39 dicot leaf diagram
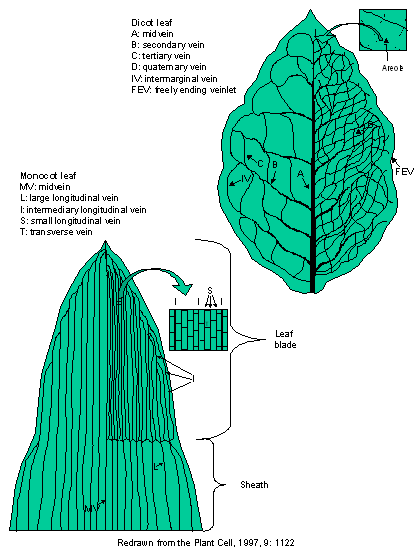
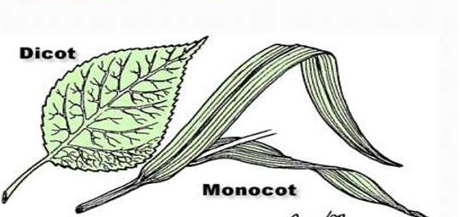
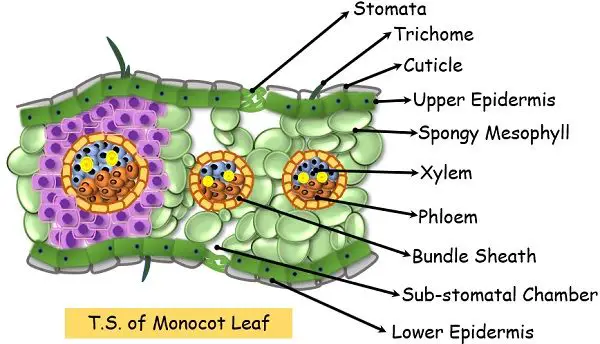
Monocot Diagram - schematron.org Monocot Leaf. Dicot Leaf. Leaf Cross Section. Plant Tissues. Monocot leaves are isobilateral i.e., both surfaces look the same and are structurally the same and are both exposed to the sun (usually vertically oriented). Venation Leaf veins are arranged either in parallel through the length of the leaf or in a reticulate arrangement throughout ... Draw a labelled diagram of Internal Structure of Dicot ... Identifying characteristics of the internal structure of dorsiventral or dicot leaf: (i) It is green, compressed with a wide lamina. (ii) Leaf-blade is enriched with reticulate venation. (iii) Mesophyll tissue is present and is composed of palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma.
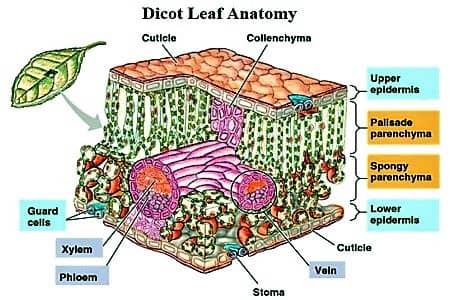
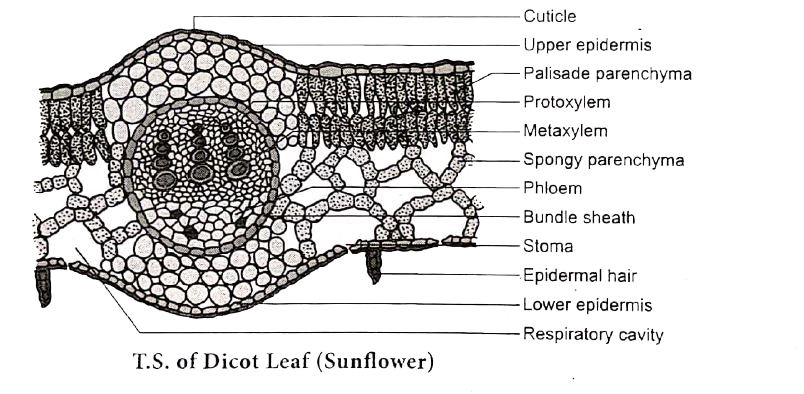
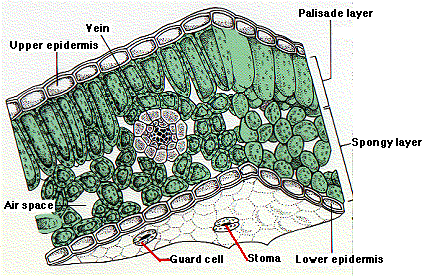
TS of Dicot Leaf under a Microscope (PPT) | Easy Biology Class Dicot Leaf Cross Section (Dorsiventral Leaf) (Anatomical Structure of a Dicot Leaf- Ixora, Mangifera, Hibiscus) Ø Leaves are structurally well adapted to perform the photosynthesis, transpiration and gaseous exchange. Ø A leaf composed of: (1). Leaf blade: also called leaf lamina is the flattened expanded part of the leaf chiefly composed of mesophyll tissue and vascular bundles.
Dicot leaf diagram
Dicot Leaf Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Dicot Leaf. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Describe the Anatomical Structure of a Dicot Leaf - QS Study Dicot is a term used to explain a group of flowering plants that have two seed leaves. It generally has secondary growth that shows up like wood and bark in their stems. The anatomical structure of a dicot leaf / dorsiventral leaf. The following arrangement of tissues are seen in the cross-section of a dorsiventral leaf. Upper epidermis. Diagram of a leaf showing typical features of a dicot | Flickr Drawing of leaf of Garden Privet (Ligustrum ovalifolium) showing the typical features of a simple dicotyledonous leaf. Leaf is approximately 60 mm long. Simple leaves have an undivided leaf blade. The leaf has a midrib containing the main vein with branching lateral veins. This is known as pinnate venation. The leaf has a short leaf stalk, or petiole, and a leaf blade, or lamina. The junction ...
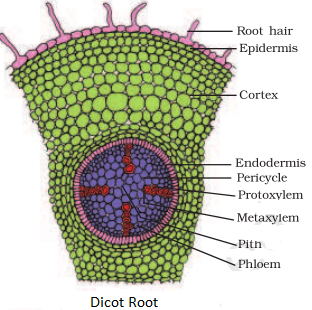
Dicot leaf diagram. Monocot and Dicot Leafs (With Diagram) | Plants ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the top two types of monocot and dicot leafs. The types are: 1. Anatomy of Monocot Leaf 2. Anatomy of Dicot Leaf. Monocot and Dicot Leaf: Type # 1. Anatomy of Monocot Leaf: Triticum-Leaf: ADVERTISEMENTS: T.S. shows prominent ridges and grooves and reveals the following tissues: Epidermis: 1. Two epidermal […] Monocot And Dicot Plants- Anatomy - BYJUS Monocot roots do not show much difference in the anatomy from that of the dicot roots. Monocot plants possess an adventitious root system. As in the dicots, the epidermis forms the outermost layer, followed by cortex, pericycle, endodermis, vascular bundles (xylem and phloem) and pith (random order). Pith is conspicuous and large. 18 Major Difference Between Monocot And Dicot Leaf (With ... Dicot Leaf Diagram Characteristics Of Dicot Leaf The guard cells of stomata are kidney-shaped in dicot leaf. A dicot leaf is broader in shape and relatively small. The epidermal cells have sinous lateral walls. The orientation of a dicot leaf can be described as dorsiventral. Root Anatomy || Monocot and Dicot Root Cross Section ROOT ANATOMY: DICOT ROOT CROSS SECTION Dicot Root Diagram Reveals Internal Structure of Dicot Root. A thin transverse section of the young dicot root of Gram, Sunflower or Pea reveals the following structures under the microscope: 1. Epiblema or Piliferous Layer. This is the outermost layer of root-derived from the protoderm of the apical meristem.
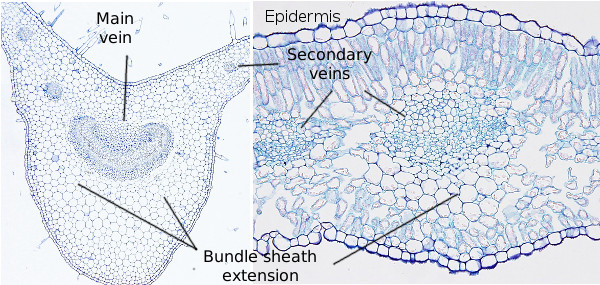
The diagram given below represents the T.S. of dicot leaf. I The diagram given below represents the T.S. of dicot leaf. Identify the parts labelled as A, B, C and D, which denote their functions and choose the correct one given below : 1078 18 KCET KCET 2013 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Report Error PDF Dicot or Monocot? How to Tell the Difference - USDA base of the leaf and are parallel to each other in each lobe of the leaf. If your plant is flowering, you can tell if it is a monocot or dicot by the number of petals and other flower parts. Monocots have flower parts in threes or multiples of threes as shown in the flowers to the left. Dicots have flower parts in multiples of fours or fives like Difference Between Dicot and Monocot Leaf - Biology Reader The main characteristic feature to distinguish the dicot and monocot leaf is the type of venation a leaf have. One can easily observe either the veins are striking or parallel by seeing a leaf. Below is the diagram of dicot and monocot leaf, where we can see the venation pattern. Anatomy of Dicot Vs Monocot Leaf Cross Section Of A Dicotyledonous Leaf Diagram of transverse section dicot leaf. If a plant has 2 seed leaves we call it a dicotyledon or dicot for short. A dicotyledonous leaf is generally dorsiventral. Leaves of dicotyledonous plants show a great variation in shape see some examples in the drawing below.
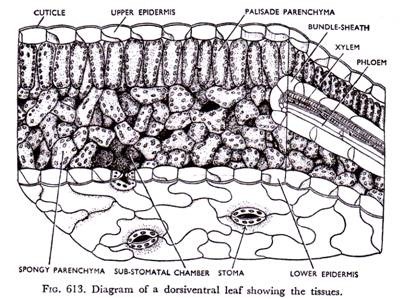
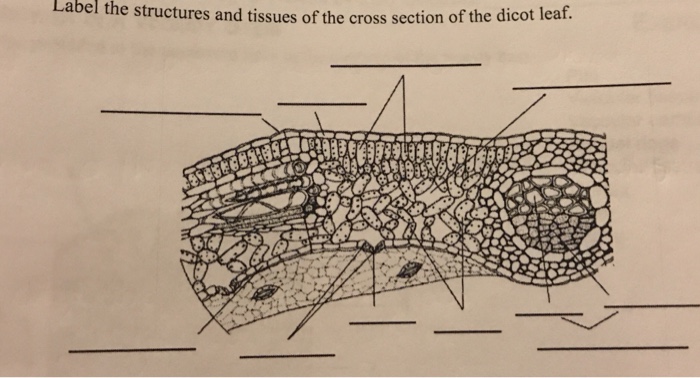
Internal Structure of Leaf (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article, we propose to discuss about the internal structure of leaf. The foliage leaves are characterised by green colour, thinness and flatness. They develop as protrusions from the shoot apex and are organs of limited growth. Leaves are very important vegetative organs, as they are chiefly concerned with the physiological process, photosynthesis […] AS Level Biology (9700) P3 Guide - Diagrams - Stude Mate For TS Leaf, the most common questions ask you to draw a plan diagram or a diagram of a certain section of the leaf clearly showing a specific number of cells. In both cases you'd have to label your diagram. Here is a plan diagram of a dicot. leaf, Ligustrum. I'd suggest you to learn all the labels and to be able to draw this diagram from ... Describe the internal structure of dicot leaf with the ... Draw a neat labeled diagram of T.S. of dicot leaf . Medium. View solution > Assertion In the dicot leaf, the epidermis covers both the upper surface and lower surface. Reason The adaxial epidermis bears more stomata than the abaxial epidermis. Dicot Leaf Diagram Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Dicot Leaf Diagram. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Explore the Difference Between Monocot and Dicot leaf Difference Between Dicot Leaf and Monocot Leaf. Dicot Leaves. Monocot Leaves. Shape. Dicot plants have leaves that are relatively smaller and broader than monocot plants. Monocot plants have leaves that are characteristically longer and slender. Stomata. Stomata in dicot leaves are kidney-shaped. Stomata in monocot leaves are dumb-bell shaped.
Cross section of dicot leaf | Things under a microscope ... Jul 27, 2018 - Anatomy of a Typical Dicot Dorsiventral Leaf Cross Section (CS) Under Microscope with Labelled Diagram, Description and PPT
OPAL- Diagram- Dicot leaf - YouTube How to draw diagrams "Transverse section of dicot LEAF" on Biology Practical copy Punjab Board Lahore by Naveed Akhtar Uppal (calligrapher & artist) Jhelum, ...
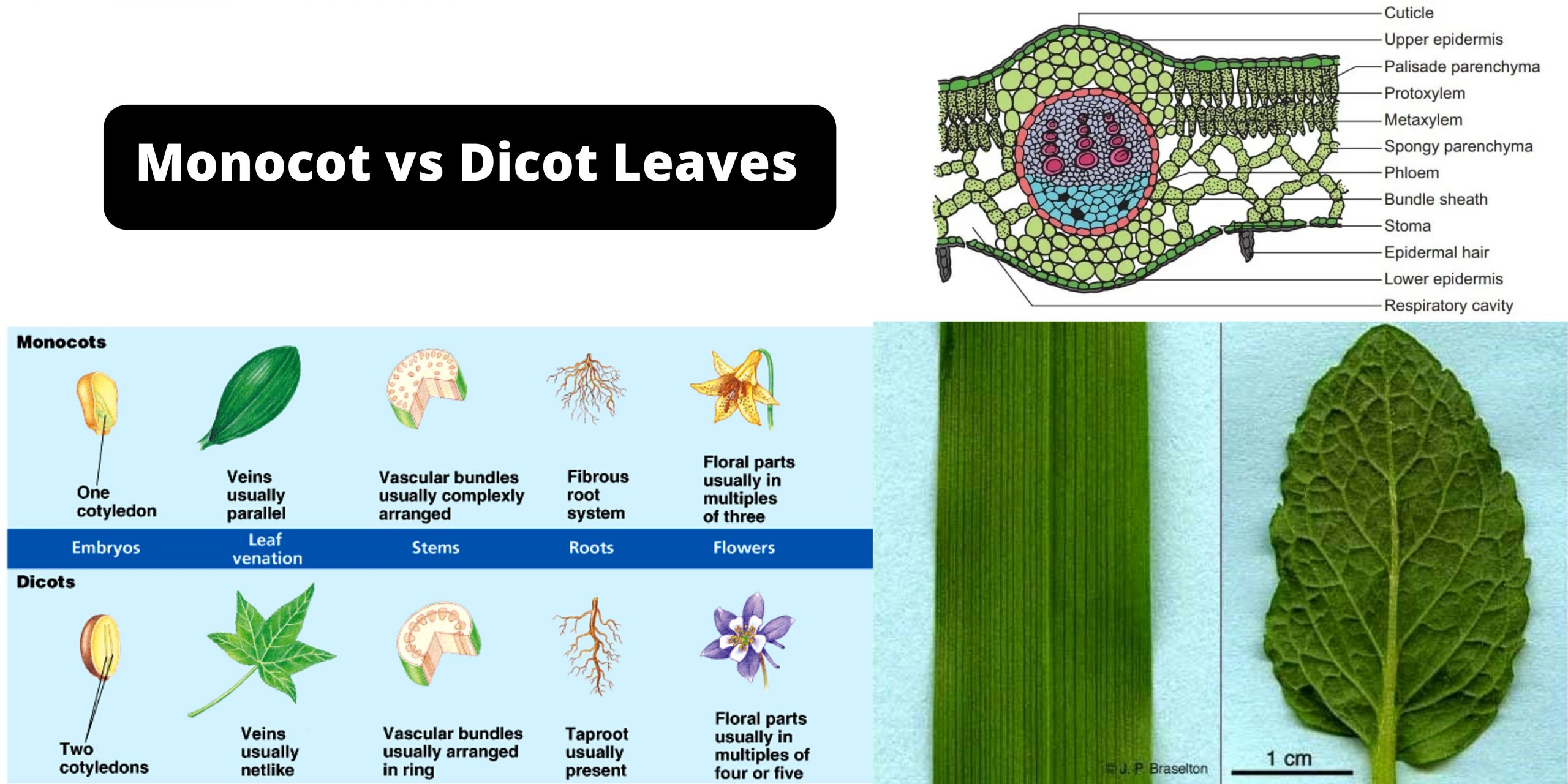
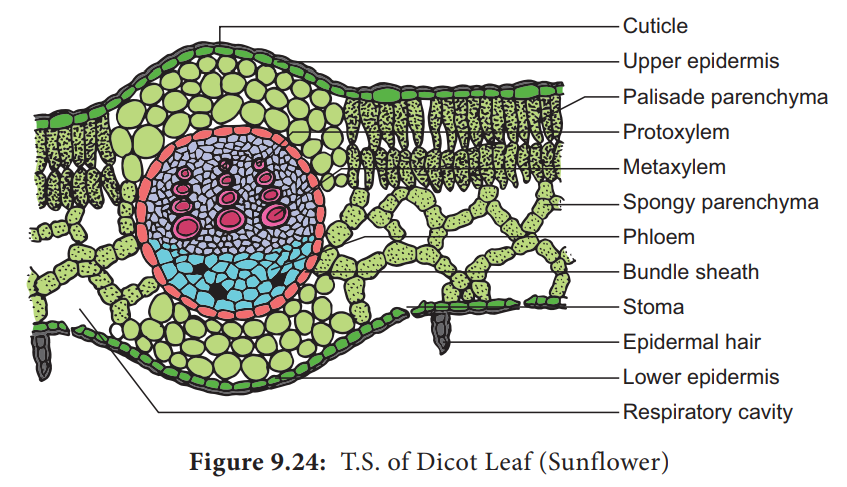
17 Structural Difference between Monocot Leaf and Dicot ... The venation of dicot leaf is reticulate whereas monocot leaf has parallel venation. Dicot leaf has a random number of stomata on the epidermis while monocot leaf has parallel stomata that are uniformly distributed. The mesophyll of dicot leaf is differentiated into Palisade and Spongy mesophyll while monocot leaf has undifferentiated.
Draw a neat labeled diagram of T.S. of dicot leaf Describe the internal structure of dicot leaf with the help of diagram. Hard. View solution > In a dicot leaf, vascular bundles are found in the. Medium. View solution > View more. More From Chapter. Anatomy of Flowering Plants. View chapter > Shortcuts & Tips . Common misconceptions > Mindmap > Cheatsheets > Diagram set >
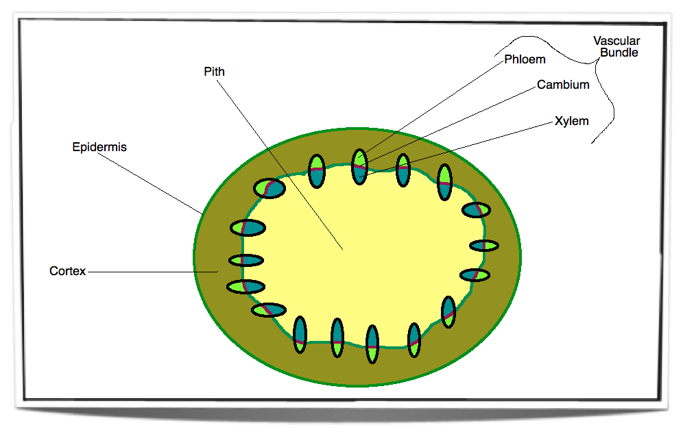
Eudicot Diagram - schematron.org Dicot Leaf. Leaf Cross Section. Plant Tissues. Monocot roots, interestingly, have their vascular bundles arranged in a ring. Dicot roots have their xylem in the center of the root and phloem outside the xylem. A carrot is an example of a dicot root. Diagram illustrating the tissue layers and their organization within monocot and dicot roots.
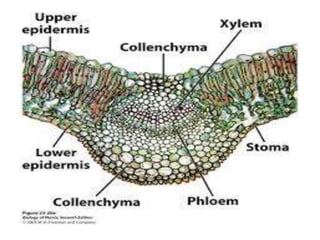
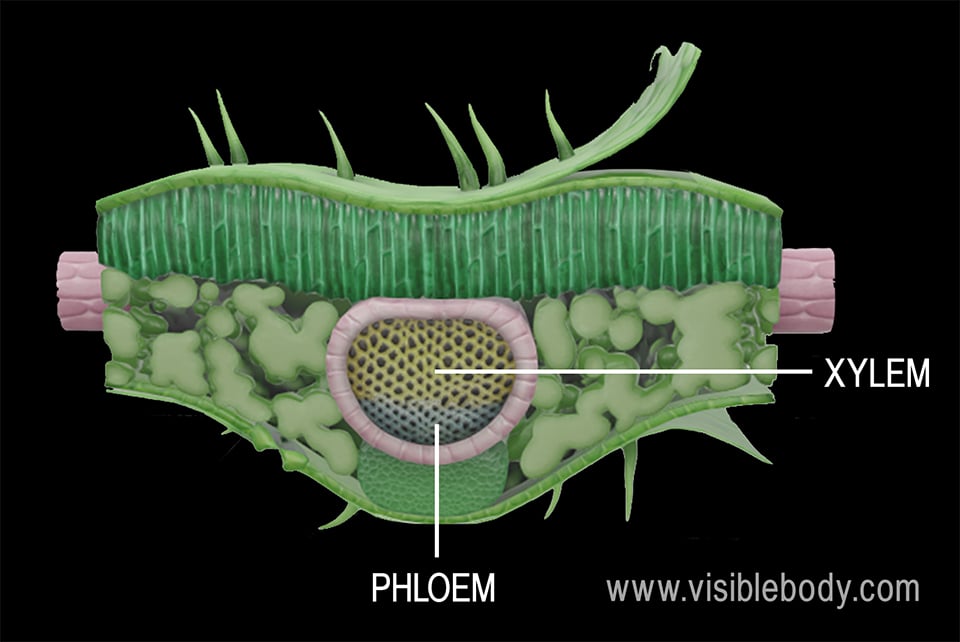
Internal Structure of Leaf: Parts, Function, Diagram - Embibe Fig: Internal Structure of Dicot Leaf. Vascular Tissue. Vascular bundles in the leaf are known as veins. The arrangement of these veins is known as venation. 1. In leaves of dicots, the venation is net-like and is called reticulate venation. 2. Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a bundle of parenchymatous cells.
Diagram Of Transverse Section A Dicot Leaf | Leafandtrees.org Apr 11, 2020 · Difference Between Dicot And Monocot Leaf With Comparison Chart Biology Reader. Schematic transverse section through a dicotyledon leaf indicating the scientific diagram monocot and dicot leafs with diagram plants 3 dorsiventral cross section of a dicot leaf with the adaxial surface scientific diagram monocot and dicot leafs with diagram plants.
Monocot and Dicot Leaves - Visible Body A leaf with a palmate pattern has veins branching out from a single one to form a shape resembling the palm of a hand. Typically, dicot leaves either have more stomata on the lower side of the leaf, or they have stomata only on the lower side of the leaf. Leaves with stomata only on the lower side are known as hypostomatous leaves.
Roots, Stems and Leaves Diagrams - Mandeville High School Roots, Stems and Leaves Diagrams. External Root Structure. Monocot Root. Dicot Root. External Structure of a Woody Stem. Monocot Stem. Woody Dicot Stem. Monocot Leaf. Dicot Leaf.
Anatomy of a dicot leaf - Sunflower leaf - BrainKart A dicotyledonous leaf is generally dorsiventral. It has upper and lower epidermis. The epidermis is usually made up of a single layer of cells that are closely packed. The cuticle on the upper epidermis is thicker than that of lower epidermis. The minute openings found on the epidermis are called stomata.
Diagram of a leaf showing typical features of a dicot | Flickr Drawing of leaf of Garden Privet (Ligustrum ovalifolium) showing the typical features of a simple dicotyledonous leaf. Leaf is approximately 60 mm long. Simple leaves have an undivided leaf blade. The leaf has a midrib containing the main vein with branching lateral veins. This is known as pinnate venation. The leaf has a short leaf stalk, or petiole, and a leaf blade, or lamina. The junction ...
Describe the Anatomical Structure of a Dicot Leaf - QS Study Dicot is a term used to explain a group of flowering plants that have two seed leaves. It generally has secondary growth that shows up like wood and bark in their stems. The anatomical structure of a dicot leaf / dorsiventral leaf. The following arrangement of tissues are seen in the cross-section of a dorsiventral leaf. Upper epidermis.
Dicot Leaf Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Dicot Leaf. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.















/Leaf_Tissue_Structure-56e6d04c5f9b5854a9f9494e.jpg)




Comments
Post a Comment