38 dna replication fork diagram labeled
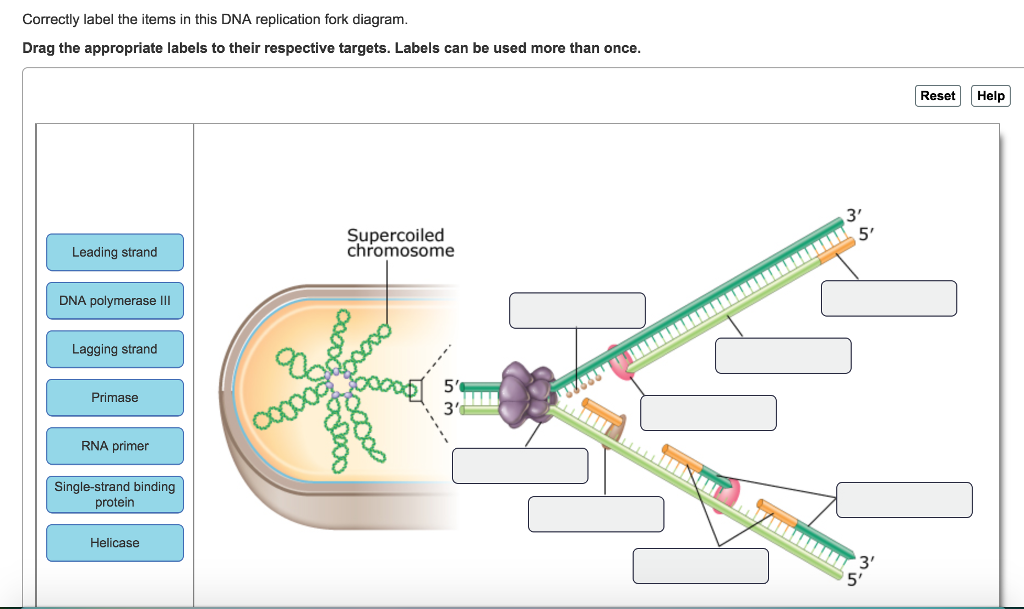
Expert Answer 97% (39 ratings) Transcribed image text: Correctly label the items in this DNA replication fork diagram. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used more than once. The helix structure is unwound. Then, the enzymes ready to create a strand of mrna by a complementary sequence of bases. Semi Conservative Replication Of Dna Diagram Biology Lessons Biology Notes A Level Biology This short rna polymer called a primer provides a. How to draw dna replication diagram. The dna replication in prokaryotes takes […]
Dna Replication Labeled. Here are a number of highest rated Dna Replication Labeled pictures upon internet. We identified it from obedient source. Its submitted by dispensation in the best field. We assume this nice of Dna Replication Labeled graphic could possibly be the most trending topic once we allocation it in google improvement or facebook.

Dna replication fork diagram labeled
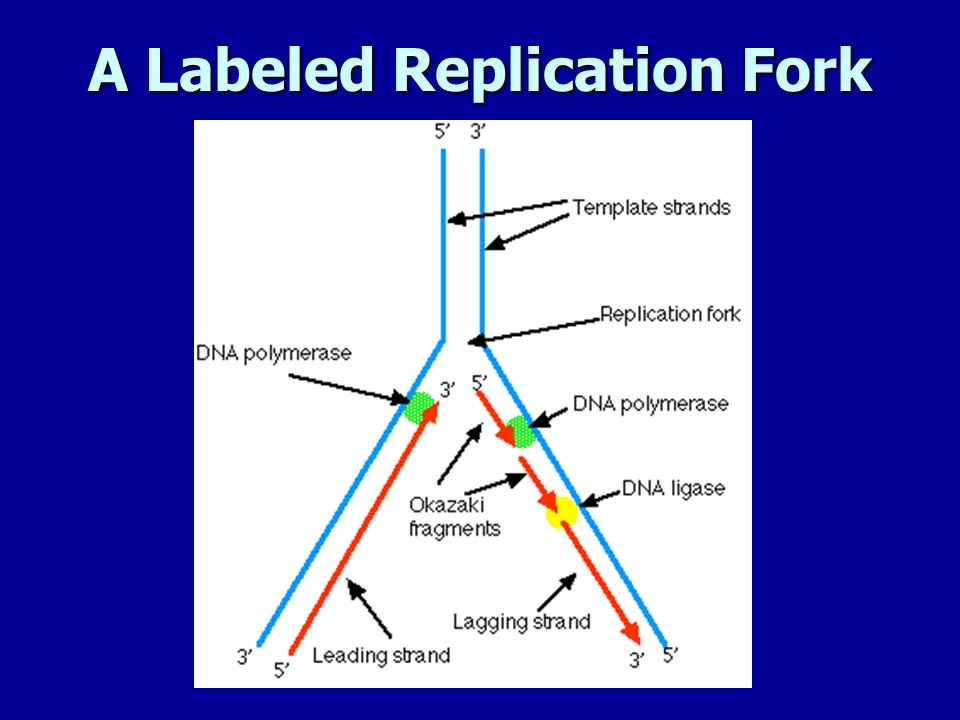
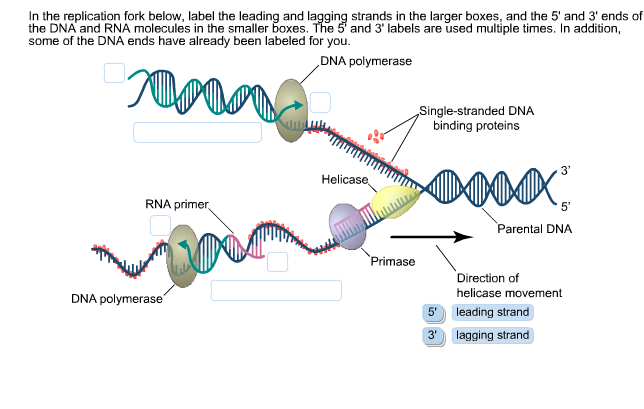
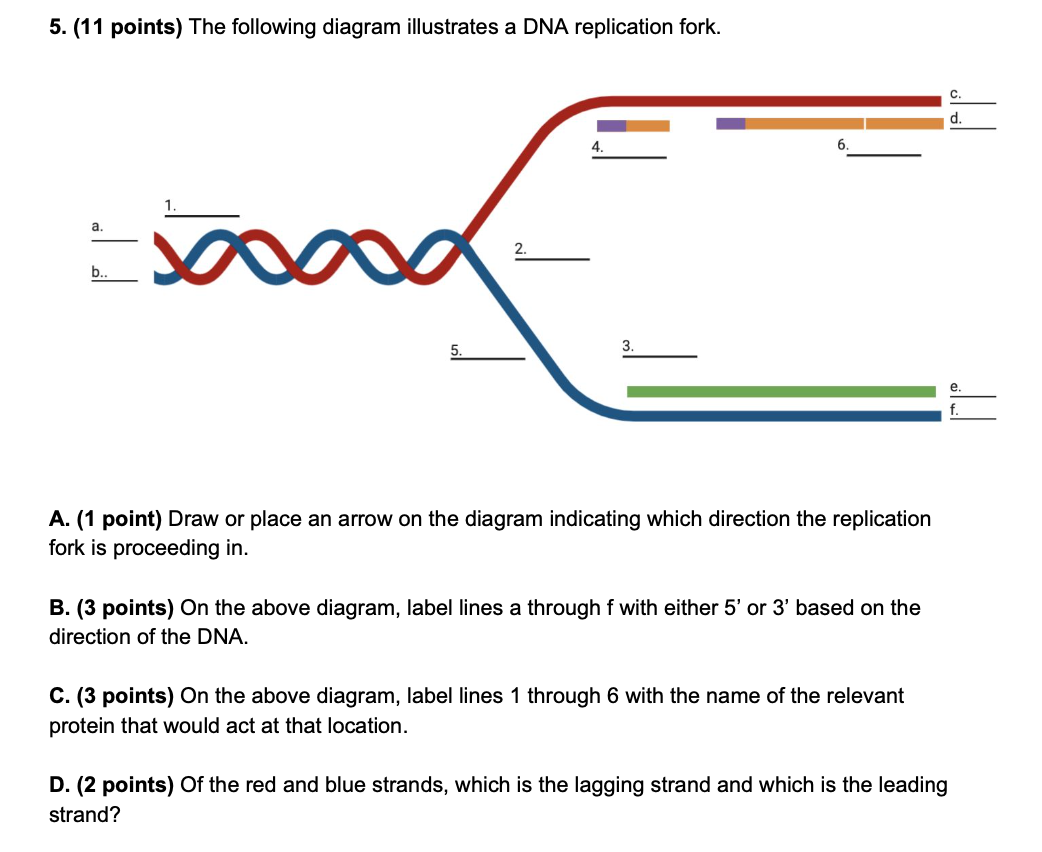
The region of replicating DNA at which the two strands of the parental DNA are separated and two new daughter DNA molecules are made, each with one parental strand and one newly synthesized strand, is called a replication fork. Dna Replication Labeling. Here are a number of highest rated Dna Replication Labeling pictures on internet. We identified it from well-behaved source. Its submitted by management in the best field. We take this nice of Dna Replication Labeling graphic could possibly be the most trending subject with we allocation it in google gain or facebook. 1. On the diagram below, label the 5’ and 3’ ends of both parental DNA strands (you can make up which is which) 2. Label the replication fork 3. Draw and label helicase 4. Label the overall direction of DNA replication 5. Draw and label single stranded binding proteins 6. Draw and label the leading strand 7.
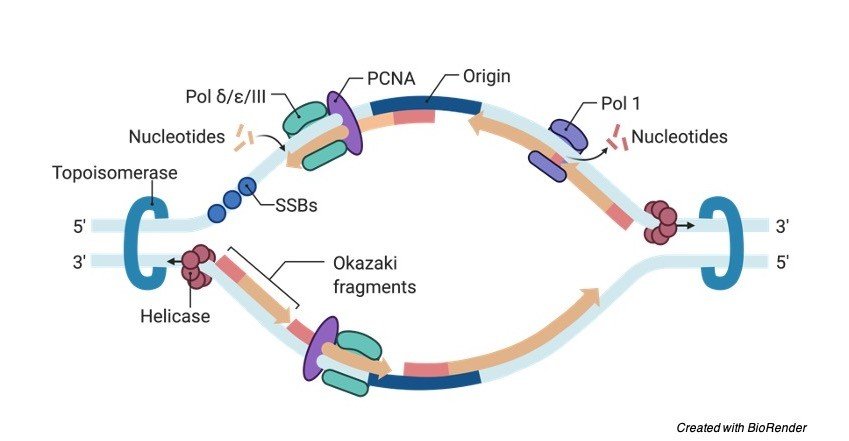
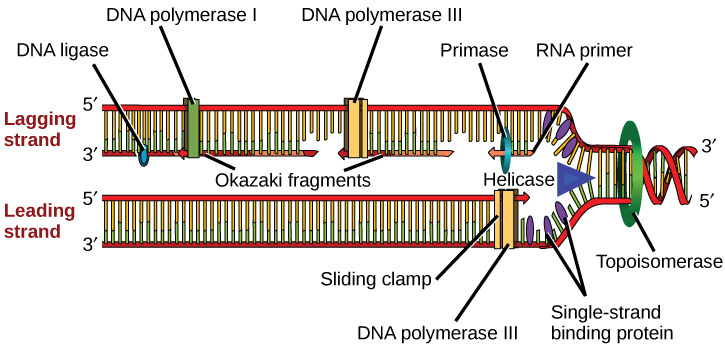
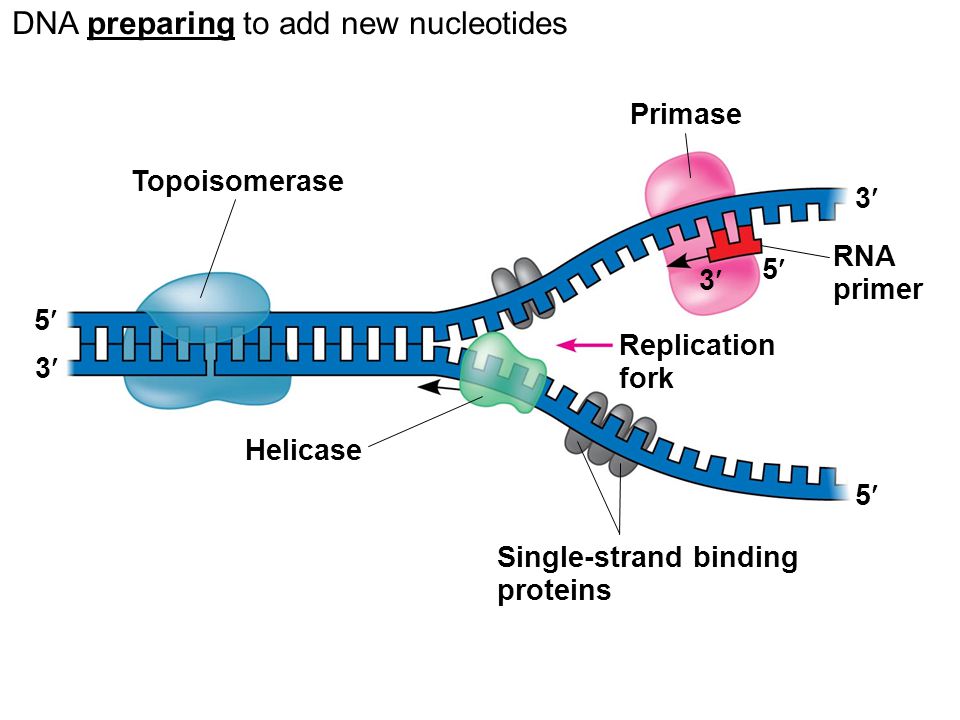
Dna replication fork diagram labeled. The diagram below shows a replication fork with the two parental DNA strands labeled at their 3' and 5 4/4(5). The diagram below shows a bacterial replication fork and its principal proteins. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the diagram to describe the name or function of each structure. DNA Replication (1 of 2): DNA Structure and Replication Machinery (BioFlix tutorial) Part A - The chemical structure of DNA and its nucleotides The DNA double helix is composed of two strands of DNA; each strand is a polymer of DNA nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases. ADVERTISEMENTS: Let us make an in-depth study of the DNA replication:- Learn about: 1. Basic Features of DNA Replication 2. Mechanism of DNA Replication 3. Meselson and Stahl Experiment 4. Enzymes of DNA Replication 5. Formation of Replication Forks & Replication Bubbles and Others. Central Dogma: Genetic material is always nucleic acid and it is […] Biology questions and answers. Label the parts of the DNA replication fork. DNA helicase Okazaki fragment Open beta clamp DNA ligase DNA polymerase III Leading strand Closed beta clamp RNA primer DNA primase Single-strand binding proteins DNA gyrase Clamp loader DNA polymerase I Parent DNA. Question: Label the parts of the DNA replication fork.
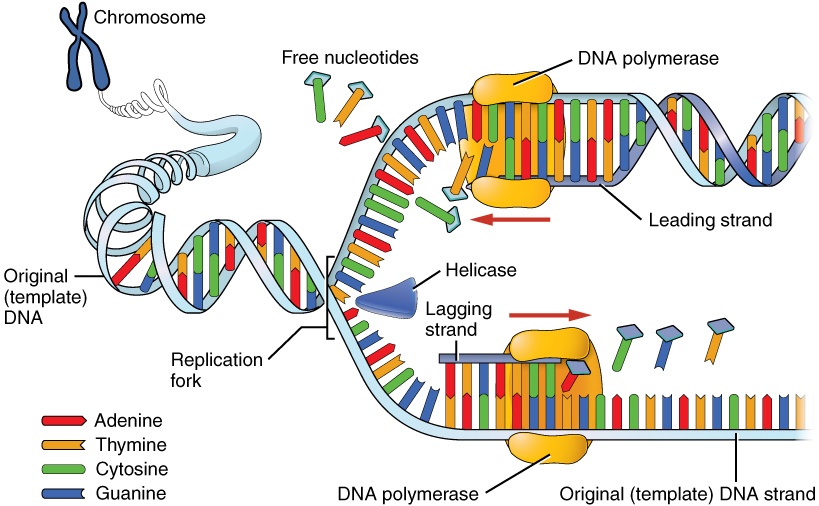
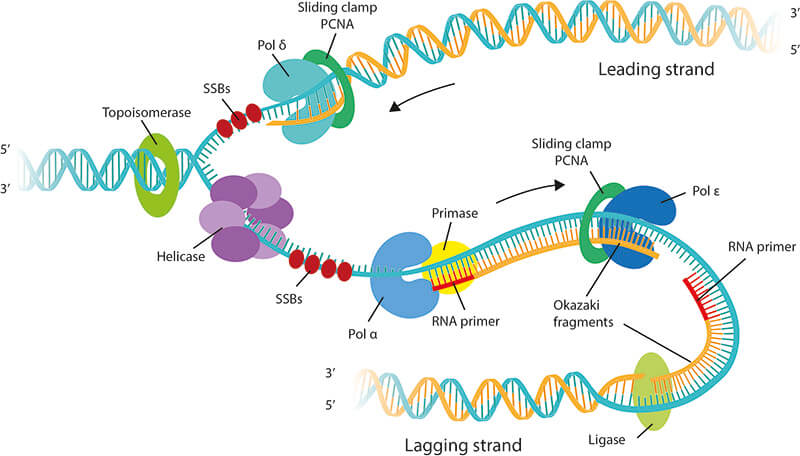
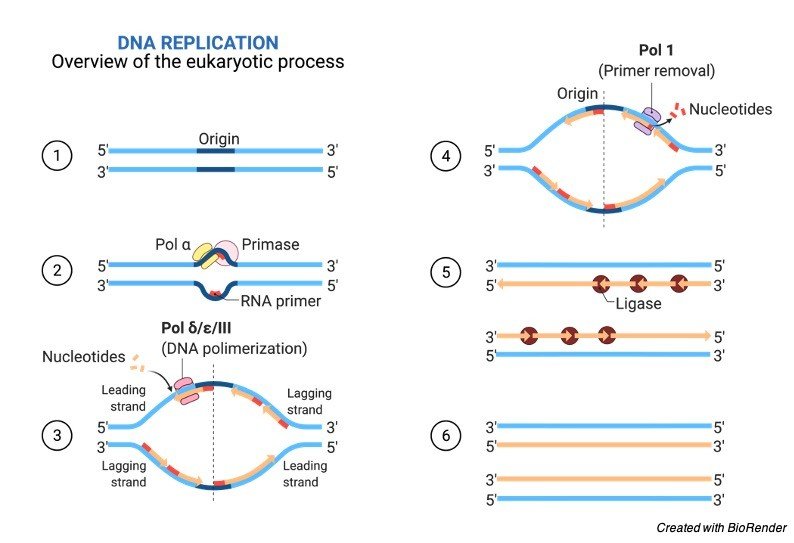
Unit 12 DNA. Diagram and label a section of dna open diagram and label a section of dna 4 810 x 1649. For the replication to begin there is a particular region called the origin of replication. Label Gallery Get some ideas to make labels for bottles jars packages products boxes or classroom activities for free. Diagram Of Dna Dvaen. And this happens when the two replication forks between the two terminals meet each other. Also Read: DNA Structure. Role of Enzymes in DNA Replication. DNA replication is a highly enzyme-dependent process. There are many enzymes involved in DNA replication, which includes the enzymes, DNA-dependent DNA polymerase, helicase, ligase, etc. This is discontinuous replication as the fragments need to be joined up later. After all, bases are matched up, the enzyme exonuclease strips away the primers. An enzyme called DNA ligase seals the sequence of DNA and makes it into two continuous double strands. Note: The replicating fork is asymmetrical because of the semi-conservative nature. By semi-conservative, we mean that after the replication of the double helix of DNA, new and old strands are formed. Aug 02, 2021 · DNA Replication Diagram. • It is made up of a number of subcomponents that each provide a specific function during the process of replication. • Replication doesn’t begin at the end of chromosomes, but toward the middle at a site called the origin of replication. • A single eukaryotic chromosome contains multiple origins on each chromosome, while replication in prokaryotes usually takes place for a single origin on the circular chromosome.
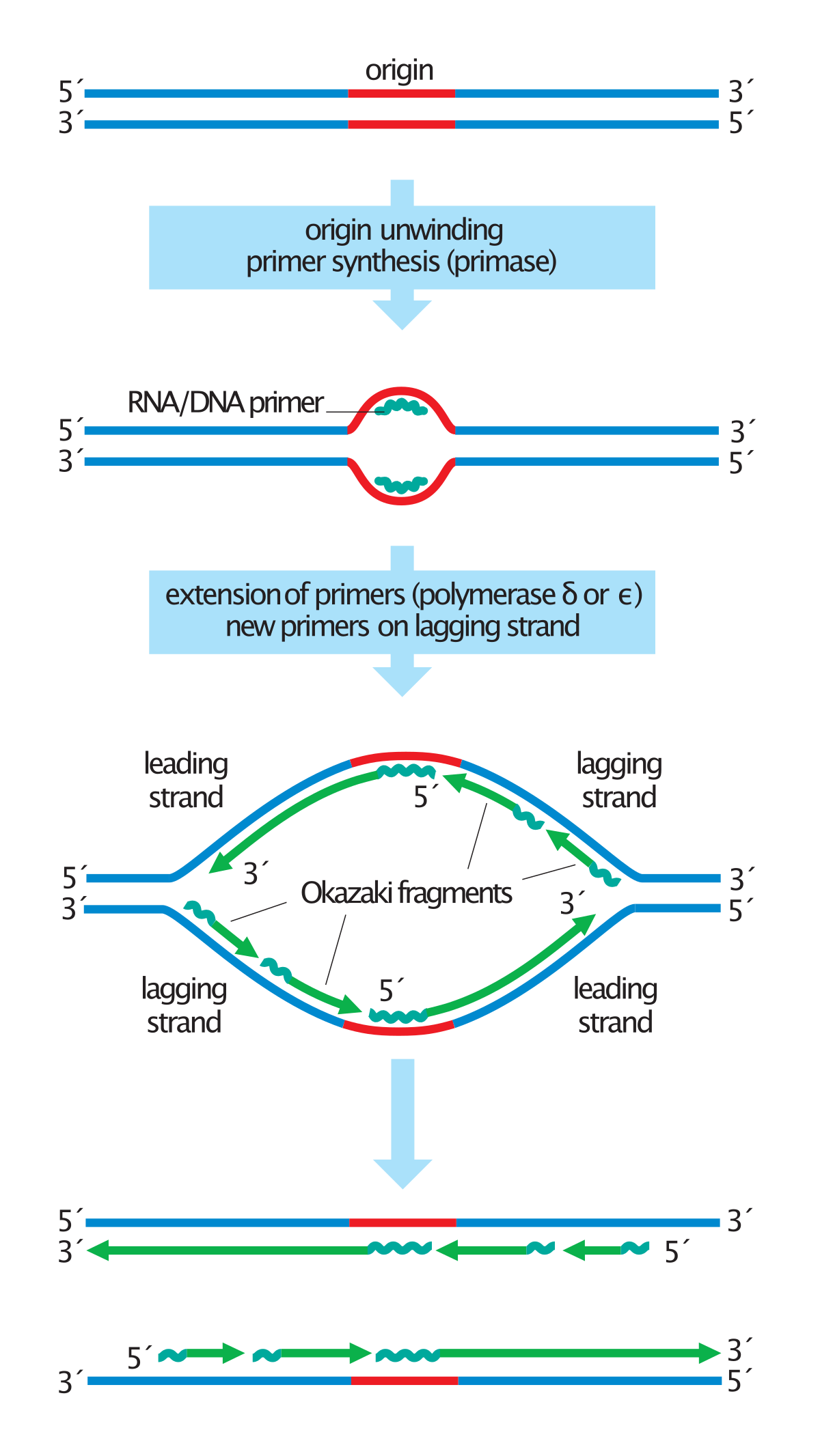
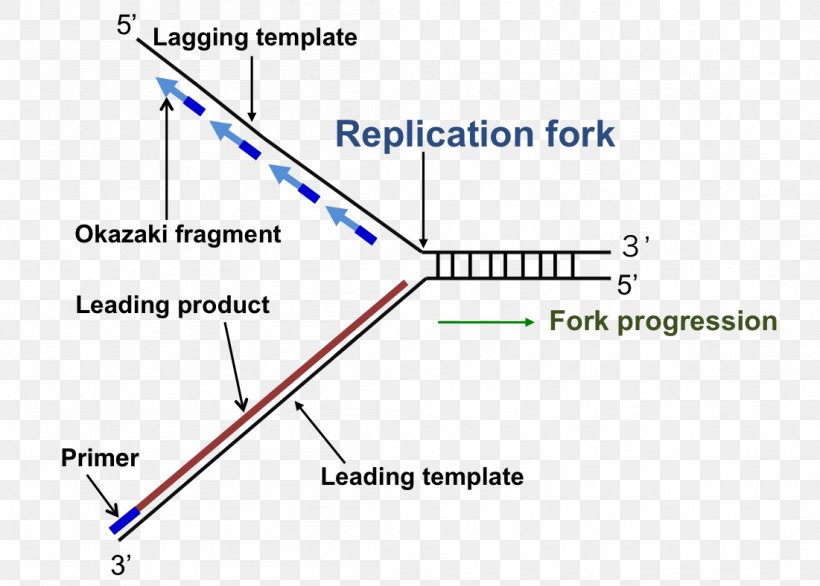
Initially, the simplest mechanism of DNA replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands, nucleotide by nucleotide, at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a DNA molecule to the other. But because of the antiparallel orientation of the two DNA strands in the DNA double helix (see Figure 5-2), this mechanism would require one daughter strand to polymerize in the 5 ... Replication forks DNA is replicated bi-directionally from each ori site A replication fork is the area of DNA that is being unwound prior to replication There are two replication forks for every one ori As DNA replication begins continuously on one strand, the first Okazaki fragment produced becomes the leading strand for the other replication fork 1. Below is a replication fork (one side of an origin): a double-stranded DNA partially opened up to provide single-stranded regions where replication can occur. Draw and label the following: RNA primers (label 3′ and 5′ ends), leading-strand DNA polymerase and new DNA (label 3′ and 5′ ends and show direction of synthesis Jul 18, 2021 · DNA Replication and Replication Fork. Generally, in molecular biology, Replication of DNA, is one of the important biological processes for producing two identical replicas of the DNA from one original DNA. The process of replication of DNA usually occurs in all living organisms which acts as the most important and essential function for the cell division during the growth and repair process of the damaged tissues, it also ensures that each new cell receives its own copy of DNA.
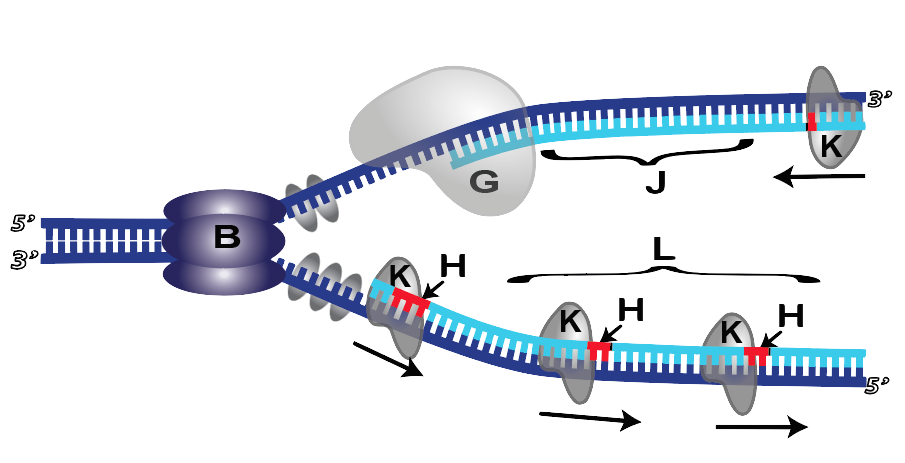
In this diagram of the process of DNA replication at a replication fork, the black boxes labeled D and E are: A RNA primers. B DNA template strands. C Okazaki fragments. D DNA polymerase. E Newly synthesized DNA strand. The Biology Project University of Arizona Thursday, October 3, 1996
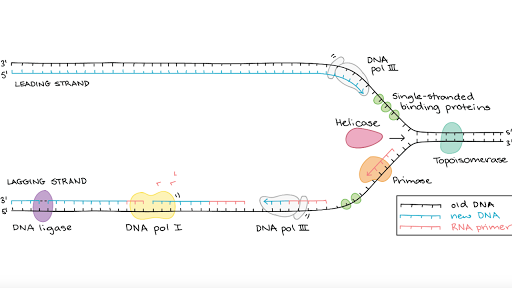
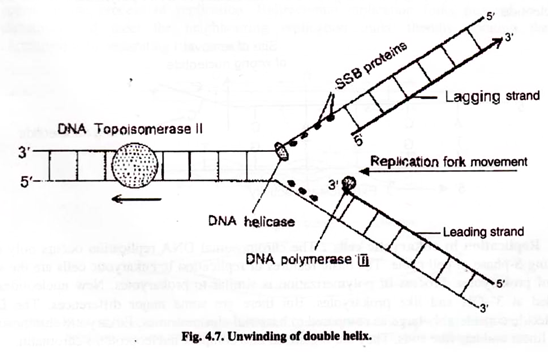
corrects "overwinding" ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands. Primase. An enzyme that creates a short RNA primer for initiation of DNA replication. RNA Primer. short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication The primer synthesized by primase enzyme.
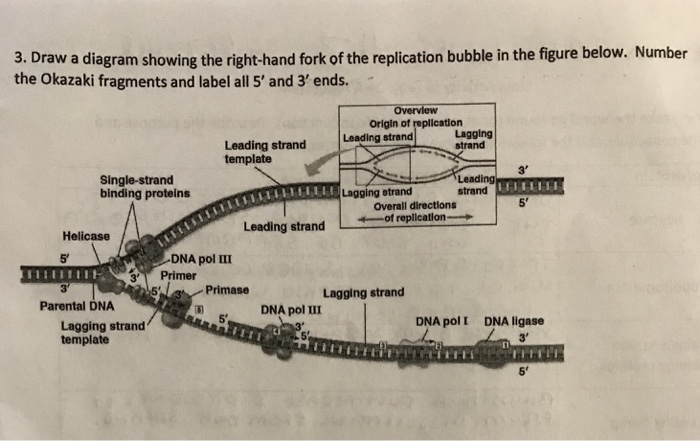
–Helicase begins to unwind the DNA at the ORIGIN OF REPLICATION (a specific DNA nucleotide sequence) It’s common to only show one strands sequence of bases, since the other can be ... • Replication fork • Leading strand • Lagging strand • Okazaki fragment • DNA polymerase I • DNA ligase . 4. DNA polymerase III adds DNA nucleoside
Dna is the genetic material that defines cells in bodies. Summary of dna replication notes is right below In one direction, dna is replicated as one continuous strand. It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in dna. Main enzyme involved in replication is dna polymerse iii.
2 Aug 2020 — At each replication fork, the parental DNA strand must unwind exposing new ... Organelles, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram, ...
When it moves away from the replication fork (towards the origin), it's on the lagging strand. A diagram of DNA replication showing the leading strand and ...
E. Steps in DNA replication 1. Binding of DnaA to oriC and initial unwinding of the helix 2. RepA helicase "melts" the DNA at the replication fork 3. Priming DNA synthesis - Primase synthesizes RNA primers. (From: AN INTRODUCTION TO GENETIC ANALYSIS 6/E BY Griffiths, Miller, Suzuki, Leontin, Gelbart 1996 by W. H. Freeman and Company.
The replication fork is the area where the replication of DNA will actually take place. There are two strands of DNA that are exposed once the double helix is opened. One strand is referred to as...
replication fork: the Y-shaped structure formed during the initiation of replication semiconservative replication: the method used to replicate DNA in which the double-stranded molecule is separated and each strand acts as a template for a new strand to be synthesized, so the resulting DNA molecules are composed of one new strand of nucleotides ...
In this diagram of the process of DNA replication at a replication fork, the strand labeled B is the: DNA Replication The two antiparallel strands are replicated simultaneously in both directions. RNA primers are used to initiate a new strand. The parent strand at the 3' end of the template determines the
Replication Fork The replication fork * is a region where a cell's DNA * double helix has been unwound and separated to create an area where DNA polymerases and the other enzymes involved can use each strand as a template to synthesize a new double helix. DNA Base RNA Base An enzyme called a helicase * catalyzes strand separation.
Thus in this procedure, when asynchronously replicating molecules are labeled for a series of pulse periods of increasing length and completed DNA molecules examined at the end of each pulse, the the terminus of replication will be labeled at the earliest time points, whereas those containing an origin will be labeled last. Figure 6.2.
The meeting of two replication forks is not regulated and happens randomly along the course of the chromosome. Once DNA synthesis has finished, the newly ...
Diagram showing 3 models of DNA replication. ... This labeled the parental DNA. ... Figure 9.4 General Overview of a DNA Replication Fork.
Label the diagram: DNA polymerase adds nucleotides (5’ to 3’) Replication fork is formed. DNA polymerase attaches to the primer. Okazaki fragments bound by ligase. DNA helicase unwinds DNA. Rearrange the steps to indicate the correct order: 1. Enzyme that unwinds DNA.
1. On the diagram below, label the 5’ and 3’ ends of both parental DNA strands (you can make up which is which) 2. Label the replication fork 3. Draw and label helicase 4. Label the overall direction of DNA replication 5. Draw and label single stranded binding proteins 6. Draw and label the leading strand 7.
Dna Replication Labeling. Here are a number of highest rated Dna Replication Labeling pictures on internet. We identified it from well-behaved source. Its submitted by management in the best field. We take this nice of Dna Replication Labeling graphic could possibly be the most trending subject with we allocation it in google gain or facebook.
The region of replicating DNA at which the two strands of the parental DNA are separated and two new daughter DNA molecules are made, each with one parental strand and one newly synthesized strand, is called a replication fork.
















Comments
Post a Comment