40 brain diagram reticular formation
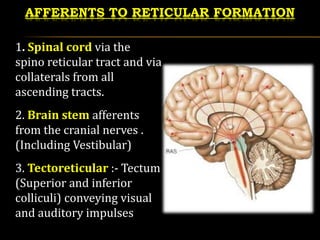
Aug 21, 2021 · Brain diagram reticular formation. It is also the origin of the descending analgesic pathways. The reticular formation cranial extension is upto the dienceph-alon subthalamus hypothalamus and. All the functions are carried out without a single glitch and before you. Peer Reviewed Journal High visibility Open Access. The reticular (from the Latin reticulum, meaning net) formation is a far-reaching network of neurons extending from the spinal cord to the thalamus, with connections to the medulla oblongata, midbrain (mesencephalon), pons, and diencephalon.
Sep 03, 2019 · The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brain stem. Its dorsal tegmental nuclei are in the midbrain while its central tegmental nuclei are in the pons and its central and inferior nuclei are found in the medulla. The Reticular Formation. Is a network of nerve pathway situated in the brainstem. This area connects the spinal cord, cerebellum and cerebrum. It mediates conscious activity and uses sensory and other impulses from the brain stem ...
Brain diagram reticular formation
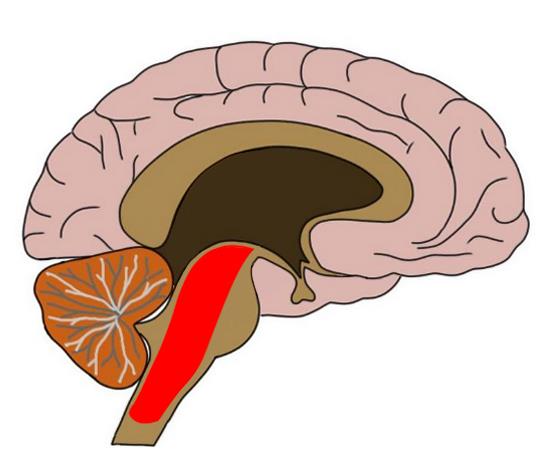
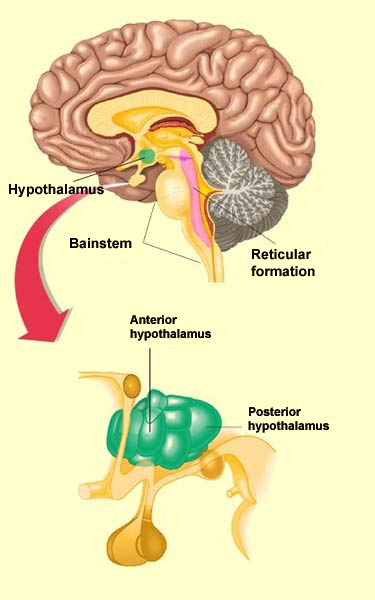
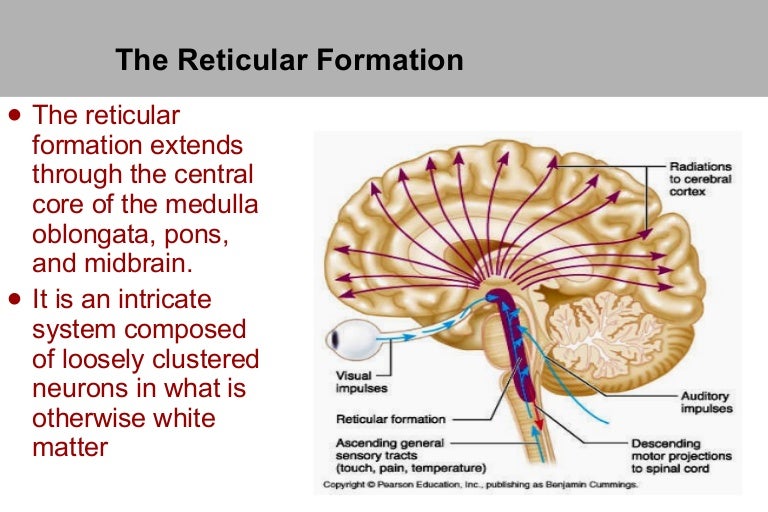
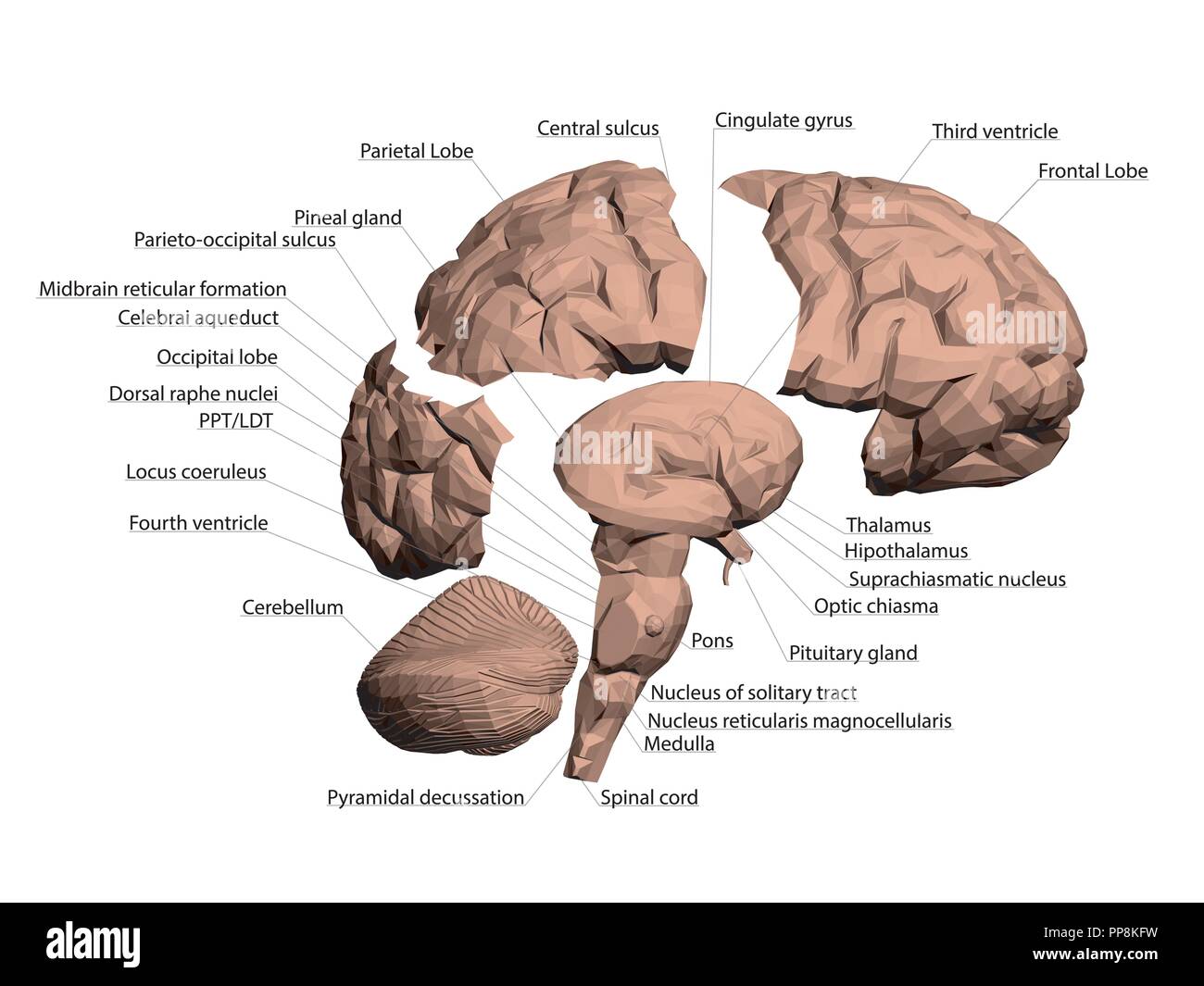
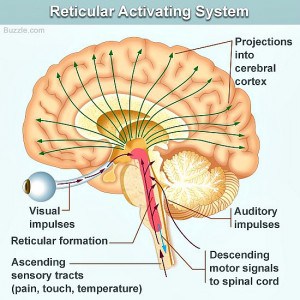
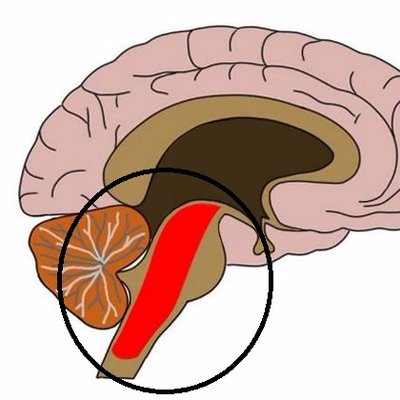
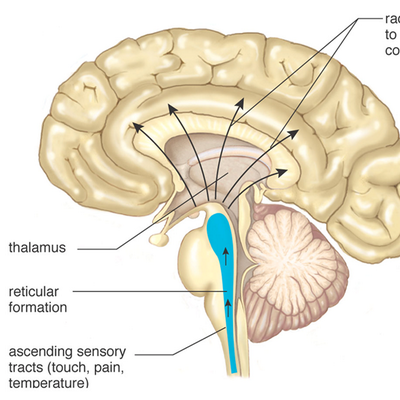
The reticular formation is located in the brain stem. It extends throughout the length of the brainstem, along the central axis, from the spinal cord to the thalamus. It occupies the anterior portions of medulla, pons, midbrain, hypothalamus, and thalamus. reticular formation. The white matter consists of myelinated tracts connecting the cerebrum with the spinal cord and various cranial nerve nuclei. Midbrain Anatomy The midbrain connects the pons and cerebel-lum with the forebrain and can be divided into a ventral part, the tegmentum, and a dorsal part, the tectal or quadrigeminal plate (Figs 2, 3). Reticular formation: This highly diverse and integrative area contains a network of nuclei responsible for many vital functions including arousal, consciousness, sleep-wake cycles, coordination of certain movements, and cardiovascular control.; Periaqueductal gray (PAG) matter: This area plays a primary role in processing pain signals, autonomic function, and behavioral responses to fear and ...
Brain diagram reticular formation. The reticular formation is the medulla, pons and midbrain and comprises the brainstem core (also known as the tegmentum). It is an arrangement of neurons throughout he brain stem. The parvocellular neurons receive information relating to arousal Dec 03, 2021 · Reticular Formation Diagram. angelo on December 3, 2021. Understanding The Brain A Work In Progress Professor Keith Kendrick Reticular Activating System Nervous System Parts System. Reticular Formation Reticular Formation Reticular Activating System Medicine. Organization of the Brainstem and Reticular Formation Competencies: In the brain stem, distinguish the locations of basilar, tegmentum and tectum components. Diagram a cross section of midbrain and locations of major tracts and nuclei. Construct a suprasegmental integrative system in the brain stem. Aug 05, 2021 · Brain stem diagram reticular formation. Some of its important functions are the following. The structure of the reticular formation forms a net-like connection of nuclei and neurons hence its name reticular which correlates to its function of integrating. The reticular formation is strategically placed among the important nuclei and the nerve.
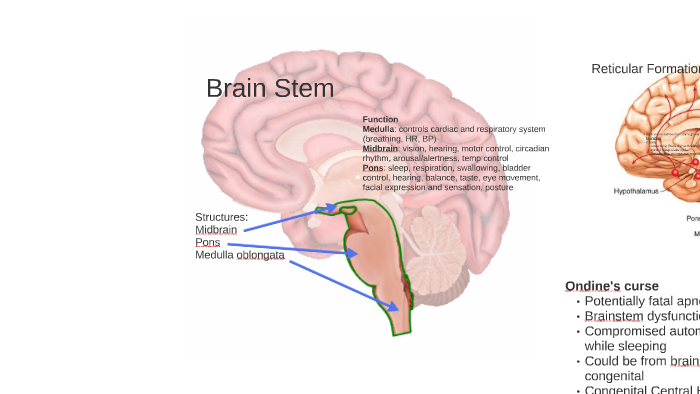
Here are a number of highest rated Reticular Formation Brain pictures on internet. We identified it from reliable source. Its submitted by organization in the best field. We admit this kind of Reticular Formation Brain graphic could possibly be the most trending subject as soon as we ration it in google improvement or facebook. Diagram showing the lobes of the brain. Image Source: Wikimedia Commons. ... the only important structure in the midbrain that you need to know is the reticular formation. The important structures in the hindbrain that you will need to know are the medulla, pons, and the cerebellum. Reticular formation Cerebellum Hypothalamus Thalamus The Brainstem: •Medulla: controls breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. •Pons: relays motor messages between cerebellum and motor cortex: influences sleep and dreaming. •Reticular Formation: affects arousal and attention. Cerebral Cortex THE BRAINSTEM A net-like structure of mixed gray and white matter known as the reticular formation is found in all three regions of the brainstem. The reticular formation controls muscle tone in the body and acts as the switch between consciousness and sleep in the brain.
Brainstem tectum, tegmentum and basal area (diagram) The tectum is the roof of the cavity while the tegmentum forms the ventral covering. The central cavity of the neural tube becomes the aqueduct of Sylvius, the fourth ventricle, and the central canal of the spinal cord. Define reticular formation. reticular formation synonyms, reticular formation pronunciation, reticular formation translation, English dictionary definition of reticular formation. n. A diffuse network of white longitudinal nerve fibers interspersed with gray matter, located in the brainstem, that regulates various autonomic functions,... Labeled Diagrams of the Human Brain Central Core The central core consists of the thalamus, pons, cerebellum, reticular formation and medulla. These five regions are the central areas that regulate breathing, pulse, arousal, balance, sleep and early stages of processing sensory information. The reticular formation is made up of a net-like structure of various brainstem nuclei and neurons and covers an expansive portion of the brainstem, beginning in the mesencephalon, extending caudally through the medulla oblongata, and projecting into the superior cervical spinal cord segments.
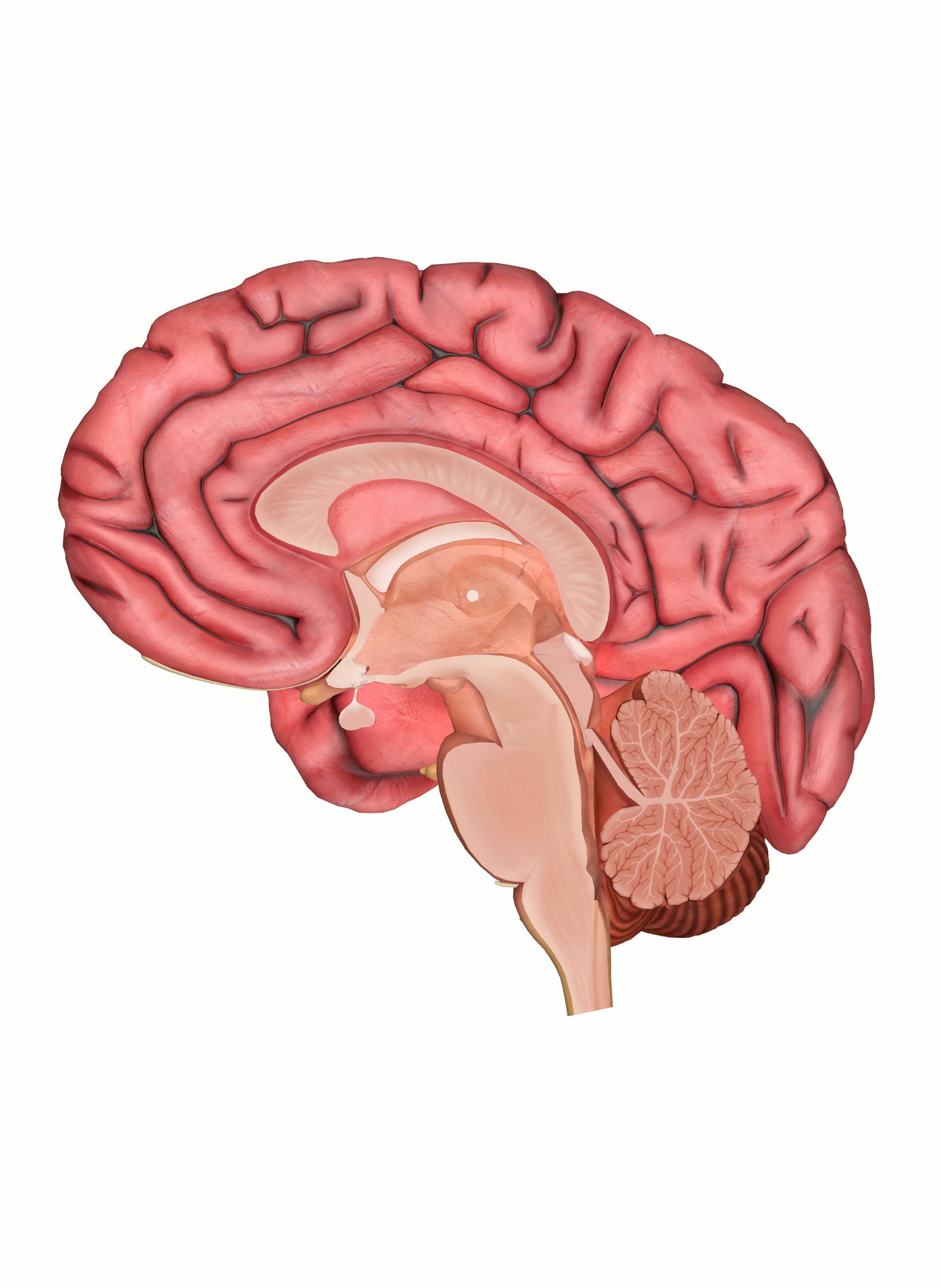
The Brain Diagram. Cerebrum. Cerebellum. Brain stem. Frontal Lobe. large part of your brain involving the four lobes. "small brain" underneath the cerebrum. in charge of basic vital functions like breathing. reasoning, planning, speech, emotions, problem solving.
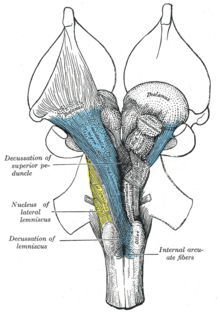
The reticular formation now fans around the posterior borders of the red nuclei. The trochlear nucleus is replaced with the oculomotor nucleus while the oculomotor nerve projects anteriorly. The medial, spinal and trigeminal lemnisci are all present in much the same location however the lateral lemnisci does not reach to this level.
•* The reticular formation is a neural network located in ... Reticular formation Important Parts of the Brain Stem . The Midbrain/ Limbic System (The Mammalian Brain) •Located in the middle of
The reticular formation is the powerhouse portion of the brain, mostly found in the brain stem. There are multiple clusters of nuclei, each responsible for different things. The reticular formation is the primary regulator of arousal and consciousness. During sleep, the center normally suppresses the individual’s level of consciousness. Efferent fibers from the reticular formation can convey sensory information to the cortex of a sleeping individual, which would awaken that person.
1 Reticular formation of the brain stem The difference between the electroencephalographic rhythms in awake and sleeping humans was initially described by Berger[1]. It became a breaking point in the development of sleep science or somnology. The appearance of the EEG method initiated a series of discoveries in sleep studies.
Lesions in the reticular formation have been found in the brains of people who have post-polio syndrome, and some imaging studies have shown abnormal activity in the area in people with chronic fatigue syndrome, indicating a high likelihood that damage to the reticular formation is responsible for the fatigue experienced with these syndromes.
Brain Divisions . The forebrain is the division of the brain that is responsible for a variety of functions including receiving and processing sensory information, thinking, perceiving, producing and understanding language, and controlling motor function. There are two major divisions of forebrain: the diencephalon and the telencephalon. The diencephalon contains structures such as the ...
Brain Diagram (15 points) This is a hand drawn (in color) picture of the human brain that includes the following structures: medulla: pons: reticular formation: cerebellum: thalamus: hypothalamus: amygdala: hippocampus: primary somatosensory cortex: primary motor cortex: frontal lobe: occipital lobe: temporal lobe:
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem.It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain.The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata.
The reticular formation is a cluster of nerves within the brainstem that relay sensory and motor signals to and from the spinal cord and the brain. It aids in the control of autonomic and endocrine functions, as well as muscle reflexes and sleep and awake states. The red nucleus is a mass of cells that aids in motor function.
Reticular Formation Helps control arousal, responds to change in monotony Thalamus Relays sensory information, switchboard between sensory neurons and higher brain regions Deals with sight, hearing, touch, taste. Transmits replies from higher brain to cerebellum and medullam Cerebellum
Reticular formation: This highly diverse and integrative area contains a network of nuclei responsible for many vital functions including arousal, consciousness, sleep-wake cycles, coordination of certain movements, and cardiovascular control.; Periaqueductal gray (PAG) matter: This area plays a primary role in processing pain signals, autonomic function, and behavioral responses to fear and ...
reticular formation. The white matter consists of myelinated tracts connecting the cerebrum with the spinal cord and various cranial nerve nuclei. Midbrain Anatomy The midbrain connects the pons and cerebel-lum with the forebrain and can be divided into a ventral part, the tegmentum, and a dorsal part, the tectal or quadrigeminal plate (Figs 2, 3).
The reticular formation is located in the brain stem. It extends throughout the length of the brainstem, along the central axis, from the spinal cord to the thalamus. It occupies the anterior portions of medulla, pons, midbrain, hypothalamus, and thalamus.





:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nervus-vestibulocochlearis/thuriZvYTnmBkZK4DUQhw_8th.png)


















Comments
Post a Comment