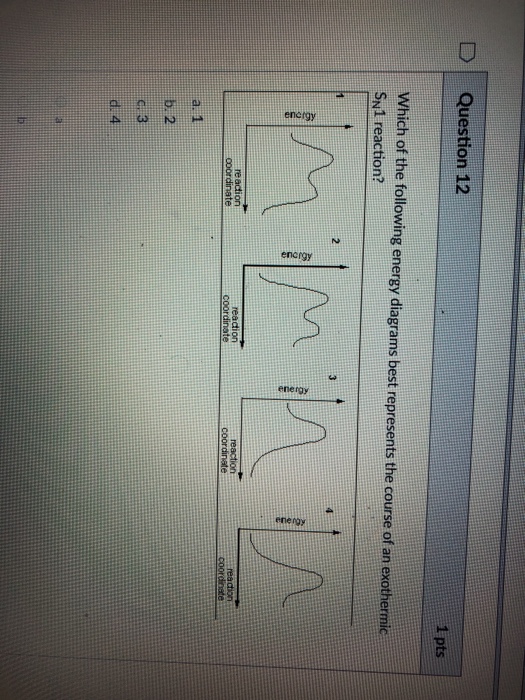
41 sn1 reaction diagram
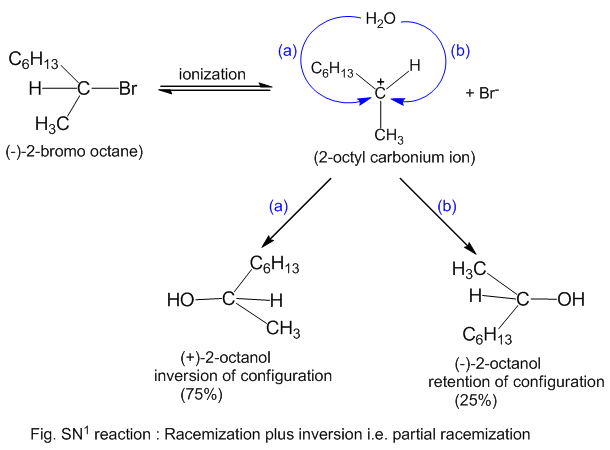
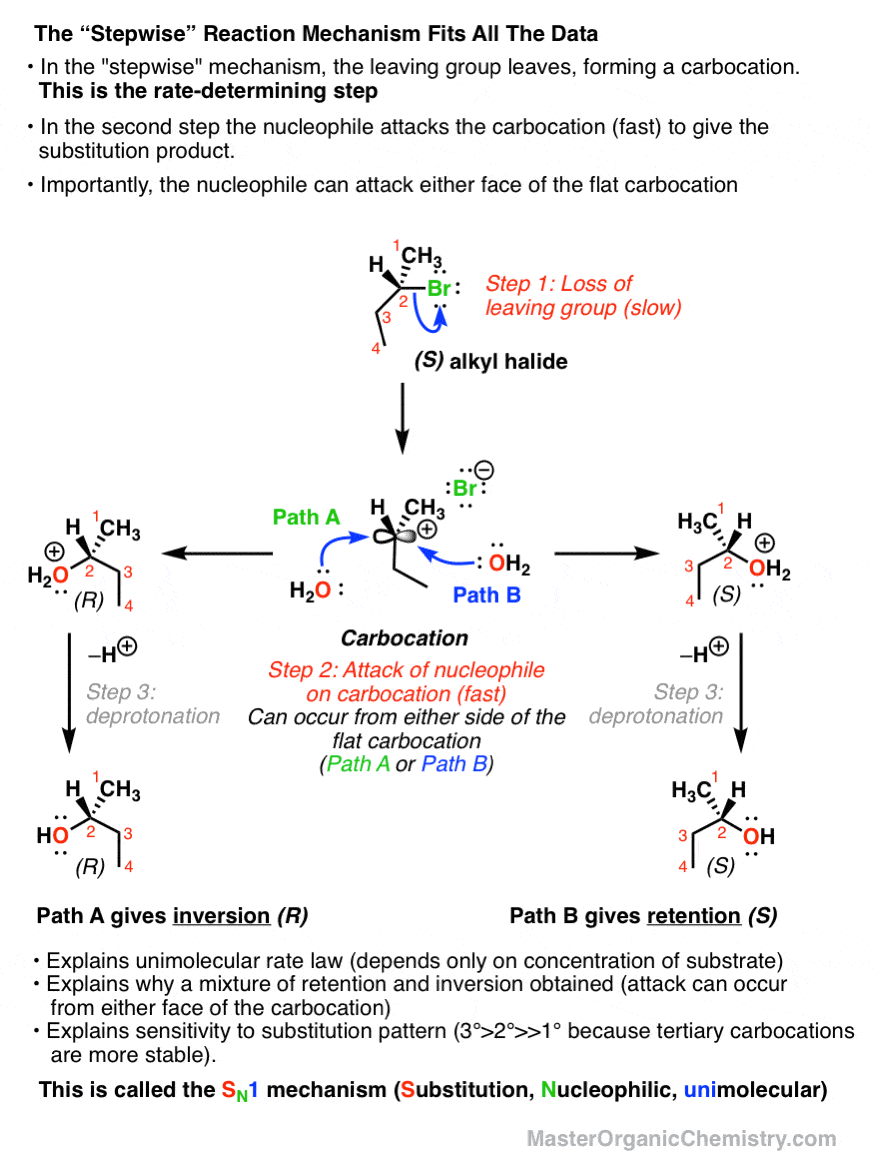
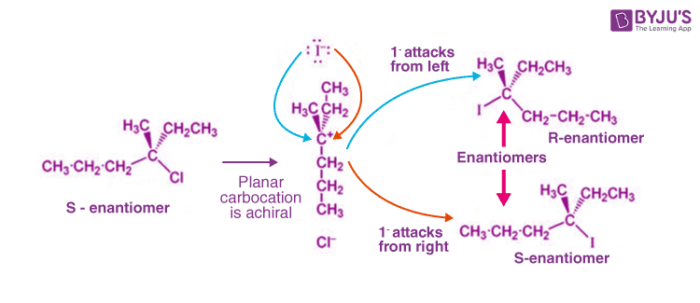
The SN1 Mechanism: Energy Diagram, Stereochemistry with ... Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions. The SN1 Mechanism: Kinetcis, Thermodynamics, Curved Arrows and Stereochemistry with Practice Problems. In the previous post we talked about the mechanism, kinetics, reactivity, rearrangements and some more features of the S N 1 reaction. The SN1 Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction. SN1 and SN2 reaction - Kinetics, Mechanism ... Energy profile diagram of SN 1 reaction: Stereochemistry of SN 1 reaction: In SN 1 reaction, carbocations are formed as the intermediate which are trigonal and planar. Carbocation has a flat structure so that nucleophile can attack it from either side (i.e. front or back) resulting in the formation of two products, one with retention of configuration and other with inversion of configuration.
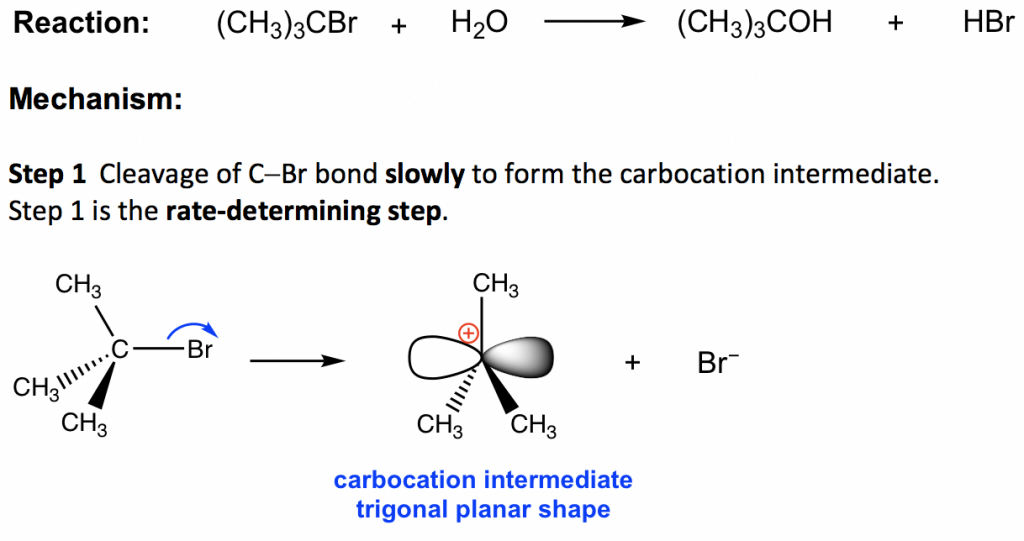
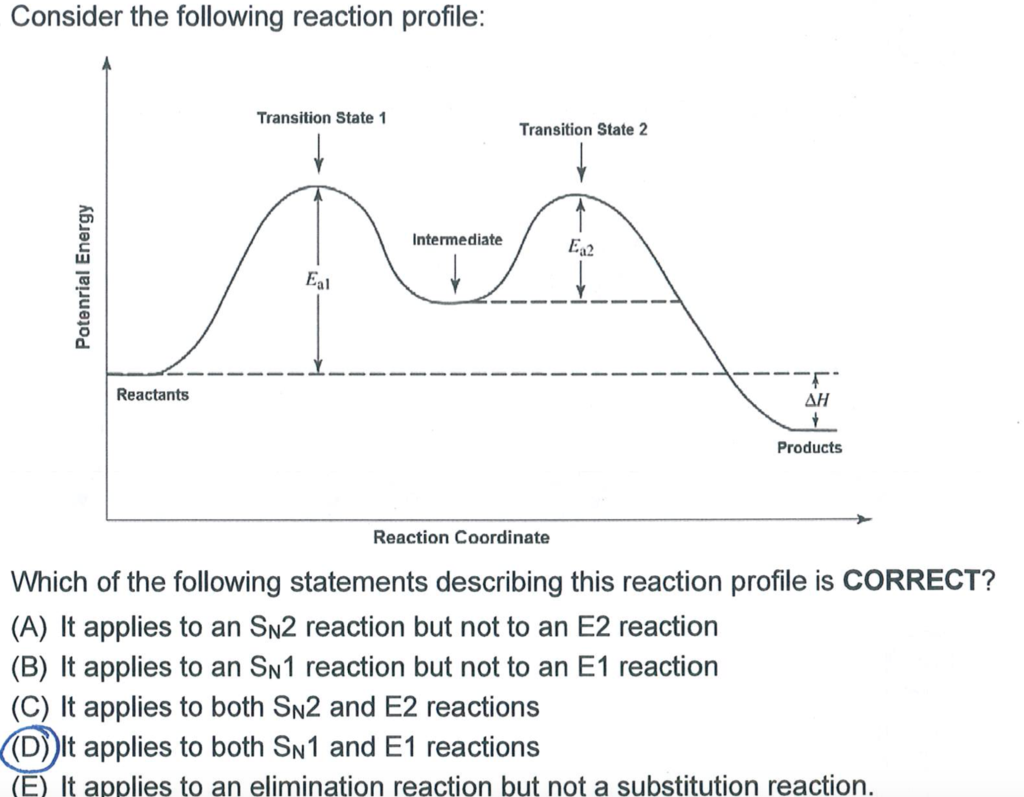
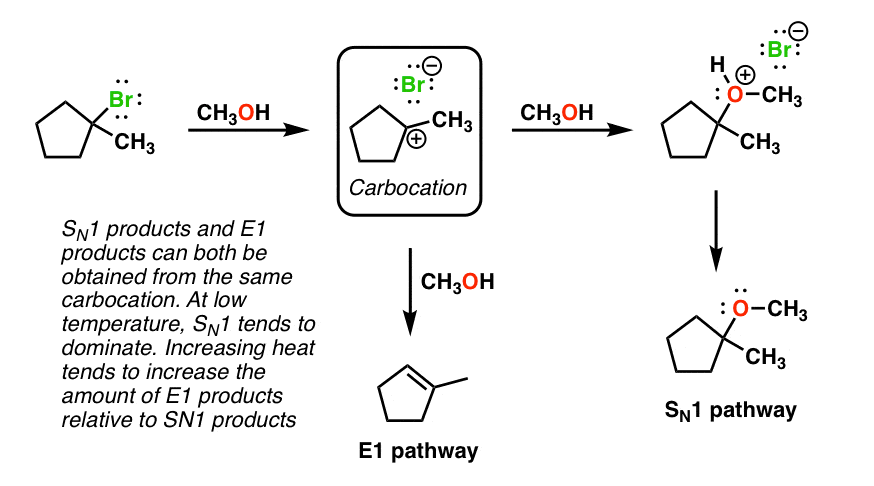
PDF 9.6 THE SN1 AND E1 REACTIONS - Macmillan Learning N1 and E1 Reactions The solvolysis of tert-butyl bromide follows a first-order rate law: rate = k[(CH 3) 3CBr] (9.52) Any involvement of solvent in the reaction cannot be detected in the rate law because the con-centration of the solvent cannot be changed. However, the nature of the solvent does play a critical role in this reaction.
Sn1 reaction diagram
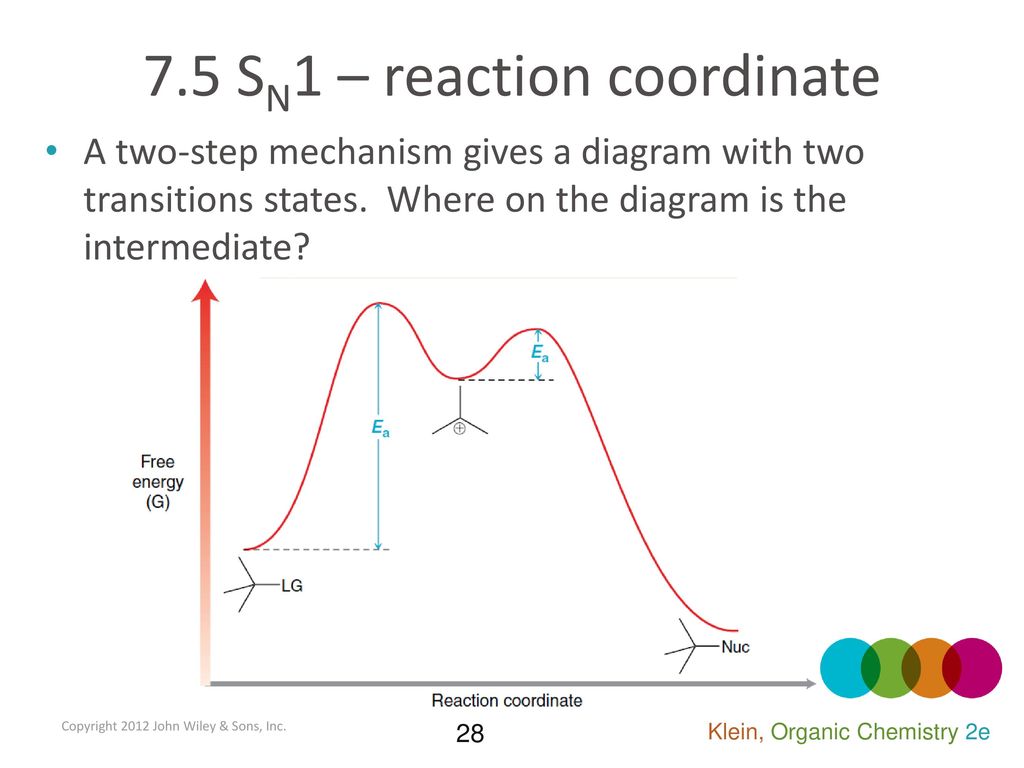
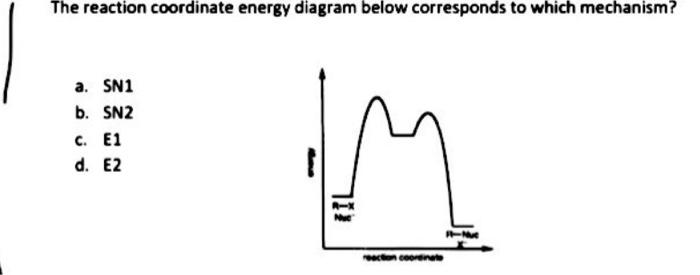
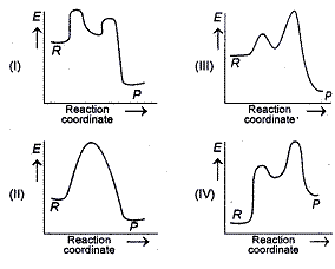
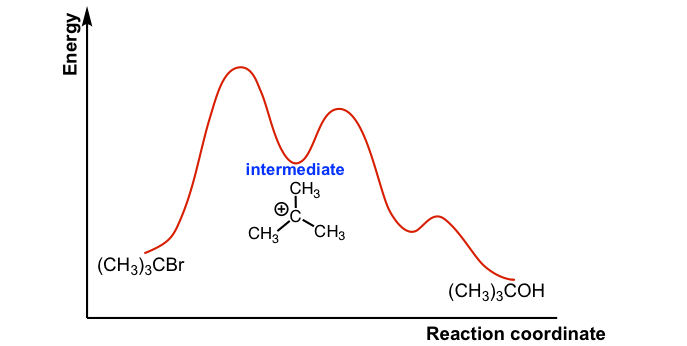
SN1 Mechanism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Figure 7.3 shows an energy diagram tracing the progress of a reaction that occurs by an S N 1 mechanism. The rate of the reaction reflects the activation energy required to form the carbocation intermediate. The activation energy required for step 2, addition of the nucleophile to the carbocation, is much smaller, so step 2 is very fast. Energy Diagram Sn1 - schematron.org on Energy Diagram Sn1. The S N 1 reaction energy diagram illustrates the dominant part of the substrate with respect to the reaction rate. The rate-determining step is the formation of the . Substitution Reactions (SN2 versus SN1) SN1. How to draw a reaction coordinate diagram for SN1 mechanism? It is also typical of SN1 reactions for the first step to be rate-limiting, as carbocation formation from a neutral reactant is thermodynamically unfavorable unless specific reaction conditions are present. The three general rules for reaction coordinate diagrams are as follows:
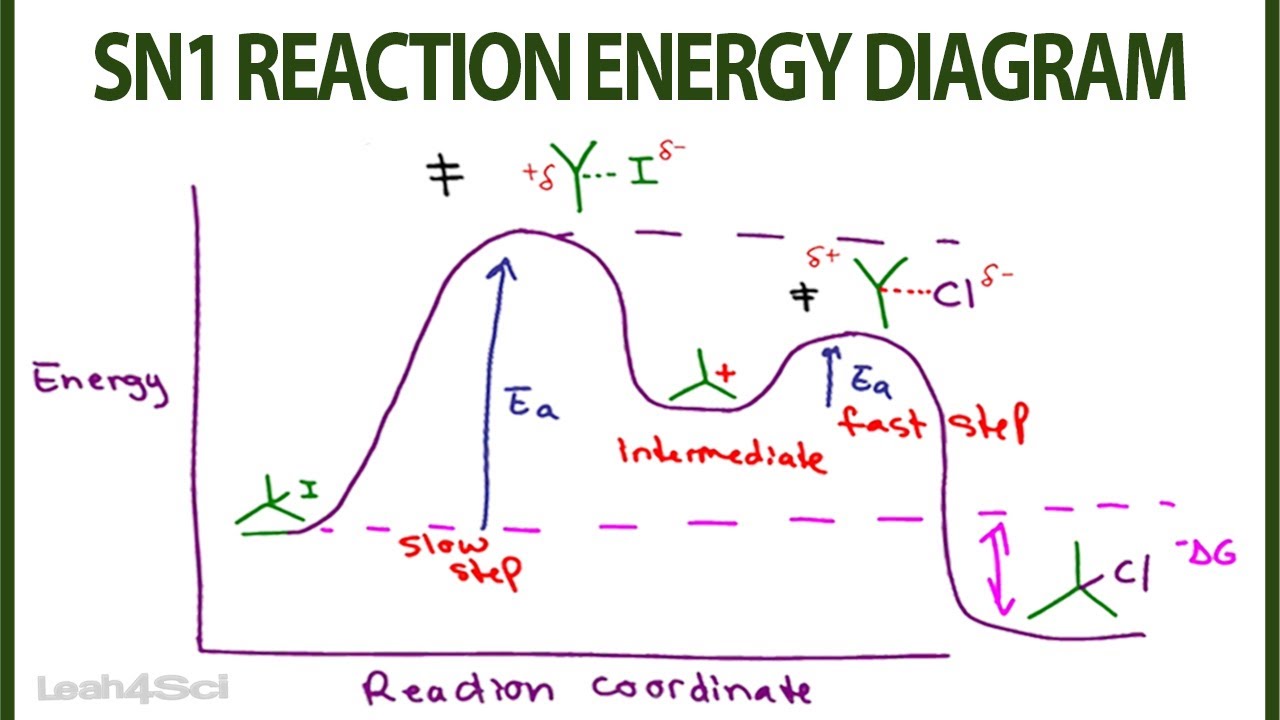
Sn1 reaction diagram. SN1 and SN2 | Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions UO Chemists Energy level diagram for Sn1 Reaction This graph represents that the intermediate formed is very reactive. Effect of solvent, substrste structure, and leaving group on Sn1: 8.2. Physical chemistry for SN2 and SN1 reactions ... A potential energy diagram for an S N 1 reaction shows that the carbocation intermediate can be visualized as a kind of "mountain valley" in the path of the reaction, higher in energy than both the reactant and product but lower in energy than the two transition states. Exercise Draw structures representing TS1 and TS2 in the reaction above. PDF SN1 and SN2 Reactions - Illinois Institute of Technology 1 Reaction SN1 reactions are nucleophilic substitutions, involving a nucleophile replacing a leaving group (just like SN2). However: SN1 reactions are unimolecular: the rate of this reaction depends only on the concentration of one reactant. SN1 reactions happen in two steps: 1. The leaving group leaves, and the substrate forms a Reaction Energy Diagram - SN1 - YouTube The reaction energy diagram for the SN1 reaction, from starting materials through the intermediate carbocation to the final substitution product. How to iden...
SN1 Examples: Detailed Insights And Facts Energy profile diagram of SN1 reaction: sn1 example t-butyl bromide and water Image credit: Jonathan Clayden, Nick Greeves, and Stuart Warren The carbocation is shown as an intermediate- a species with a finite (short) lifetime. The SN1 Reaction Mechanism and SN1 Practice Problems The fast reaction of the carbocation with the nucleophile is the driving force of the S N 1 reaction since it pulls the equilibrium to the right according to the Le Châtelier's principle. S N 1 - A Two-Step Mechanism. Let's break down all the steps in the following S N 1 reaction looking at the energy diagram: Step [1] Breaking the C - LG bond. 7.4 SN1 Reaction Mechanism, Energy Diagram and ... Energy diagram of SN1 mechanism Because S N 1 is a multiple-step reaction, so the diagram has multiple curves, with each step can be represented by one curve. Out of the three steps, the activation energy for step 1 is the highest, therefore step 1 is the slowest step, that is the rate-determining step. SN1 Reaction Mechanism - Detailed Explanation with Examples The S N 1 reaction is often referred to as the dissociative mechanism in inorganic chemistry. Given below are some examples of an S N 1 type of nucleophilic substitution reaction. Effect of Solvent. A solvent that can facilitate the formation of the carbocation intermediate will speed up the rate determining step of the S N 1 reaction.
SN1 Reaction Energy Diagram - YouTube SN1 Reaction Energy Diagram - YouTube. SN1 Reaction Energy Diagram. Watch later. Share. Copy link. Info. Shopping. Tap to unmute. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. SN1 Reaction Mechanism - Graphical Representation, Steps ... For SN1 reaction, rate of reaction can be expressed as - r = R − L G (General representation) where r = rate of reaction, R = alkyl group and LG = leaving group. Example of SN1 reaction - (image will be uploaded soon) In the above reaction - leaving group - Br- Nucleophile - OH- Graphical Representation of SN1 Reaction Pathway Learn About Energy Diagram For Sn1 Reaction | Chegg.com Energy Diagram for SN1 Reaction Definition Substitution nucleophilic unimolecular reactions S N 1 {{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1 S N 1 involve only one reactant species in the rate-determining step. The analysis of the energy diagram for S N 1 {{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1 S N 1 reaction shows that the reaction is comprised of two steps which contain two high energy unstable transition states and one stable intermediate. Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram - schematron.org SN1 Reactions & Substrate Reactivity. SN1 indicates a substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular reaction, described by the expression rate = k reaction coordinate diagram for a two step process.Potential Energy Diagrams for Multistep Reactions: The SN1 Mechanism The potential energy diagram for a multistep mechanism is simply a collection of the potential energy diagrams for the individual steps.
Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram SN1 indicates a substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular reaction, described by the expression rate = k reaction coordinate diagram for a two step process. SN1 reaction The S1 reaction is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry. or process an energy profile (or reaction coordinate diagram) is a theoretical.
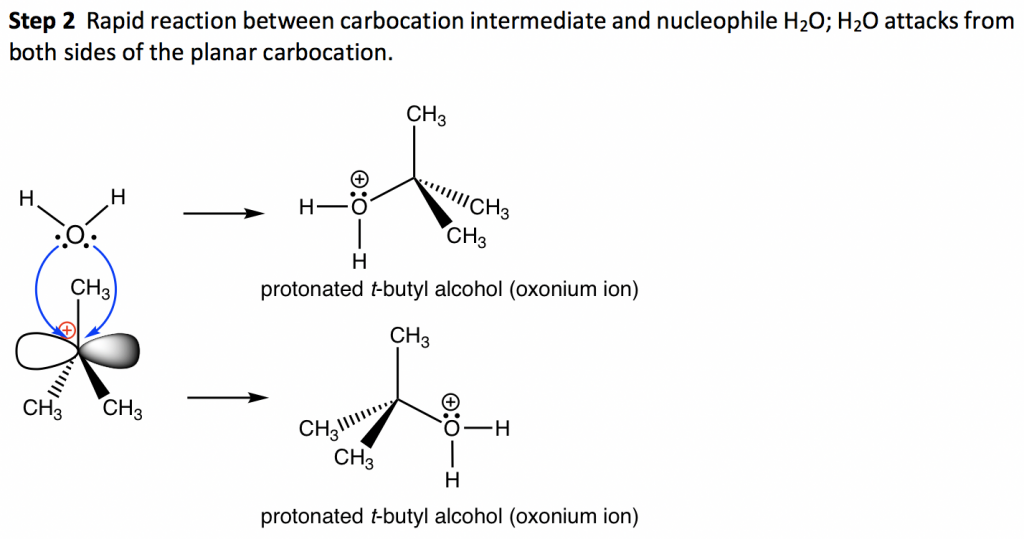
Sn1 Reaction - ChemTalk The diagram above shows an sn1 reaction mechanism between methyl tert-butyl ether and hydrogen bromide. Firstly, the oxygen atom in the electrophile bonds with a hydrogen that has dissociated from the HBr. This is because CH 3 O is a poor leaving group, but CH 3 OH is a good leaving group. Thus, as the oxygen bonds with this hydrogen, the leaving group improves and can carry out the first step of the sn1 reaction, detaching from the molecule.
How to draw a reaction coordinate diagram for SN1 mechanism? It is also typical of SN1 reactions for the first step to be rate-limiting, as carbocation formation from a neutral reactant is thermodynamically unfavorable unless specific reaction conditions are present. The three general rules for reaction coordinate diagrams are as follows:
Energy Diagram Sn1 - schematron.org on Energy Diagram Sn1. The S N 1 reaction energy diagram illustrates the dominant part of the substrate with respect to the reaction rate. The rate-determining step is the formation of the . Substitution Reactions (SN2 versus SN1) SN1.
SN1 Mechanism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Figure 7.3 shows an energy diagram tracing the progress of a reaction that occurs by an S N 1 mechanism. The rate of the reaction reflects the activation energy required to form the carbocation intermediate. The activation energy required for step 2, addition of the nucleophile to the carbocation, is much smaller, so step 2 is very fast.


















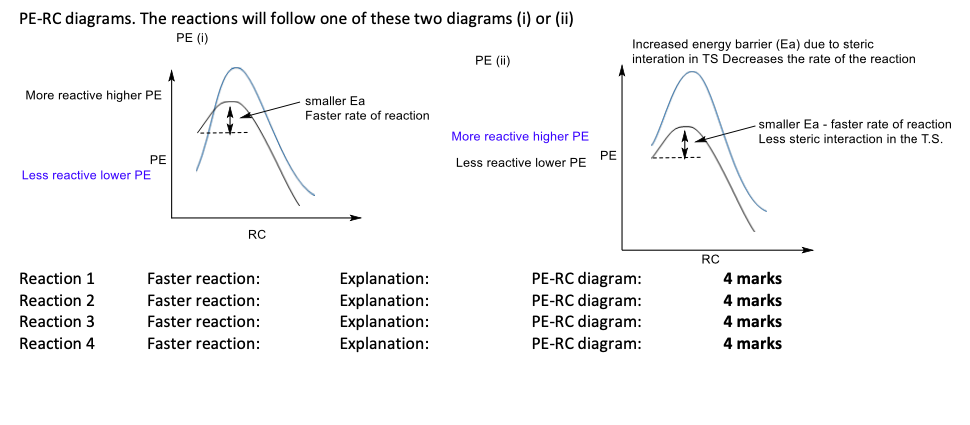


Comments
Post a Comment