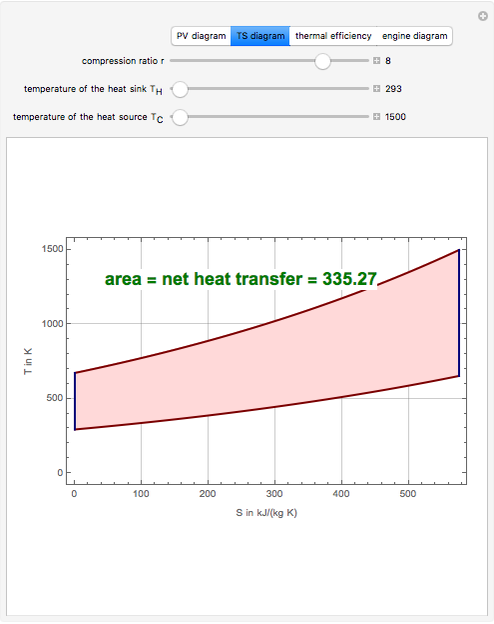
43 otto cycle ts diagram
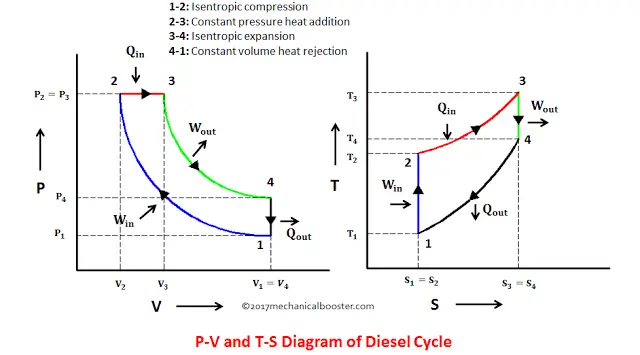
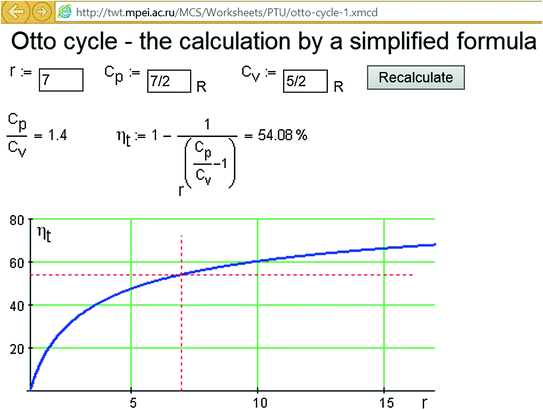
The Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle proposed by Nikolaus August Otto in 1876. This cycle describes the functioning of a typical reciprocating piston engine (see snapshot 4 or the "engine diagram" button). This thermodynamic cycle is used in automobile engines. This cycle consists of two adiabatic and two isochoric transformations. Power cycle 2:OTTO CYCLE. Q.3) Draw Otto Cycle on PV and TS diagram?Write formula for its efficiency. Ans : The air-standard-Otto cycles is the idealized cycle for the spark-ignition internal combustion engines (SI engines or Petrol Engines).This cycles is shown above on P-V and T-S diagrams.
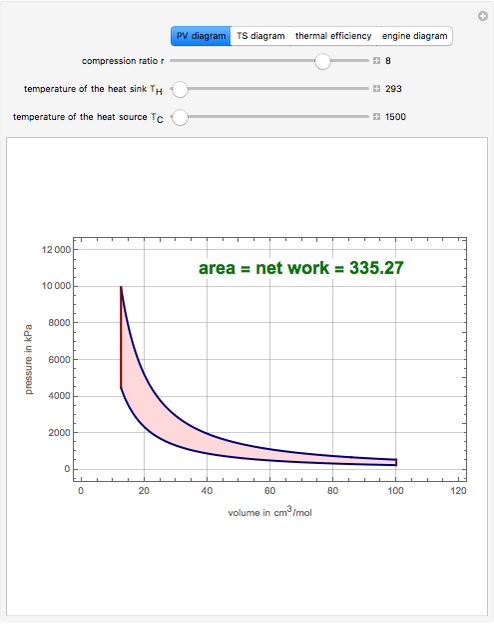
pV diagram of Otto Cycle. The area bounded by the complete cycle path represents the total work that can be done during one cycle. The Otto cycle is often plotted on a pressure-volume diagram (pV diagram) and a temperature-entropy diagram (Ts diagram).When plotted on a pressure-volume diagram, the isochoric processes follow the isochoric lines for the gas (the vertical lines), adiabatic ...
Otto cycle ts diagram
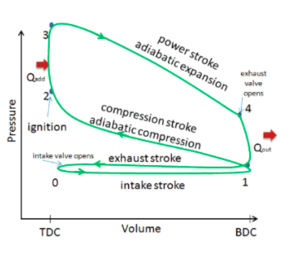
Answer (1 of 2): The above diagram is the T-S diagram for an Otto cycle. Process 1–2 - This represents the isentropic compression process. It is carries out reversibly and adiabatically i.e. isentropically. So the entropy remains constant. The temperature changes according to the relation - T_... Otto cycle is a thermodynamic cycle upon which a spark ignition engine works. Spark Ignition (or SI) engine uses petrol (or Gasoline) as fuel. Otto cycle was invented by Nicolas Otto in 1876. Spark ignition engine is a type of internal combustion engines.. Below are P-V and T-S Diagrams of the Otto Cycle. PV and TS diagram of Otto cycle Intake Stroke (Green line): In this stroke, the piston sucks air and petrol mixture into the combustion cylinder by moving from TDC to BDC. During the piston's movement toward the BDC, the chamber volume increases due to that a vacuum creates inside the chamber.
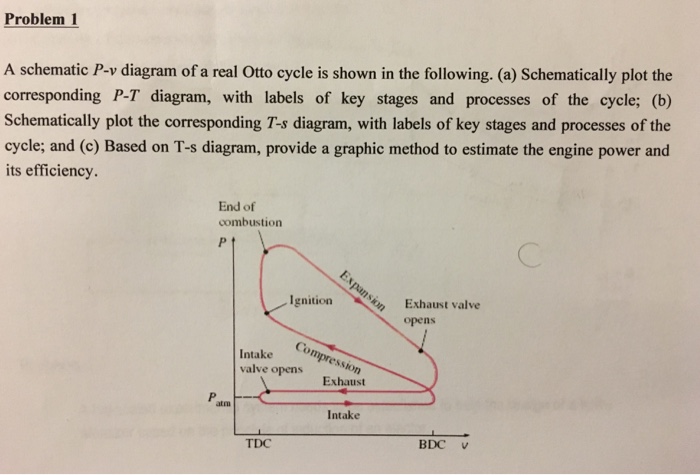
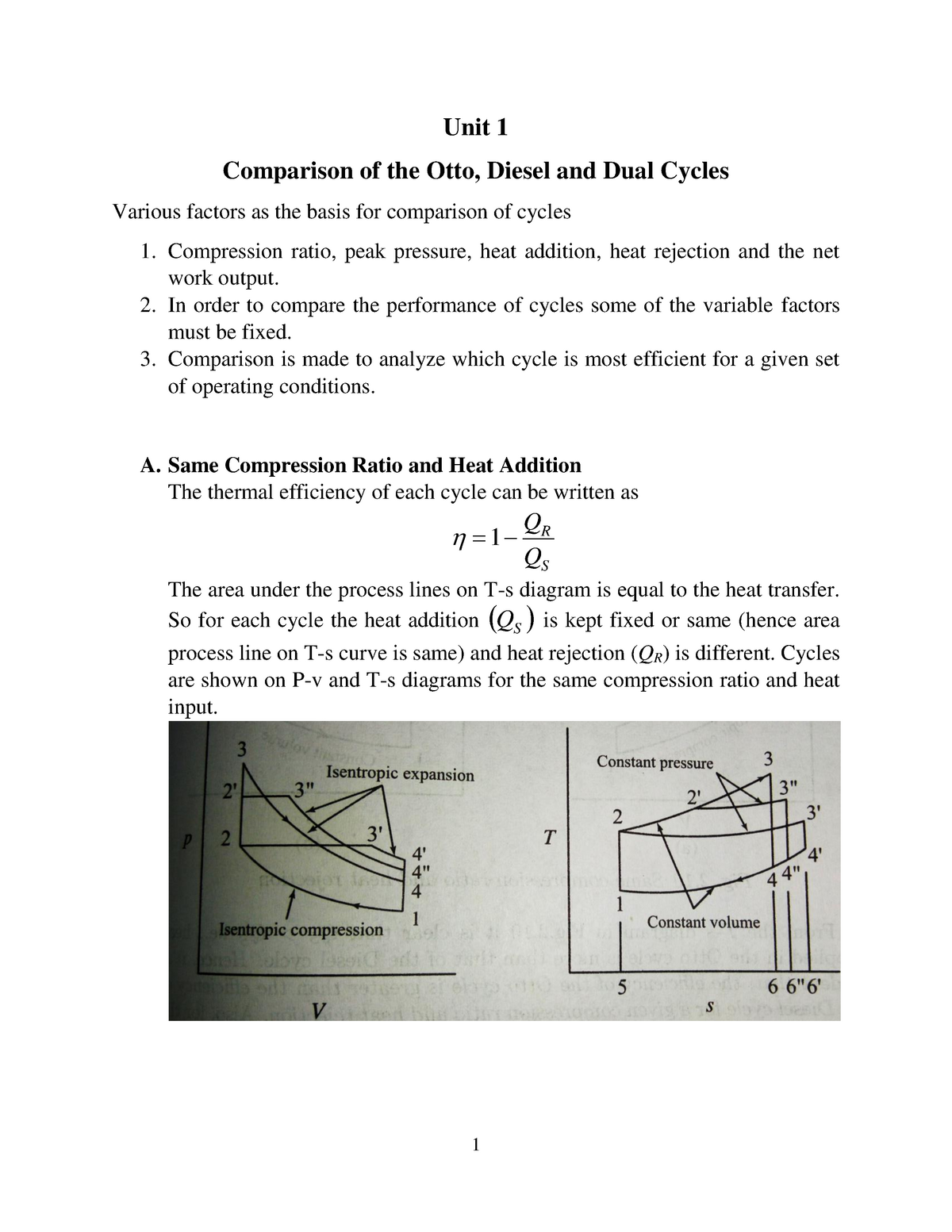
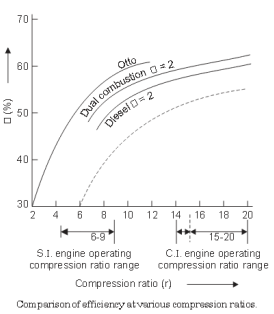
Otto cycle ts diagram. Answer (1 of 10): Carnot Cycle Carnot cycle is a reversible cycle where a working fluid goes under a cycle with working process Isothermal heat addition, Icentropic expansion, Isothermal heat rejection and finally Icentropic compression. Carnot cycle has the most efficiency of all the working c... Diesel Cycle is used in two-stroke and four-stroke diesel engine. The diesel cycle produces more amount of power compared with less fuel to the Otto cycle. The diesel engine is used in heavy vehicles like Car, Trucks, Generator, and Buses extra. The fuel system is larger here but where in Otto cycle has smaller. Otto Cycle: 8. Ideal Diesel Cycle: 9. Dual Cycle: 10. Carnot Cycle: A Carnot Cycle acting as a heat engine illustrated on a temp-entropy diagram. The Cycle takes place between a hot reservoir and a cold reservoir. The Carnot Cycle describes the operation of refrigerators, the Otto Cycle describes the operation of internal combustion engines, and the Brayton Cycle describes the operation of gas turbine engines. P-V and T-s diagrams are often used to visualize the processes in a thermodynamic cycle and help us better understand the thermodynamics of engines.
A PV diagram of the air standard Otto cycle is shown in Figure 2. The constant-volume process is thermodynamically efficient and, in principle, a feasible cycle ... It is description of cycle diagram of the otto, diesel and dual cycle.. Hope you like it. What is Otto Cycle – P-V and T-S Diagram Easiest Explanation? The Otto cycle was given by Dr. Nikolaus August Otto. It is a gas power cycle that is used in spark ignition engine (i.e. petrol engine) for its working. The entire modern petrol engine works on Otto cycle. It consist of four processes, Two isentropic (reversible adiabatic ... Here we understand what is otto cycle T-S diagram and otto cycle P-V diagram. There are four processes in the cycle: Isentropic (reversible adiabatic) compression Constant volume (Isochoric) heat addition Isentropic (reversible adiabatic) Expansion Constant volume of heat rejection.
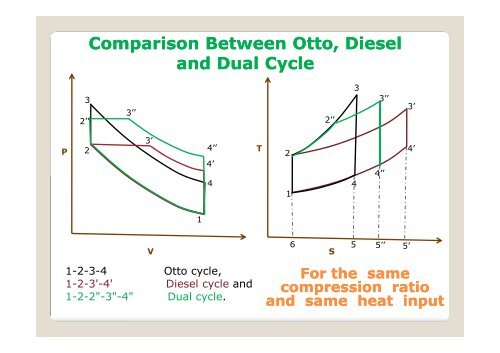
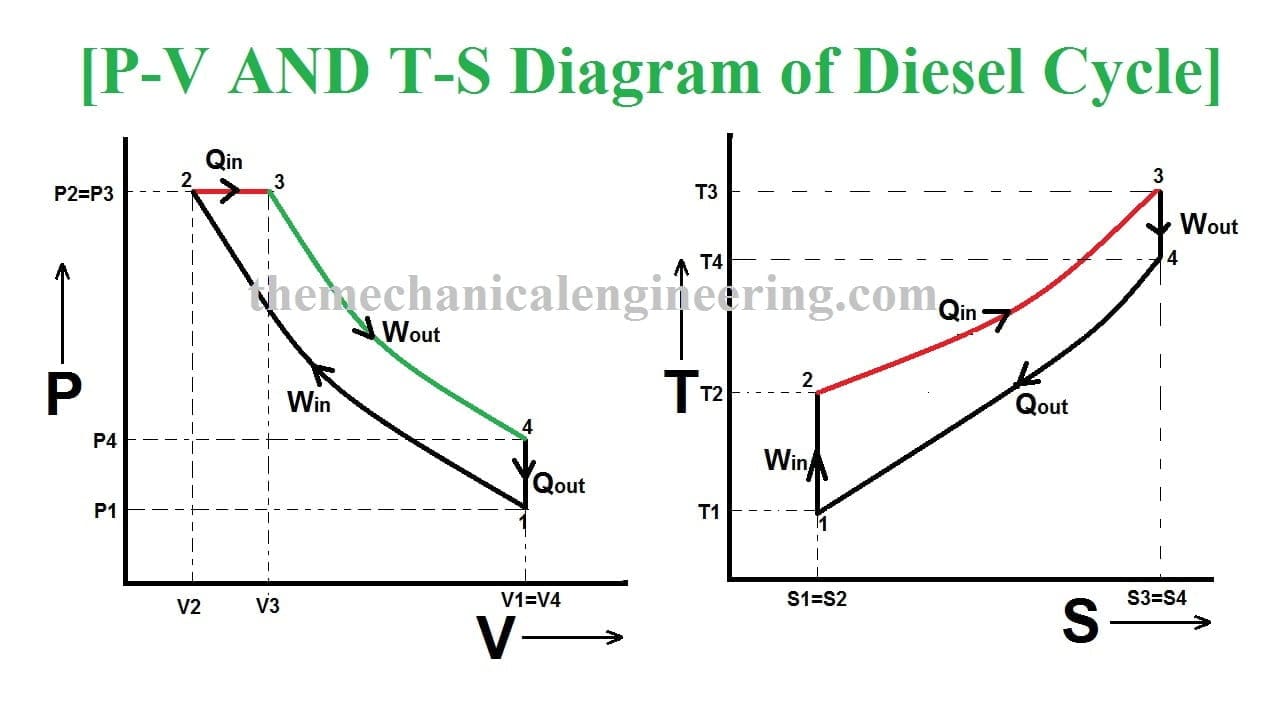
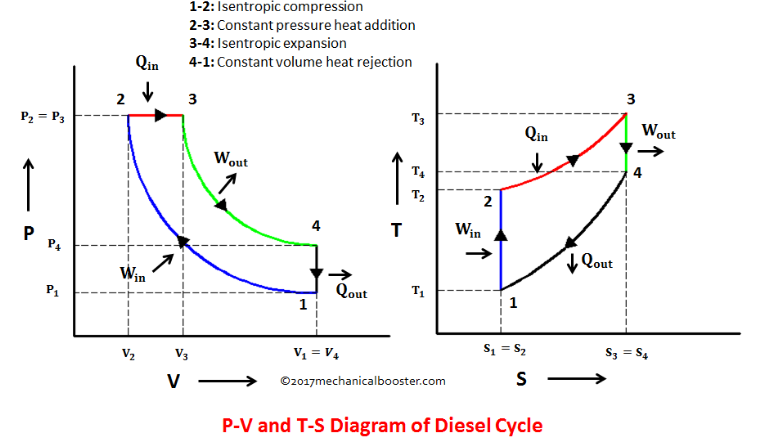
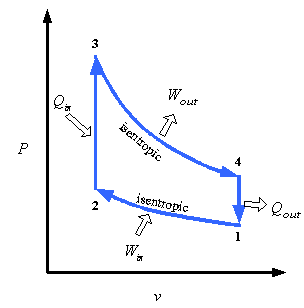
12 Difference Between Diesel Cycle And Otto Cycle (With Diagram) SHARE. Facebook. Twitter. An Otto cycle is an ideal thermodynamic cycle that describes the function of a spark ignition piston engine. The idea of Otto cycle was first proposed by Nicolas Otto back then in 1876. It is the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines. Efficiency of the Otto Cycle vs. Carnot Cycle • There are only two temperatures in the Carnot cycle • Heat is added at T H ... State Diagrams for the Diesel Cycle. Diesel Cycle Otto Cycle The only difference is in process 2-3. Consider Process 2-3 • This is the step where heat is transferred into the Diesel Cycle - Process with P-V and T-S Diagram. The diesel cycle was invented by Rudolph Diesel in 1893. He put forward an idea by which we can attain higher thermal efficiency, with a high compression ratio. All diesel engine works on this cycle. Diesel is used as fuel in this cycle as it can be compressed at higher compression ratio. The following diagrams represent the Otto cycle in a 4-stroke engine in both PV and TS coordinates. The thermodynamic transformations that take place during the Otto cycle are: 1-2. Adiabatic and isentropic transformation (without heat exchange with the outside).
An isentropic process is athermodynamic process in which the entropy of the fluid or gas remains constant. It means the isentropic process is a special case of an adiabatic process in which there is no transfer of heat or matter. It is a reversible adiabatic process. The assumption of no heat transfer is very important since we can use the adiabatic approximation only in very rapid processes. Isentropic Process and the First Law For a closed system, we can write the first law of thermodynamics in terms of enthalpy: dH = dQ + Vdp or dH = TdS + Vdp Isentropic process (dQ = 0): dH = Vdp → W = H2– H1→ H2– H1= Cp(T2– T1) (for ideal gas) Isentropic Process of the Ideal Gas The isentropic process (a special case of the adiabatic process) can be expressed with the ideal gas lawas: pVκ= constant or p1V1κ = p2V2κ in which κ = cp/cv is the ratio of thespecific heats (or heat capacities) for the gas. One for constant pressure (cp) and one for constant volume (cv). Note that this ratio κ = cp/cv...
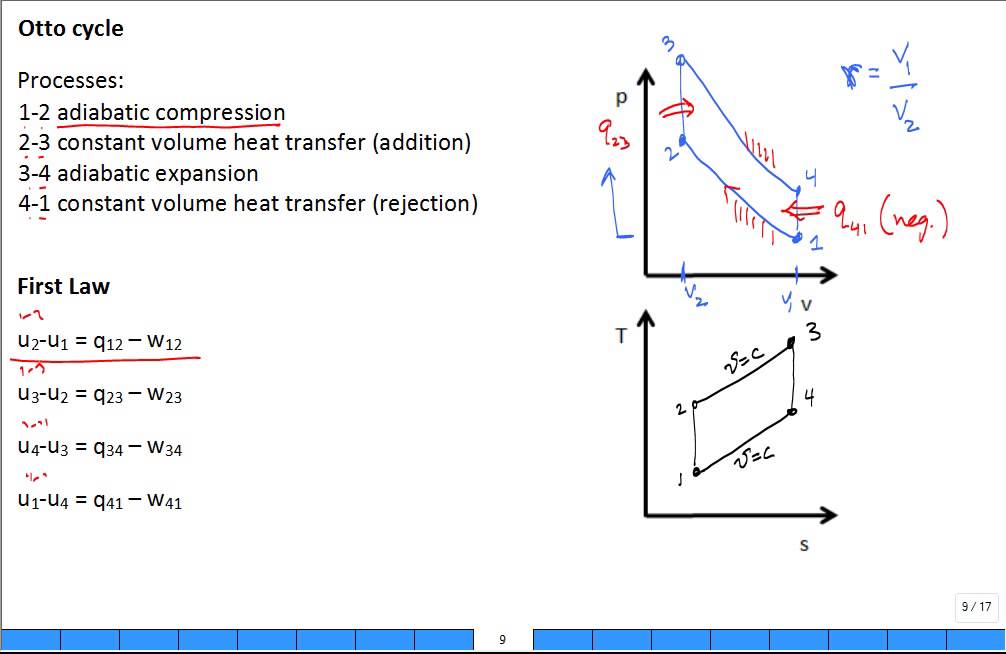
Otto Cycle is a constant volume cycle on which petrol and gas engines work. The Otto cycle consists of 4 processes and are as follows. Process 1-2: Reversible Adiabatic Compression or Isentropic Compression. Process 2-3: Constant Volume heat supply. Process 3-4: Reversible Adiabatic Expansion or Isentropic Expansion.
The above diagram is the T-S diagram for an Otto cycle. Process 1-2 - This represents the isentropic compression process. It is carries out reversibly and adiabatically i.e. isentropically. So the entropy remains constant. The temperature changes according to the relation - T 2 / T 1 = (V 1 / V 2) γ − 1 S 1 = S 2 Process 2-3 -
otto cycle, otto cycle in hindi, otto cycle derivation, otto cycle pv and ts diagram, thermodynamicsintroduction to Thermodynamics, System and Its Types- htt...
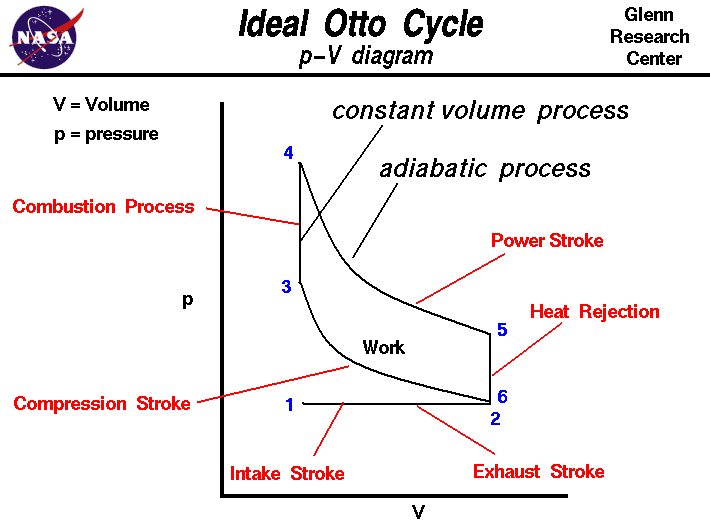
Pressure-Volume (p-v) Diagram of Four-stroke Otto cycle Engine. The ideal Otto cycle consists of two constant volume and two reversible adiabatic or isentropic processes as shown on PV and T-S diagrams. Let the engine cylinder contains m kg of air at point 1. At this point, let p1, T1, andV1 be the pressure, temperature and volume of air.
The actual exhaust and intake stroke has been replaced by process 4-1, as described in Section IV.A.Representation of the Otto cycle on a pressure-volume (PV) diagram and temperature-entropy (TS) diagram is provided in Fig. 2.
Otto Cycle – pV, Ts diagram pV diagram of Otto Cycle. The area bounded by the complete cycle path represents the total work that can be done during one cycle. The Otto cycle is often plotted on a pressure- volume diagram (pV diagram) and on a temperature-entropy diagram (Ts diagram).
P - v and T - s diagrams of the Otto cycle. BDC, bottom dead center; TDC, top dead center. The Otto cycle is the ideal cycle for spark-ignition (SI) engines. This cycle was presented in the late 19th century after Nikolaus Otto demonstrated the four-stroke SI engine successfully [1]. Description of the processes is given as follows: •
This cycle is so named as it was conceived by 'Otto'. On this cycle, petrol, gas and many types of oil engines work. It is the standard of comparison for internal combustion engines. Figs. shows the theoretical p-V diagram and T-s diagrams of this cycle respectively. The point 1 represents that cylinder is full of air with volume V1 ...
Therefore first let us see an overview of an Otto cycle with the help of PV diagram and TS diagram as displayed here in following figure. As we can see in below figure, there will be two isentropic or adiabatic processes and two constant volume processes. We will determine the various properties for unit mass of working fluid.
The diesel cycle has high thermal efficiency. 2. It has a low compression ratio. But This one works on a high compression ratio. 3. Otto cycle is also called a Constant volume cycle. The diesel cycle is called a constant pressure cycle. 4. Otto cycle system is light in weight.
May 22, 2019 · The Otto cycle is often plotted on a pressure- volume diagram ( pV diagram) and on a temperature-entropy diagram (Ts diagram). When plotted on a pressure volume diagram, the isochoric processes follow the isochoric lines for the gas (the vertical lines), adiabatic processes move between these vertical lines and the area bounded by the complete ...
The idealized diagrams of a four-stroke Otto cycle Both diagrams: the intake ( A ) stroke is performed by an isobaric expansion, followed by an adiabatic compression ( B ) stroke. Through the combustion of fuel, heat is added in a constant volume ( isochoric process) process, followed by an adiabatic expansion process power ( C ) stroke.
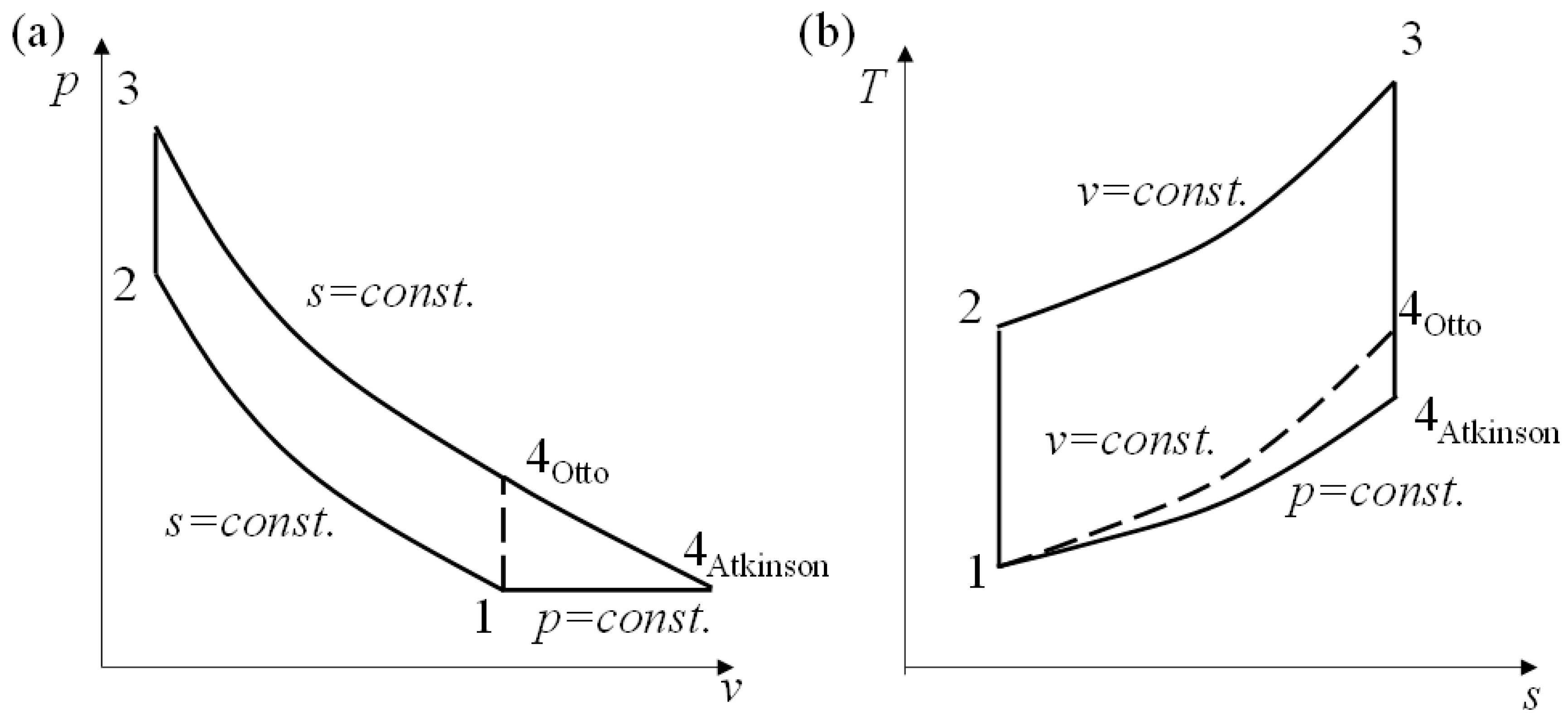
Model the cycle in the car engine as an ideal Otto cycle and an ideal Diesel cycle, respectively. P-v and T-s Diagram of the Otto Cycle (1) Determine the thermal efficiency and compression ratio using ideal Otto-cycle model. The P-v and T-s diagrams of the ideal Otto cycle are shown on the left.
PV and TS diagram of Otto cycle Intake Stroke (Green line): In this stroke, the piston sucks air and petrol mixture into the combustion cylinder by moving from TDC to BDC. During the piston's movement toward the BDC, the chamber volume increases due to that a vacuum creates inside the chamber.
Otto cycle is a thermodynamic cycle upon which a spark ignition engine works. Spark Ignition (or SI) engine uses petrol (or Gasoline) as fuel. Otto cycle was invented by Nicolas Otto in 1876. Spark ignition engine is a type of internal combustion engines.. Below are P-V and T-S Diagrams of the Otto Cycle.
Answer (1 of 2): The above diagram is the T-S diagram for an Otto cycle. Process 1–2 - This represents the isentropic compression process. It is carries out reversibly and adiabatically i.e. isentropically. So the entropy remains constant. The temperature changes according to the relation - T_...






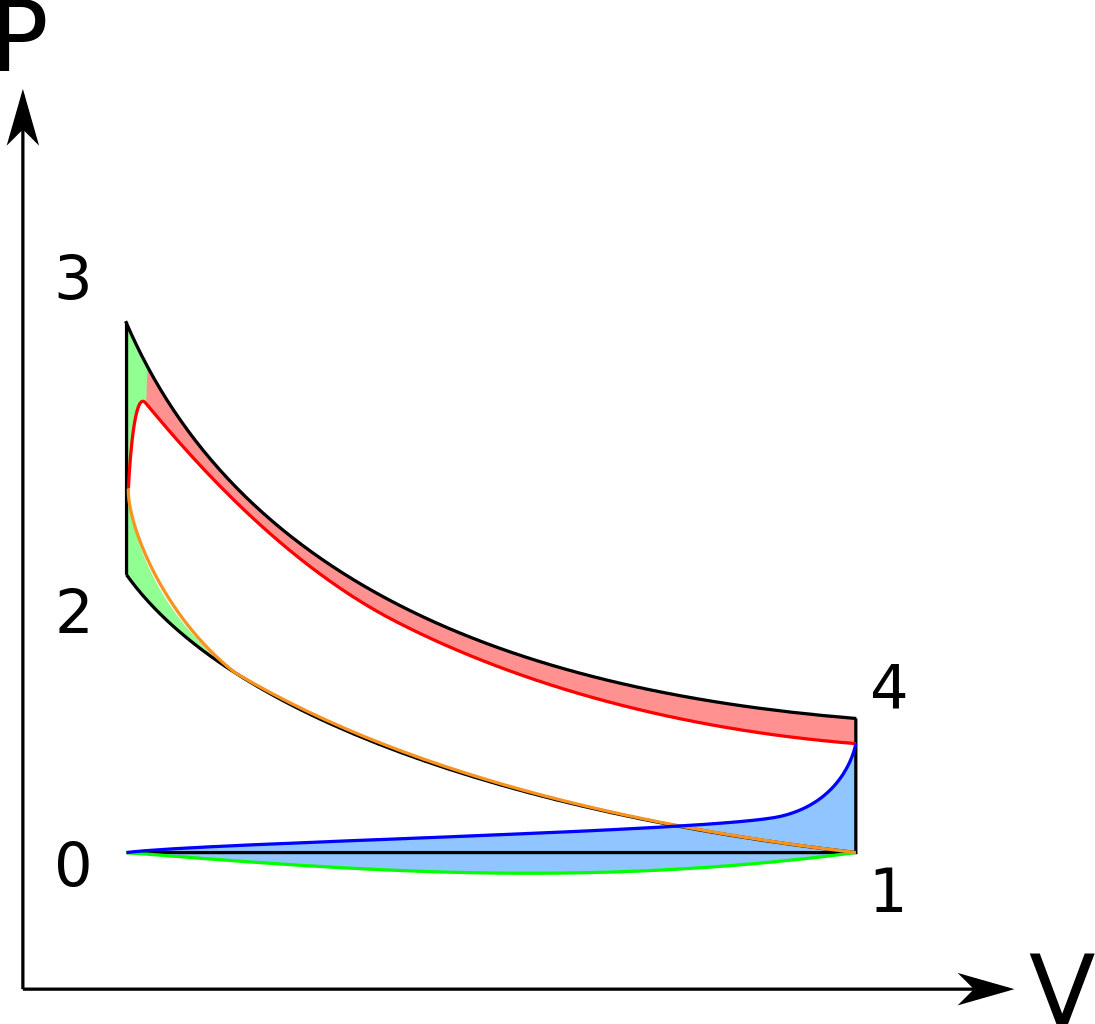





![Difference Between Otto Cycle and Diesel Cycle [Notes & PDF]](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/Difference-between-Otto-and-Diesel-Cycle.jpg)











Comments
Post a Comment