39 ecg axis diagram
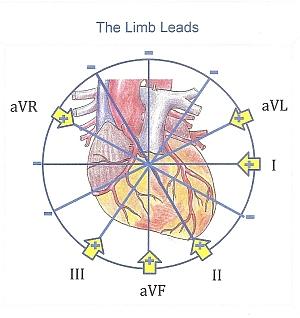
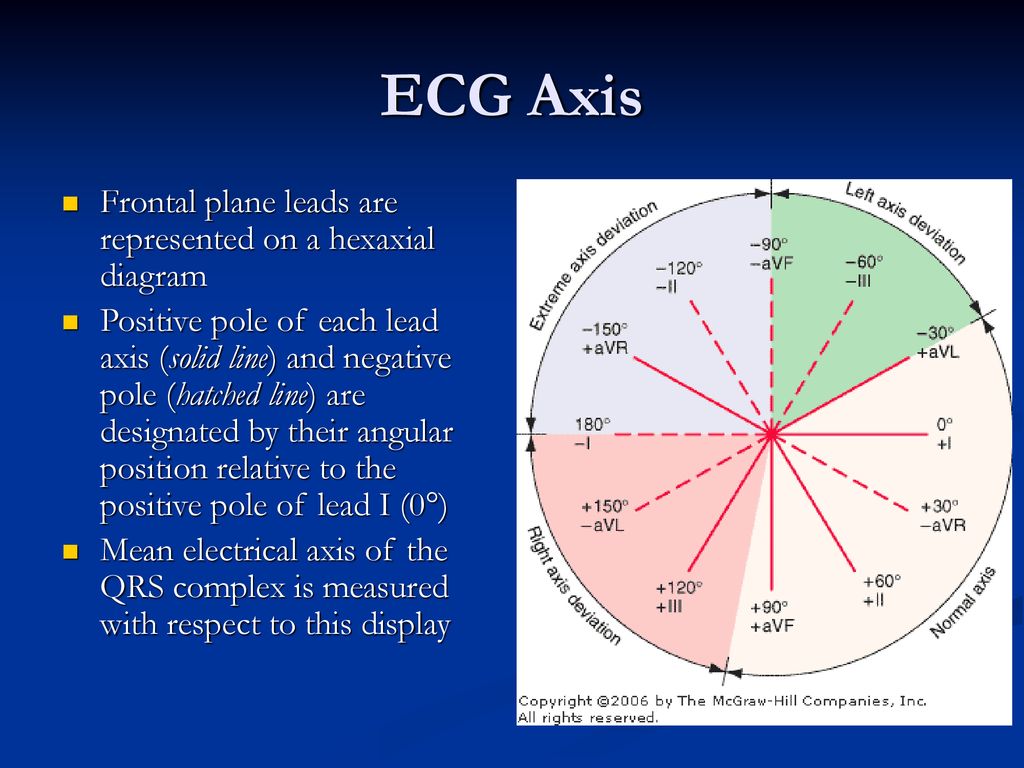
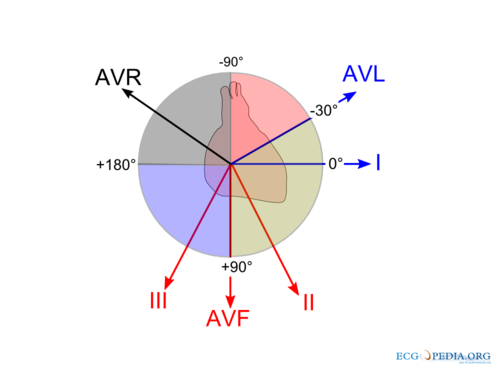
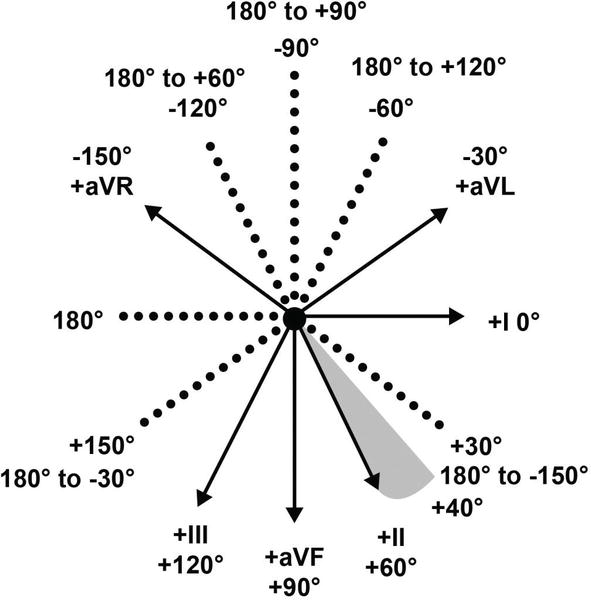
The electrical axis of the heart (heart axis): ECG ... The electrical axis of the heart (heart axis). As evident from the figure, the normal heart axis is between -30° and 90°. If the axis is more positive than 90° it is referred to as right axis deviation. If the axis is more negative than -30° it is referred to as left axis deviation. The axis is calculated (to the nearest degree) by the ECG machine. 12-Lead ECG Placement Guide with Illustrations 3-Lead ECG A 3-Lead ECG uses 3 electrodes that are labeled white, black, and red. These colors are not universal as two coloring standards exist for the ECG (discussed below). These 3 leads monitor rhythm monitoring but doesn't reveal sufficient information on ST elevation activity. 5-Lead ECG. A 5-Lead ECG uses 4 limb leads and 1 chest lead.
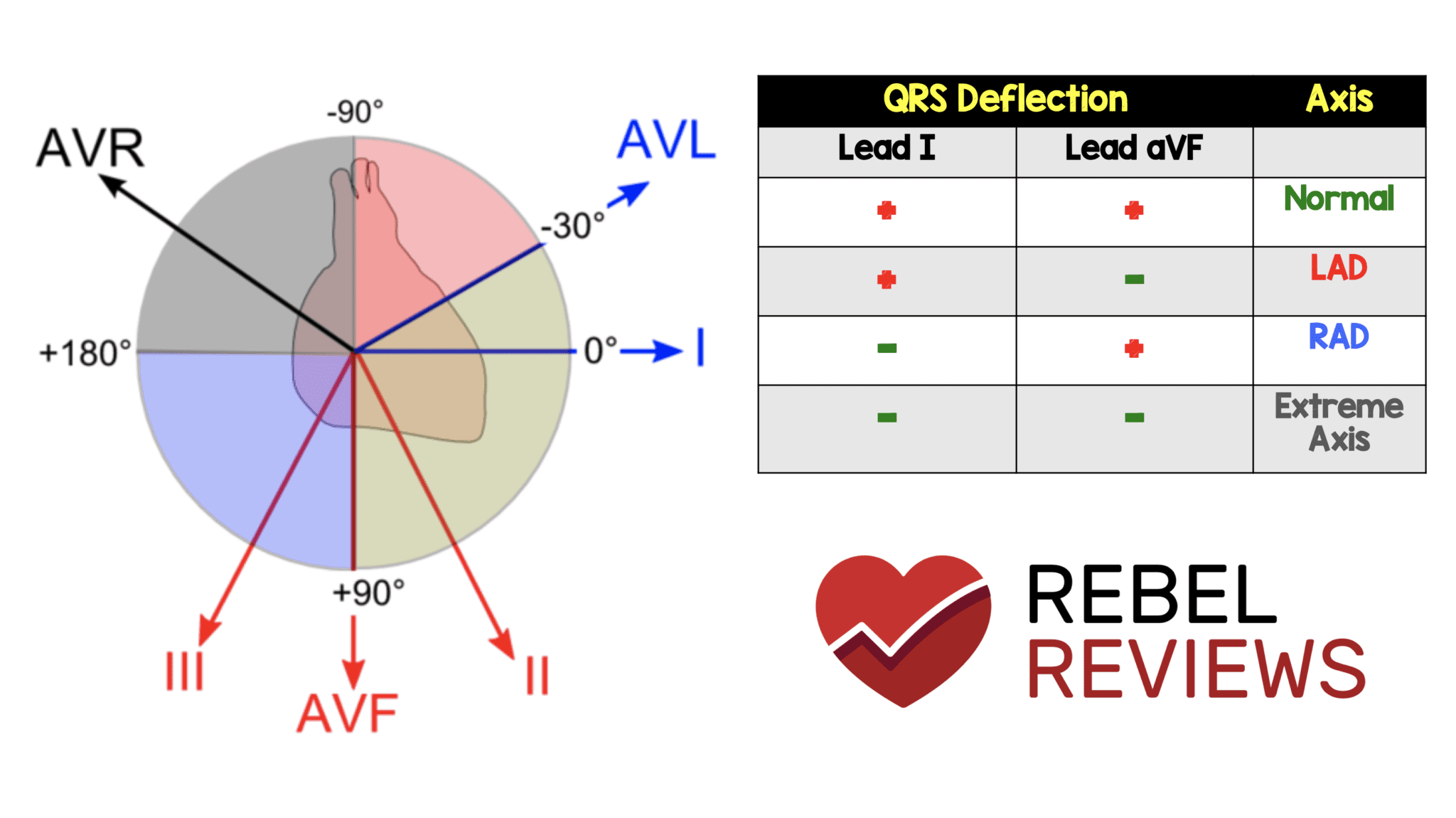
EKG (ECG) Axis Deviations Diagram #Diagnosis #Cardiology ... EKG (ECG) Axis Deviations Diagram #Diagnosis #Cardiology #ECG #EKG #Axis #Deviations #LAD #RAD #ERAD. Contributed by. Dr. Gerald Diaz @GeraldMD. Board Certified Internal Medicine Hospitalist, GrepMed Editor in Chief 🇵🇭 🇺🇸 - Sign up for an account to like, bookmark and upload images to contribute to our community platform.

Ecg axis diagram
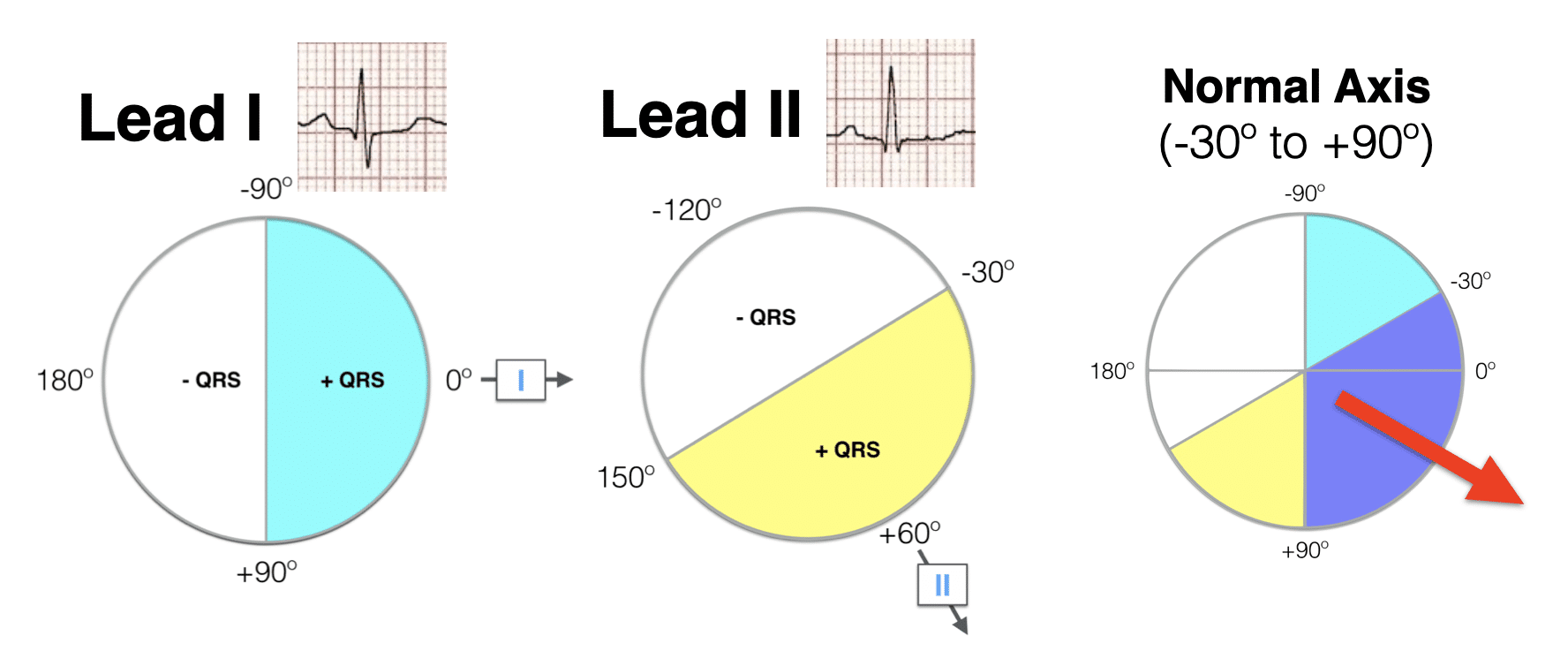
ecgwaves.com › topic › ekg-ecg-leads-electrodesThe ECG leads: electrodes, limb leads, chest (precordial ... The electrocardiograph presents one diagram for each lead. Voltage is presented on the vertical (Y) axis and time on the horizontal (X) axis of the diagram. The ECG paper has small boxes (thin lines) and large boxes (heavy lines). Small boxes are squares of 1 mm 2 and there are 5 small boxes inside each large box. Refer to Figure 15. Micro EKG - Mad Scientist Software See the diagram: if the axis is in the direction labeled "II" the axis is +60 degrees. Right axis deviation is seen on the ECG when more electrical forces are moving to the right than normal. This is usually due to hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RVH). Causes of right axis deviation include COPD, pulmonary emboli, valvular disease, septal ... › books › NBK2214Conquering the ECG - Cardiology Explained - NCBI Bookshelf A wide QRS complex despite sinus rhythm is the hallmark of bundle branch block. Left bundle branch block (LBBB) can cause the ECG to look extremely abnormal (see Figure 13). When faced with such an ECG – after calculating rate, rhythm, and axis – check the width of the QRS complex. If it is more than three small squares wide, it is abnormal.
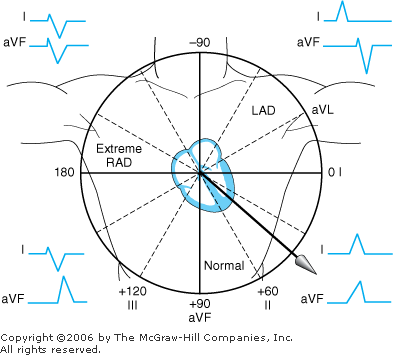
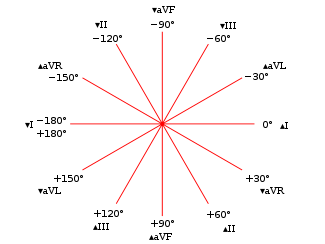
Ecg axis diagram. PDF The Basic 12 Lead Electrocardiogram How to read an EKG • The paper - Up and down 1 box = 0.1 mV -Across 1 box = 4 ms • The rate - 10 seconds per page. How to read an EKG • The Waveform. ... Axis • General direction of electrical activity • Will not change your management. Interval •PR - Block between atria and ventricles ECG Axis Interpretation Diagram - Quizlet The diagram below illustrates the relationship between QRS axis and the frontal leads of the ECG. -Normal Axis = QRS axis between -30° and +90°. -Left Axis Deviation = QRS axis less than -30°. -Right Axis Deviation = QRS axis greater than +90°. -Extreme Axis Deviation = QRS axis between -90° and 180° (AKA "Northwest Axis"). › at-a-glance-1 › the-ecg-explained-easyThe ECG explained easy - The Cardio Research Web Project When talking about to the ECG axis is it generally the QRS axis that is being referred to. The normal QRS axis is between -30 and +90 degrees. The most efficient way to estimate axis is to look at leads I + aVF. The diagram below illustrates the relationship between QRS axis and the frontal leads of the ECG. Heart Axis Calculation - My EKG Before calculating the heart axis, we must understand that each lead represents a different point of view of the same electrical stimulus.. To calculate the cardiac axis we will only use the limbs leads. Taking the example of the bus, the Limbs Leads are 6 windows that look to the heart in the frontal plane, that is: from above, below, left and right.. Never from the front or back si
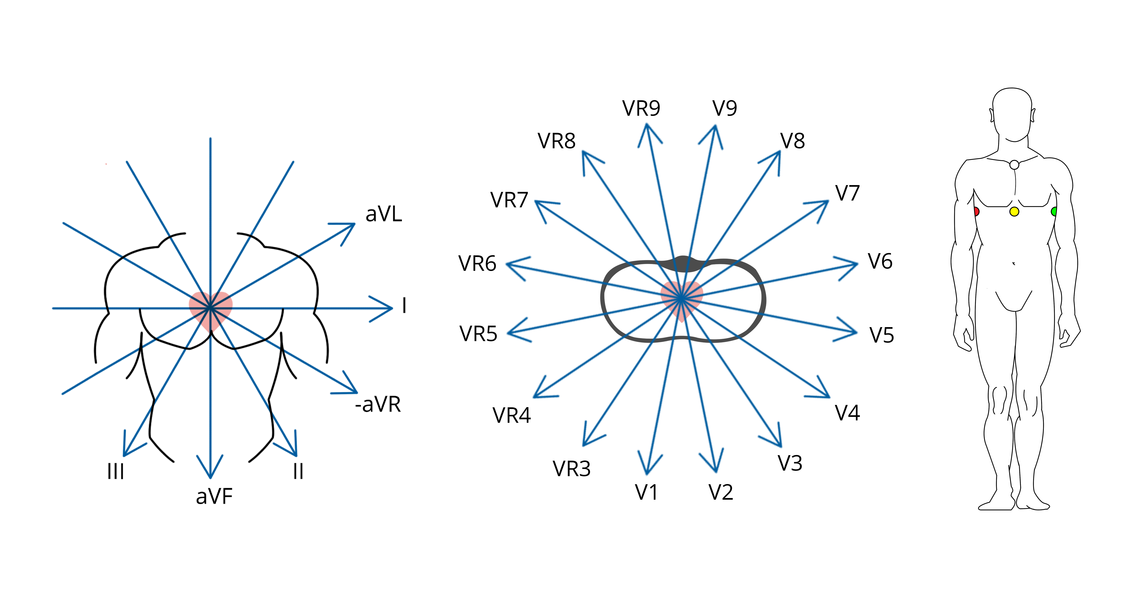
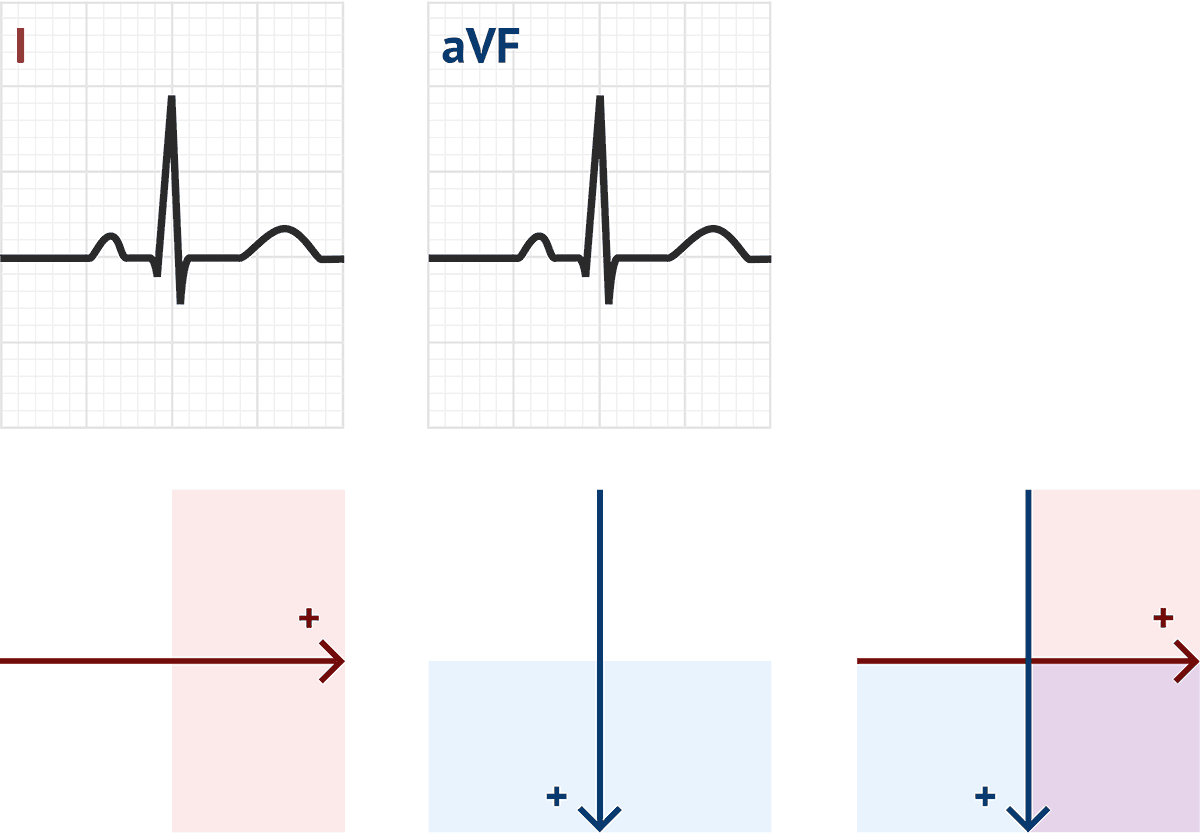
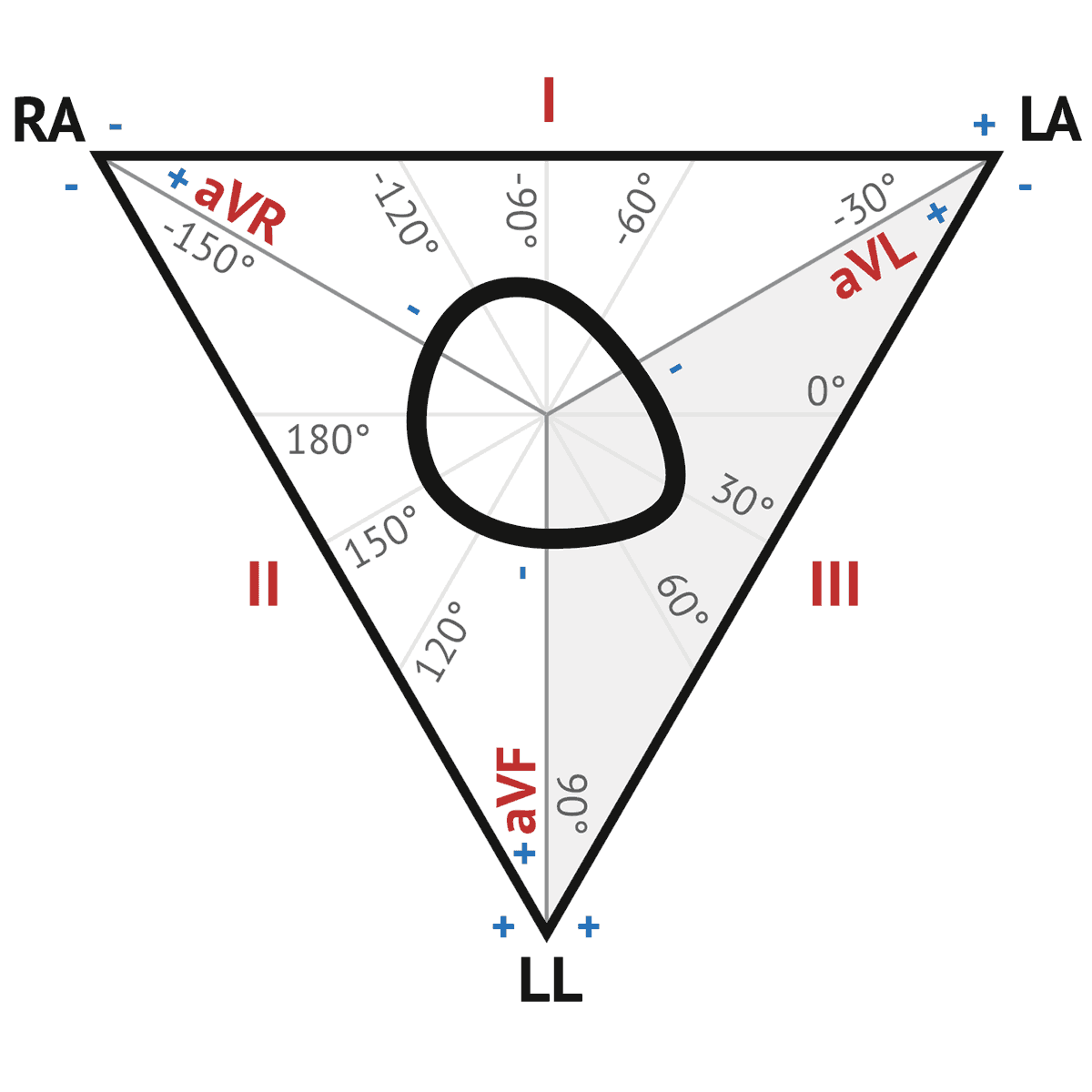
PDF Ecg Interpretation:Ecg Interpretation Axis • The direction of an ECG waveform in the frontal plane measured inplane measured in degrees •Represents the flow of the majority of electrical activity • NllhQRSNormally the QRS complex is measured . Axis • Each lead has its own axis. Lead PlacementLead Placement ECG (EKG) Interpretation - Oxford Medical Education Assessing the axis on an ECG Axis is the sum of all the electrical activity in the heart. The contraction travels from the atria to the right and left ventricles. As the left ventricle is larger and more muscular normal axis lies to the left (at -30 degrees to 90 degrees - see Figure 5). PDF ECG Measurement and Analysis Figure 2: System of limb lead ECG. lead eld idea in that there is the lead vector for each of the three limb leads, I, II, and III, that correspond to the sides of the Einthoven triangle. In this lab, you will record the standard limb leads in sequence, according to the diagram in Figure 2. Axis - University of Wisconsin-Madison You can make a diagram and shade in the positive half of the circle: To find the axis overlap the two circles. The common shaded area is the quadrant in which the axis lies. In this example, the axis lies in the normal quadrant, which on a patient, points down and to the left. You can repeat this process for any two leads, but I and aVF are the ...
PDF ECG Basics - Boston College electrical axis of the ventricle . Ventricular Depolarization . Lead Placement • Limb leads 10 cm from heart • Precordial leads placed exact ... • With vector manipulation ECG machine creates aVR, aVL, & aVF . Hexaxial System • Used to determine electrical axis • What is the normal axis for the heart? • -30 to +90 . ECG Learning Center - An introduction to clinical ... In the diagram below the normal range is identified (-30° to +90°). Left axis deviation (i.e., superior and leftward) is defined from -30° to -90°, and right axis deviation (i.e., inferior and rightward) is defined from +90° to +150°. Click to see causes of abnormal axis (lesson 4). QRS Axis Determination litfl.com › ecg-lECG Lead positioning • LITFL • ECG Library Basics Jan 30, 2022 · Right sided ECG electrode placement. There are several approaches to recording a right-sided ECG: A complete set of right-sided leads is obtained by placing leads V1-6 in a mirror-image position on the right side of the chest (see diagram, below). Determining Axis | Learn the Heart - Healio The axis of the ECG is the major direction of the overall electrical activity of the heart. It can be normal, leftward (left axis deviation, or LAD), rightward (right axis deviation, or RAD) or...
Electrocardiography - Wikipedia Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization ...
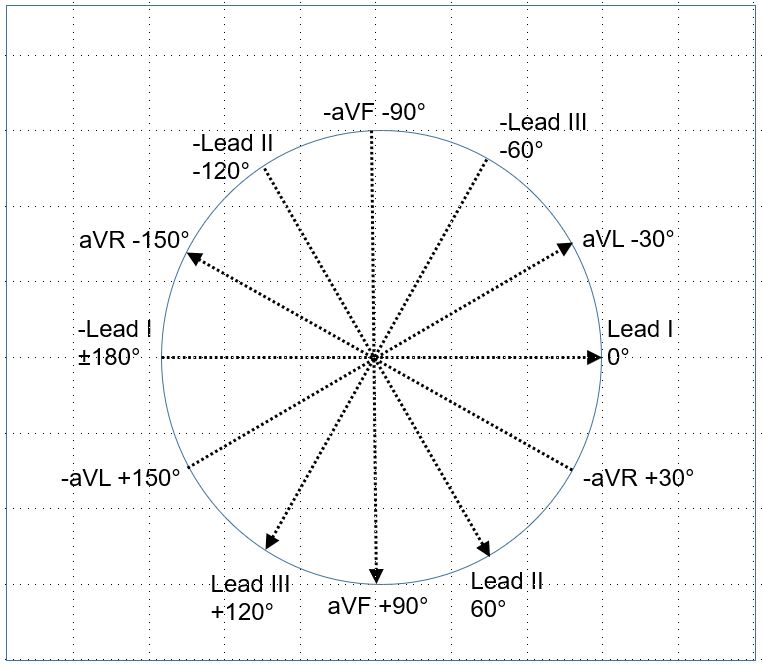
"A" is for Axis - ECG Course The electrical axis is described as the vector direction of the resultant depolarization wave of the free right, left ventricle and the septum. This vector can be found by the resultant of two vectors directed at 90 degrees to each other. We will agree to use the following two vectors: Lead avF (pointing straight downward) and
ECG Axis Interpretation • LITFL • ECG Library Basics Normal Axis = QRS axis between -30° and +90°. Abnormal axis deviation, indicating underlying pathology, is demonstrated by: Left Axis Deviation = QRS axis less than -30°. Right Axis Deviation = QRS axis greater than +90°. Extreme Axis Deviation = QRS axis between -90° and 180° (AKA "Northwest Axis").
litfl.com › super-axis-man-samSuper Axis Man SAM • LITFL • ECG Library Basics Nov 03, 2020 · (5) Now for some 5 th grade maths. Using a right angled triangle; SAM tells you that there are several right angled triangles in this diagram. But, the simplest one to use is the one that starts from 0° and ends at 90°.
PDF A Guide to Reading and Understanding the EKG Axis Next we need to determine the AXIS of the EKG tracing. To do this we need to understand the basic 6 leads and their geometry. The EKG waveform comes from a measurement of surface voltages between 2 leads. A wave that is travelling towards the positive (+) lead will inscribe an upwards
Basics - ECGpedia The 3 channel ECGuses 3 or 4 ECG electrodes. Red is on the right, yellow on the left arm, green on the left leg ('sun shines on the grass') and black on the right leg. These basic leads yield enough information for rhythm-monitoring.
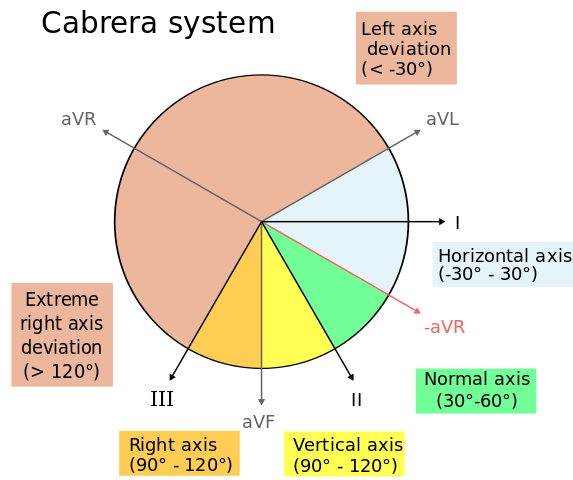
What does rightward axis mean on ECG? What does rightward axis mean on ECG? On a hexaxial diagram (see figure 1): If the electrical axis falls between the values of -30° to +90° this is considered normal. If the electrical axis is between -30° to -90° this is considered left axis deviation. If the electrical axis is between +90° to +180° this is considered right axis ...
Determining Cardiac Axis - The Student Physiologist Looking at the ECG pictured, we can see that aVL is the most isoelectric lead. On the diagram, lead II crosses it at 90° Lead II shows a positive deflection on the ECG, so on the diagram, we move towards the arrow and to +60°, ergo: This patient has a normal cardiac axis; Method 3. The Precise Calculation
Hexaxial reference system - Wikipedia The hexaxial reference system is a diagram that is used to determine the heart's electrical axis in the frontal plane. The hexaxial reference system, better known as the Cabrera system, is a convention to present the extremity leads of the 12 lead electrocardiogram, that provides an illustrative logical sequence that helps interpretation of the ...
Understanding an ECG | ECG Interpretation | Geeky Medics An ECG electrode is a conductive pad that is attached to the skin to record electrical activity. An ECG lead is a graphical representation of the heart's electrical activity which is calculated by analysing data from several ECG electrodes. A 12-lead ECG records 12 leads, producing 12 separate graphs on a piece of ECG paper.
quizlet.com › 388944195 › ecg-module-quiz-questionsECG module quiz questions Flashcards | Quizlet The upgoing wave labeled with a red asterisk in the diagram below would be named: a. Q b. R c. T d. S e. R' (R-prime) ... Examine the ECG below. Type in the QRS axis ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Right_axis_deviationRight axis deviation - Wikipedia The electrical axis of the heart is the net direction in which the wave of depolarization travels. It is measured using an electrocardiogram (ECG).Normally, this begins at the sinoatrial node (SA node); from here the wave of depolarisation travels down to the apex of the heart.
Note from LITFL: ECG Axis Interpretation - Foamed The diagram below illustrates the relationship between QRS axis and the frontal leads of the ECG. Normal Axis = QRS axis between -30° and +90°. Left Axis Deviation = QRS axis less than -30°. Right Axis Deviation = QRS axis greater than +90°. Extreme Axis Deviation = QRS axis between -90° and 180° (AKA "Northwest Axis").
ECG Axis Interpretation - Internal Medicine | ECG ... ECG Axis InterpretationAxis interpretation using the schematic illustration demonstrates the relationship between QRS axis and the frontal leads of the ECG.Normal Axis = QRS axis between -30° and +90°. Left Axis Deviation = QRS axis less than -30°. Right Axis Deviation = QRS axis greater than +90°. Extreme Axis Deviation = QRS axis between -90°…
› books › NBK2214Conquering the ECG - Cardiology Explained - NCBI Bookshelf A wide QRS complex despite sinus rhythm is the hallmark of bundle branch block. Left bundle branch block (LBBB) can cause the ECG to look extremely abnormal (see Figure 13). When faced with such an ECG – after calculating rate, rhythm, and axis – check the width of the QRS complex. If it is more than three small squares wide, it is abnormal.
Micro EKG - Mad Scientist Software See the diagram: if the axis is in the direction labeled "II" the axis is +60 degrees. Right axis deviation is seen on the ECG when more electrical forces are moving to the right than normal. This is usually due to hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RVH). Causes of right axis deviation include COPD, pulmonary emboli, valvular disease, septal ...
ecgwaves.com › topic › ekg-ecg-leads-electrodesThe ECG leads: electrodes, limb leads, chest (precordial ... The electrocardiograph presents one diagram for each lead. Voltage is presented on the vertical (Y) axis and time on the horizontal (X) axis of the diagram. The ECG paper has small boxes (thin lines) and large boxes (heavy lines). Small boxes are squares of 1 mm 2 and there are 5 small boxes inside each large box. Refer to Figure 15.






















Comments
Post a Comment