38 free body diagram equations
sorry if this question is a lil stupid compared to the things i see on here but i’m struggling. when i’m greeted with a problem where i have to draw a free body diagram i can do that just fine, but my problem arises when i try to write formulas. for example, on a problem, “a 650 N crate slides done the 38° ramp of a large U-haul truck at 2.2 m/s^2. find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the ramp.” my problem is comes when i try to write the formulas such as fn = fw - fv. ... Free Body Diagrams A Free Body Diagram (FBD) is a part cut from a larger force system. When the FBD is cut free, all "exposed" forces are shown If the complete system is in static equilibrium, then the FBD with forces at the cut will also be in equilibrium
Free-Body Diagram. Solving the Free-Body Diagram In order to solve the problem, the force on the rope necessary to move the box up the incline must be found. This is the tension force. Finding this force requires a system of equations. Although there is currently one known variable, the weight, there are three unknown variables; therefore,
Free body diagram equations
This video is one of two covering how to create a pair of force equations from a single free body diagram. It does not cover the sources of the forces. It is... The free-body diagram is used to identify the unknown forces acting on the object when applying the equilibrium equation (1.1) to the object. The procedure for solving equilibrium problems is therefore as follows: 1. Draw a free-body diagram—you must choose an object to isolate that results in a free-body diagram including Free Body Diagrams and Kinetic Diagrams max may I P F W N x y = 1. Isolate body 2. Axes 3. Applied forces 4. Replace supports with forces 5. Dimensions 6. Kinetic diagram 4 in 8 in Free Body Diagrams and Kinetic Diagrams The ladder AB slides down the wall as shown. The wall and floor are both rough. Draw the FBD and KD for the ladder.
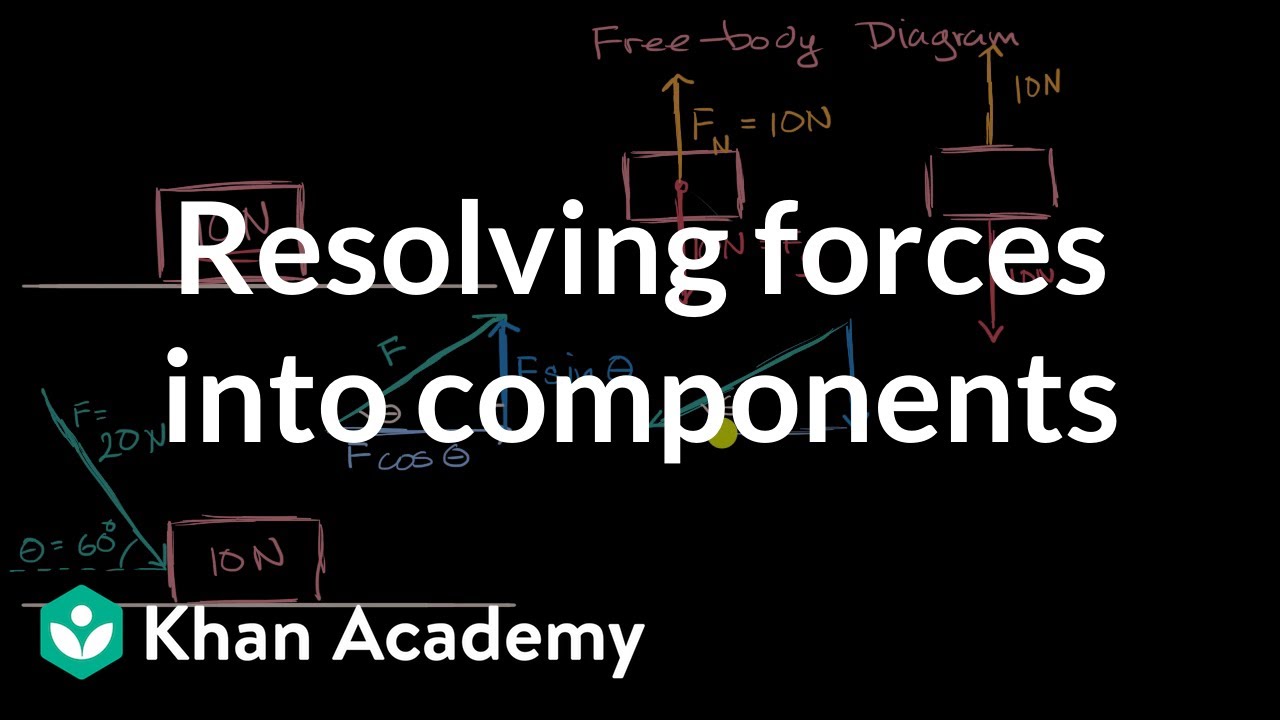
Free body diagram equations. Free-Body Diagrams Getting the Differential Equations for Systems The main purpose of modelling systems is to obtain the differential equation describing the system. The differential equation will tell how the actual system will behave. Two techniques will be used to obtain the differential equations, free body diagrams and linear graphs. Free body diagram examples calculation equations Find out the value of force in newton which should be applied to the rope for moving the metal block up the incline. Process to Draw Free Body Diagram Step 1: Draw the object Draw the object on which the force is applied without any vectors or arrows. The “free-body” in free-body diagram means that the body to be analyzed must be free from the supports that are physically holding it in place Simply sketch a quick outline of the object as if it is floating in space disconnected from everything. The idea is to use the free body diagram to help you figure out what equations you can write down and solve. It is supposed to be an exhaustive list of the forces acting on a particular body. One normally puts only one free body in a free body diagram. Things get cluttered when you have three bodies.
Since the Free Body Diagram shows the forces, if you know the mass you can use the equation F=ma. F is the force, M is the mass and A is the acceleration. The action reaction forces are equal to each other and are in opposite directions. Thanks! Yes No Not Helpful 5 Helpful 6 Question What are the best equations to solve a free body diagram? 9 Free Body Diagrams Wednesday, October 3, 2012 Equilibrium Expanded ! When we remove that restriction, we can add a second condition for equilibrium M ∑=0 F ∑=0 10 Free Body Diagrams Wednesday, October 3, 2012 Equilibrium Expanded ! The sum of the forces acting on a system must be equal to 0 ! The sum of the moments generated by the Free-Body Diagrams and Newtonian Physics 1. Draw a sketch of the situation. 2. Draw a free-body diagram for the object of interest, showing all the forces acting on the object. Also, include any unknown forces that you must solve for. Do not show any forces that chosen object exerts on other objects. Instead draw free-body diagrams for Then we need to draw a free-body diagram showing all the external (active and reactive) forces. (Hard part is support reactions) Finally, we need to apply the equations of equilibrium to solve for any unknowns. FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (Section 5.2) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated
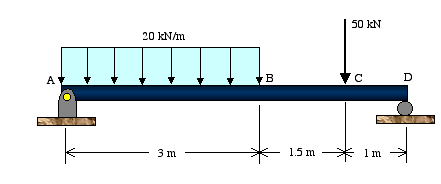
Using mechanics of materials principles (i.e., equations of mechanical equilibrium applied to a free-body diagram), derive Equations 7.4a and 7.4b. (a) Calculate the diffusion coefficient for copper in aluminum at 500. C. (b) What time will be required at 600. C to produce the same diffusion result (in terms of concentration at a specific point ... constraints from number of equations) • Free body diagram for each element • Write equations relating loading to deformation in system elements • Apply Newton's 2nd Law: -F = ma for translation motion -T = Iαfor rotational motion chp3 13 develop the free body diagram, and use the . University of Arizona J. H. Burge 3 equations of static equilibrium to solve for reaction forces and moments. ... The equation summing forces in the Y direction only has one unknown because all cut members except A-B are horizontal. Free Body Diagram. Deviation Slope Equations. Displacement Magnitude. Magnitude of the Degrees of Freedom and the free body diagram with its values. The vertical reaction at support A. Diagram of Shears and Moments of the WHOLE Frame. Take EI constant. The distributed load is located in the middle of the BC section. Equations :
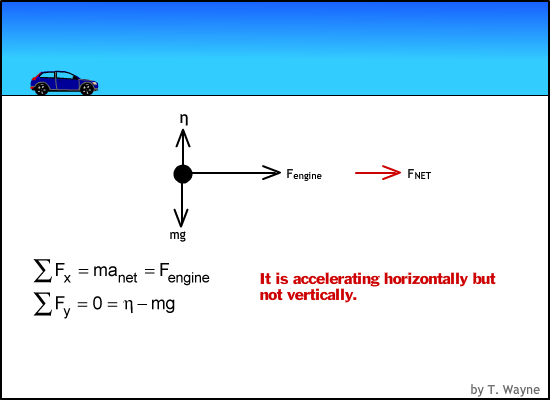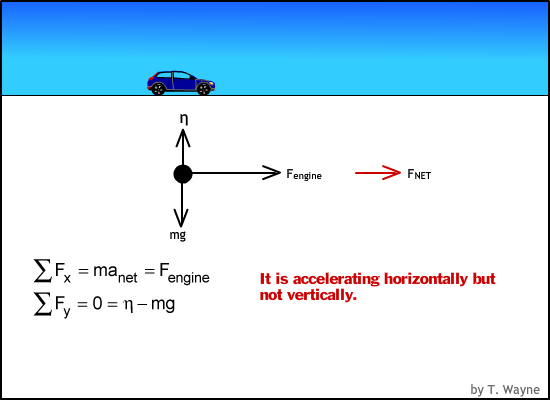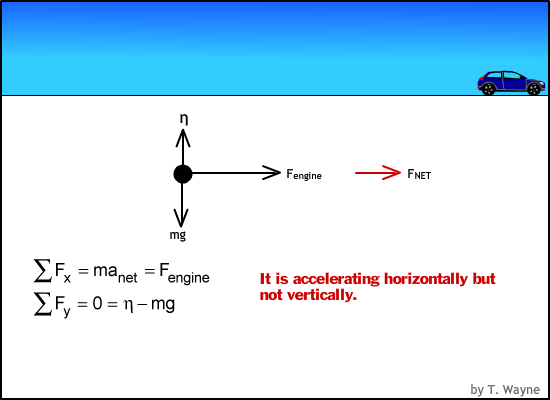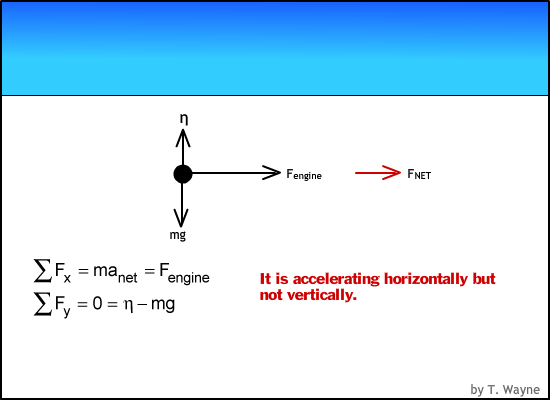
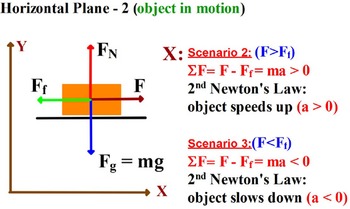
Net Force equations from Free Body Diagrams F n F a F g F k T o 6 F F F ma x a x k x, n 6 F F F F y n a y g, 0 o 6 F F F ma x a k x cosTsin 0 n 6 F F F F y n a g T Pulled up at an angle with friction Pushed down at an angle with friction F a cosT F a sinT F F ma a k x cosT sin 0 F F F n a g T Description FBD Net Force Equations
This video is one of two covering how to create a pair of force equations from a single free body diagram. It does not cover the sources of the forces. It is...
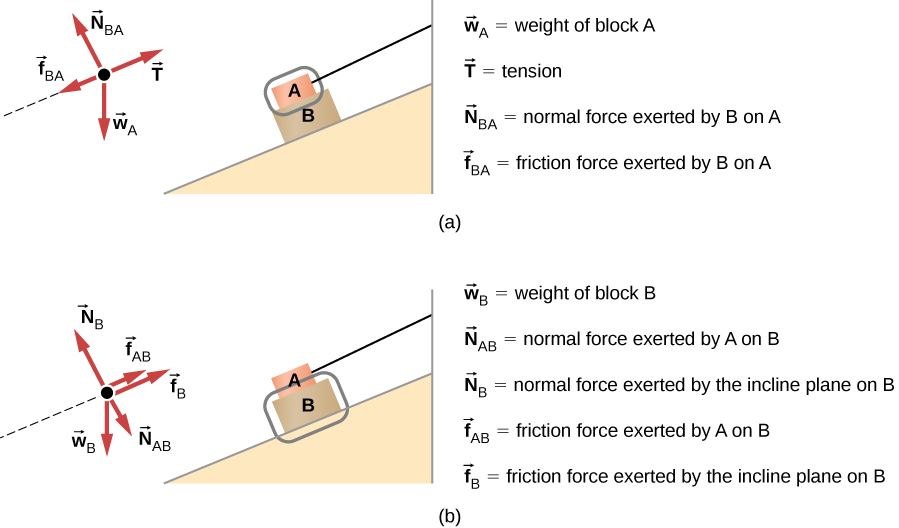
Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Be sure to consider Newton's third law at the interface where the two blocks touch. Solution Significance A → 21 is the action force of block 2 on block 1. A → 12 is the reaction force of block 1 on block 2. We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton's Laws . Example 5.16
Hey everybody, this is an online physics assignment http://imgur.com/a/6bbNM honestly have no idea how to do this one :( http://imgur.com/a/BMBYl (just #13 in this one) For this one, my friend and I thought we did it the right way, getting 1.91 N, but it says its wrong. Thank you so much in advance!
I'm building a climbing training apparatus in my garage that both rests on the ground and hangs by a rope from a hook attached to a ceiling joist. I'm missing something from my free body diagram that's keeping me from setting up and solving my equilibrium equations. I have the full problem laid out, with included pictures and diagrams, at the StackExchange post [here](https://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/674883/statics-question-free-body-diagram-help-for-garage-construction-project). I'd...
The Free Body Diagram Interactive is shown in the iFrame below. There is a small hot spot in the top-left corner. Clicking/tapping the hot spot opens the Interactive in full-screen mode. Use the Escape key on a keyboard (or comparable method) to exit from full-screen mode. There is a second hot-spot in the lower-right corner of the iFrame.
1. Draw one Free Body Diagram for each object (see below for what is a good FBD). 2. Break the forces up into components. 3. For each object and each direction, write down Σ F = (sum of forces) = ma . 4. Solve this set of equations. If there are N unknowns then you need N equations. Often you
Hi friends have a basic physics question I'm having trouble understanding. So the situation is that there is a truck accelerating to the right, and there is a box on the truck that isn't moving. If I were to draw a free body diagram for just the box, there would be the normal force, weight force, and the static friction force pointing to the right that is preventing the box from moving. The box isn't accelerating since it's not moving, so what force am I missing that is pointing to the left?
A free-body diagram is a way to visually inventory these forces, and helps with developing the algebraic equations needed to solve these types of problems. There are five rules for drawing...
Hi! I'm currently studying OVS's SPH4U course. I'm wondering if anybody can help me by laying out all the steps to follow when drawing free body diagrams. I just found the video instructions too unclear and hard to follow. Thanks!
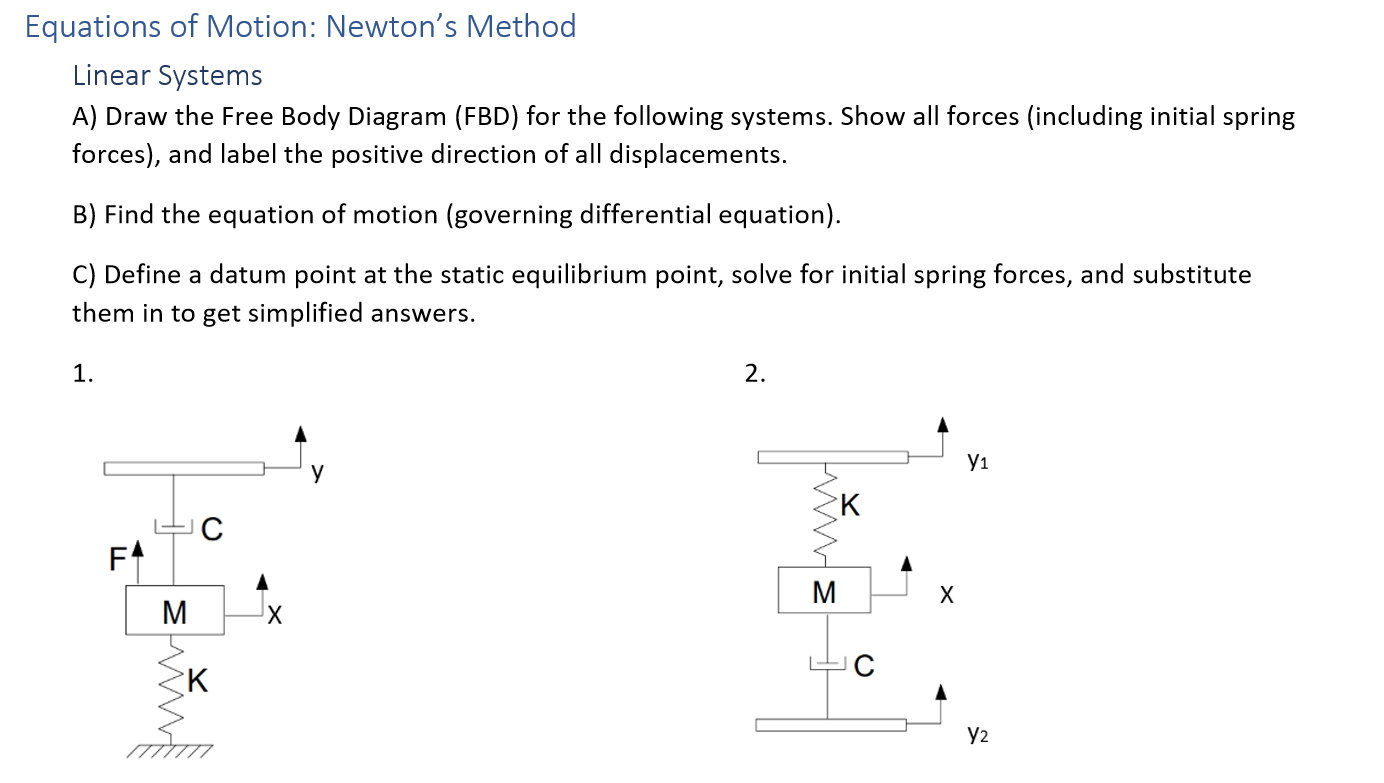
Draw free-body diagrams that conform to the assumed displacement positions and their resultant reaction forces (i.e., tension or compression). c.Apply to the free body diagrams to obtain the governing equations of motion. The matrix statement of Eqs.(3.123) is The mass matrix is diagonal, and the stiffness matrix is symmetric.
https://imgur.com/a/g6QvNX5 If you’re given the applied force, would you draw another arrow next to the parallel component (mg sin theta), or is the parallel component the applied force?
Hi! This problem is a practice exercise from the 'Introduction to Engineering Mechanics' course in Coursera. The main problem is that I don't understand what I'm being asked. I also have no idea what does M=m1/m2 mean. I would like an explanation on what is being asked. I would also like if someone solved it. I've tried using this formula: X = (m1)(x1)+(m2)(x2)/m1+m2 but I couldn't move from there. Here is the problem. Link: [Imgur: The magic of the Internet](https://imgur.com/a/F6HFVeN) ...
Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Solution Significance Each block accelerates (notice the labels shown for →a 1 a → 1 and →a 2 a → 2 ); however, assuming the string remains taut, they accelerate at the same rate. Thus, we have →a 1 = →a 2 a → 1 = a → 2.
Download scientific diagram | Free body diagrams. (a) rear wheel, (b) rear wheel and frame, (c) front wheel and (d ) entire bicycle. from publication: Hands-free circular motions of a benchmark ...
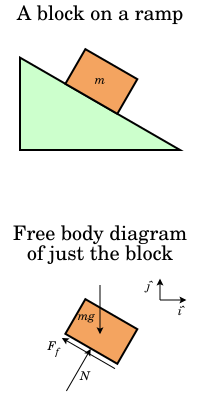
A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram:
FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS, EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & CONSTRAINTS FOR A RIGID BODY Today’s Objective: Students will be able to: a) Identify support reactions in 3-D and draw a free body diagram, and, b) apply the equations of equilibrium.
A free-body diagram is a diagram that is modified as the problem is solved. Normally, a free body diagram consists of the following components: A simplified version of the body (most commonly a box) A coordinate system. Forces are represented as arrows pointing in the direction they act on the body. Moments showed as curved arrows pointing in ...
FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (Section 5.2) 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) support reactions, and, c) the weight of the body. Idealized model. Free-body diagram (FBD) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape.
This seems like the most basic thing ever but I can't figure it out for the life of me. The problem asks for [the equation for an object at equilibrium on an incline](http://i.imgur.com/8jiXJLv.jpg) but why does it imply that you divide M by (m1-m2)? Shouldn't it be the other way around?
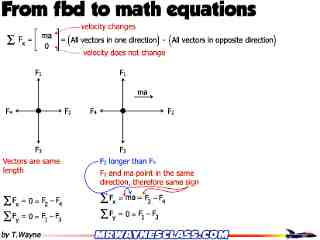
In the free body diagram for x 1 (at the left side of spring k 2) the arrow for k 2 (x 1-x 2) is to the left; the free body diagram for x 2 (at the right side of spring k 2) has the arrow going to the right. In all equations, the signs of x 1 and all of its derivatives are the same (i.e., either all positive or all negative).
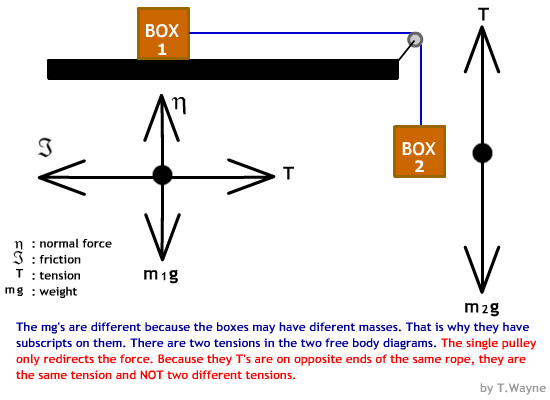
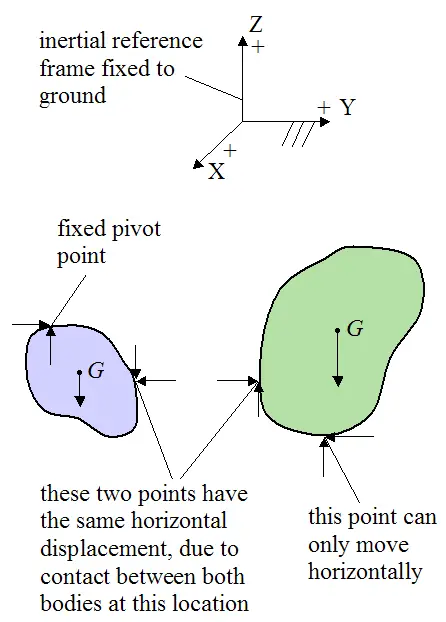
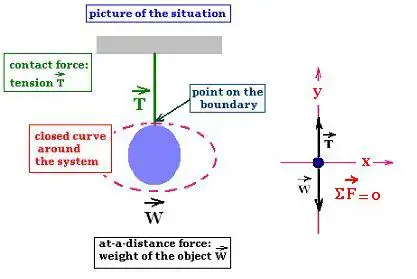
Sometimes you see the tension of a rope included in a free-body diagram where it is actually an *internal* force for that system. In other words, both the action and its reaction are drawn in the same FBD, but to do it correctly you would actually need 2 separate FBDs. In engineering it is a big no-no to draw internal forces in an FBD.
Free body diagrams are either a box or a dot representing a mass that has arrows stemming from it in various directions. The arrows represent all of the forces on the mass. This type of diagram...
I'm building a climbing training apparatus in my garage that both rests on the ground and hangs by a rope from a hook attached to a ceiling joist. I'm missing something from my free body diagram that's keeping me from setting up and solving my equilibrium equations. I have the full problem laid out, with included pictures and diagrams, at the StackExchange post [here](https://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/674883/statics-question-free-body-diagram-help-for-garage-construction-project). I'...
Free Body Diagrams and Kinetic Diagrams max may I P F W N x y = 1. Isolate body 2. Axes 3. Applied forces 4. Replace supports with forces 5. Dimensions 6. Kinetic diagram 4 in 8 in Free Body Diagrams and Kinetic Diagrams The ladder AB slides down the wall as shown. The wall and floor are both rough. Draw the FBD and KD for the ladder.
The free-body diagram is used to identify the unknown forces acting on the object when applying the equilibrium equation (1.1) to the object. The procedure for solving equilibrium problems is therefore as follows: 1. Draw a free-body diagram—you must choose an object to isolate that results in a free-body diagram including
This video is one of two covering how to create a pair of force equations from a single free body diagram. It does not cover the sources of the forces. It is...























Comments
Post a Comment