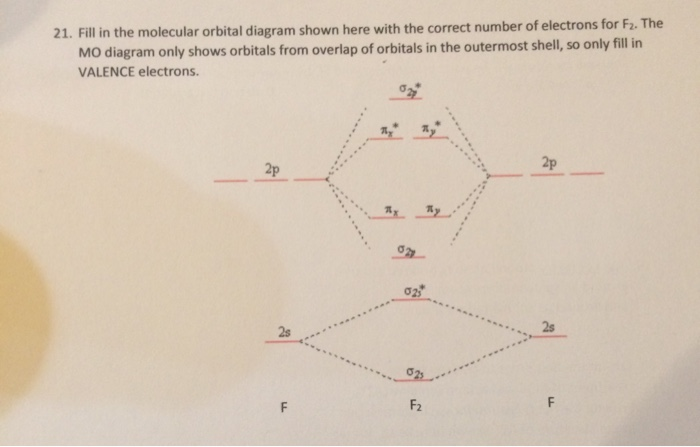
Chapter 9 Molecular Orbitals in Chemical Bonding (Midterm) | Quizlet molecular orbital diagram for F2. number of elections in the sigma*2p molecular orbital is. their molecular orbital diagrams are more symmetrical than those of homonuclear diatomic molecules. which of the following statements about nitrogen oxide, NO, is FALSE.
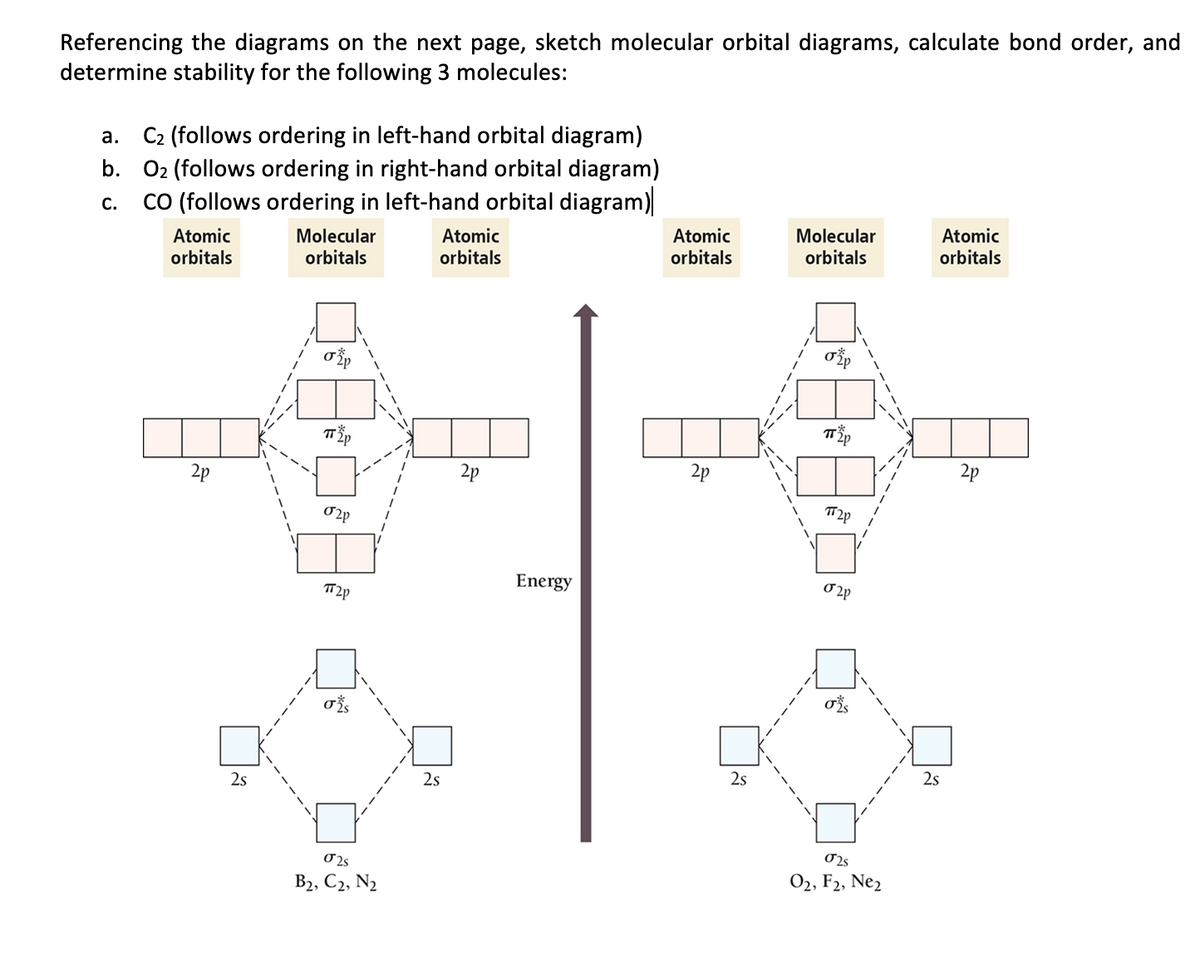
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory... Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. • When bonds are formed, atomic orbitals combine according to their symmetry. C2 12 2 0 N2 14 3 0 O2 16 2 2 F2 18 1 0 Ne2 20 0 0.
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.ppt... CD contains interactive energy diagrams. • It is a waste of both the lecturers and students time if the tutorial to ends up being a lecture covering questions. 5. An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.
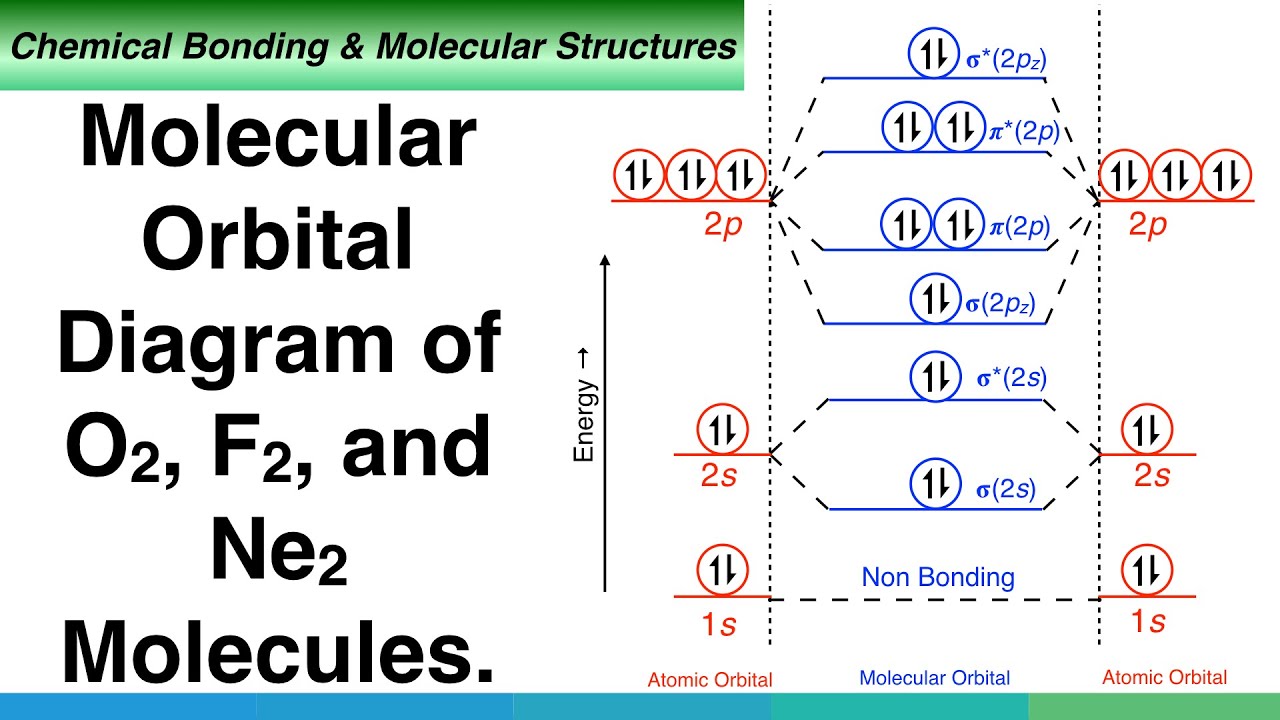
Molecular Orbital Diagram of O2, F2, and Ne2 Molecules. - YouTube Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram of Polyatomic molecules Beryllium dihydride (BeH2) and Water (H2O).
What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2? - Quora Something went wrong. Wait a moment and try again. Try again.
PDF Microsoft Word - Handin8s2017ans.docx 1. Sketch the qualitative molecular orbital diagram for XeF2. The molecule is linear and symmetric. The XeF2 is an electron excess molecule. You can think of the molecule as the complex between Xe and F2, both of which are closed shell.
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals - Chemical Bonding and... Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons. 3) If Nb = Na ,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of...
electronic configuration - Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and... I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. Now note that even in this advanced molecular orbital theory a bunch of approximations is introduced, and the answer in general depends on at...
What is the molecular orbital diagram for B_2? | Socratic Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy.
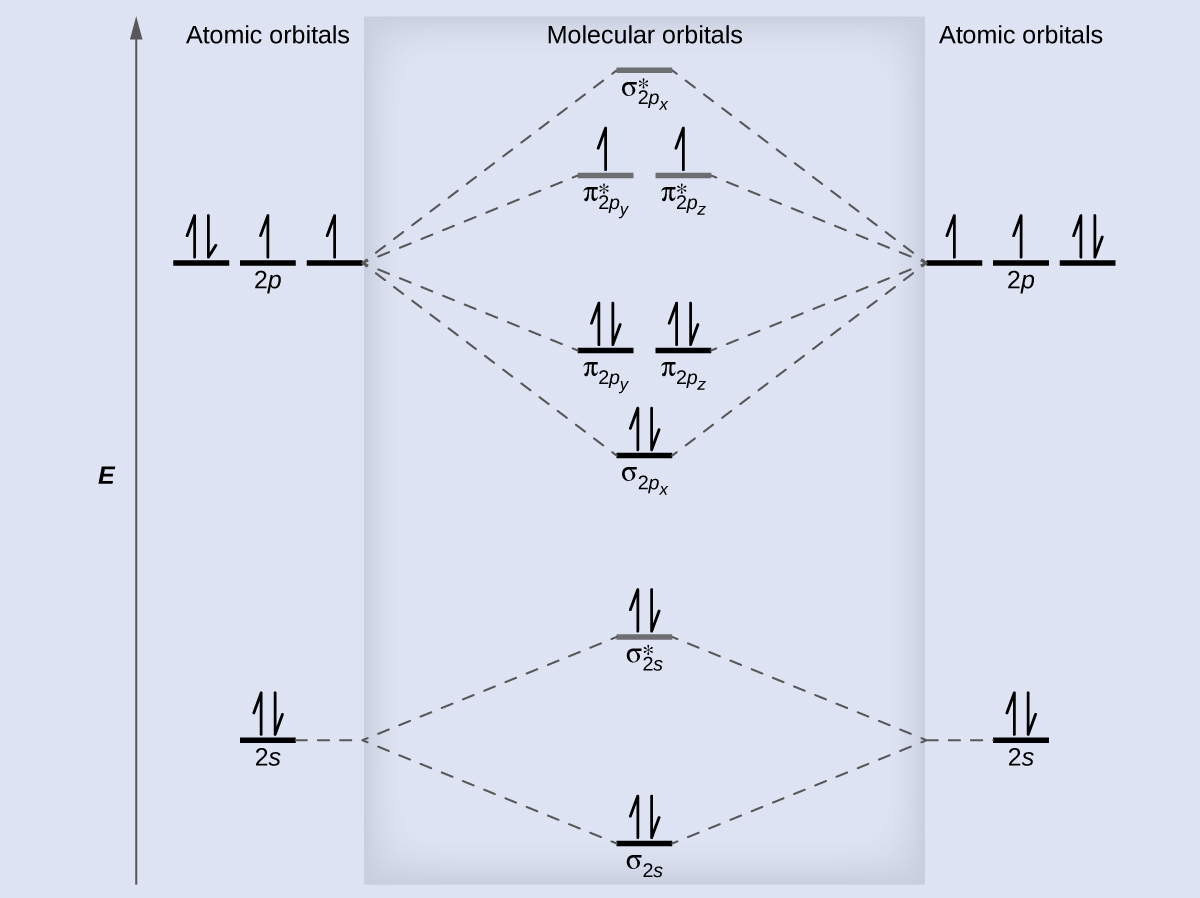
8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Figure 8.34 This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic.
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
AP Chemistry - Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Diatomic molecules: The bonding in F 2 2p xA + This produces an MO around both F atoms that has two nodes: one on the Diatomic molecules: MO diagrams for Li 2 to F 2 Molecular Orbital Theory In this diagram, the labels are for the valence shell only - they ignore the...
Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals) The diagram shows how the molecular orbitals in lithium hydride can be related to the atomic orbitals of the parent atoms. Notice that the relative energies of the 2p-derived σ and π bonding molecular orbitals are reversed in O2 and F2. This is attributed to interactions between the 2s orbital each atom...
Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center. Atomic orbitals (AO) energy levels are shown for comparison. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.













Comments
Post a Comment