43 mo diagram benzene
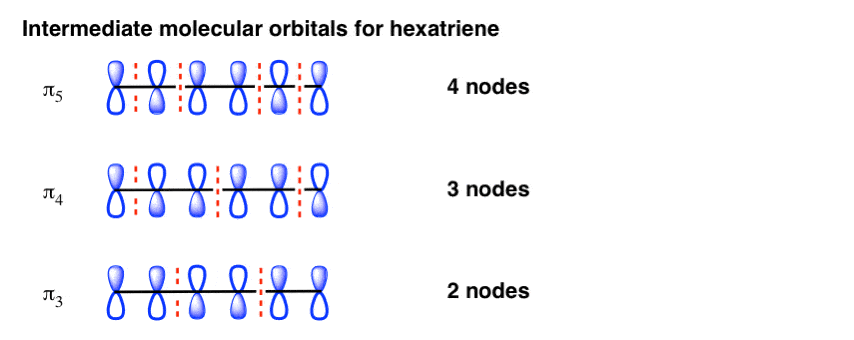
In addition, the aromatic benzene ring on BA could decrease not only the hydrophilicity of GG, hence, overcoming the intrinsic hydrophilicity obstacles of GG, but also could assist the preparation of novel complex materials due to numerous intermolecular interaction that the aromatic benzene ring might offer. ... The MO diagram of GG-BA monomer ... May 5, 2017 — 2. Building The Pi Molecular Orbital Diagram For Benzene: Hexatriene and Benzene Each Have Six Pi Molecular Orbitals · 3. The Lowest-Energy ...
Complete the MO diagram (below) to determine if O₂ is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. A) paramagnetic B) diamagnetic. A) Paramagnetic. The molecular orbital energy diagram for F₂ is shown below. Based on this diagram, what is the bond order of F₂? 1. A π bond could be formed ... Where are the π electrons delocalized in a benzene (C₆H₆ ...

Mo diagram benzene
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or ions by the combination of several contributing structures (or forms, also variously known as resonance structures or canonical structures) into a resonance hybrid (or hybrid structure) in valence bond theory.It has particular value for describing delocalized electrons … Catalytic hydropyrolysis via the introduction of external hydrogen into catalytic pyrolysis process using hydrodeoxygenation catalysts is one of the major approaches of bio-oil upgrading. In this study, hydrodeoxygenation of acetone over Mo/HZSM-5 and HZSM-5 were investigated with focus on the influence of hydrogen pressure and catalyst deactivation. It is found that doped MoO3 could prolong ... Figure 1. π-molecular orbital diagrams for (a) benzene, (b) fluorobenzene, (c) m-difluorobenzene, (d) 1,3,5-trifluorobenzene, (e) 1,2,3,5-tetrafluorobenzene, (f) pentafluorobenzene, and (g) hexafluorobenzene. Conventional aromatic orbitals are shown in black while additional π-
Mo diagram benzene. Compare the stability of cyclohexene, 1, 3-cyclohexadiene, and benzene bases on heat of hydrogenation. (Use the information in Figure 16-2) 2). (10 points) Does the MO energy diagram of cyclooctatetraene (Figure 16-8) appear to be a particularly stable or unstable configuration? Explain. 3). (10... 20/12/2021 · The molar mass of benzene is 78.11 g/mol. It's melting and boiling points are 5.53 °C and 80.1 °C respectively. The Flashpoint of benzene is less than 0°F, therefore it is less dense than water. Hence, slightly soluble in water. Now, let us focus on the properties such as structure, geometry, hybridization, and MO diagram of ... Molecular Orbitals of Benzene. 1,963 views1.9K views. Jul 12, 2020 ... Molecular orbital (MO) diagrams in organic chemistry. Jeremy McCallum. After the construction of the energy level diagram, the filling of molecular orbital with electrons will be according to: Pauli exclusion principle; ... Benzene is an aromatic compound having a molecular formula C 6 H 6. The number of σ (sigma) and π (pi) bonds in benzene are 12 and 3 respectively. [C-C = 6], [C-H = 6], and [C=C = 3].
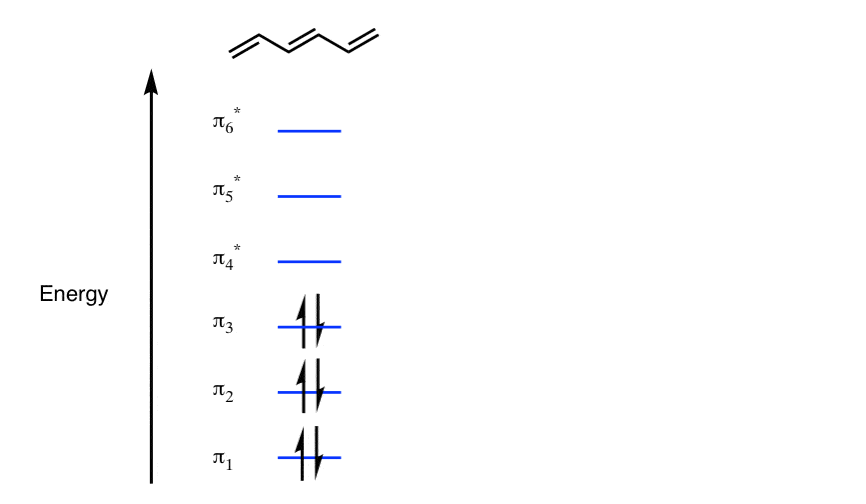
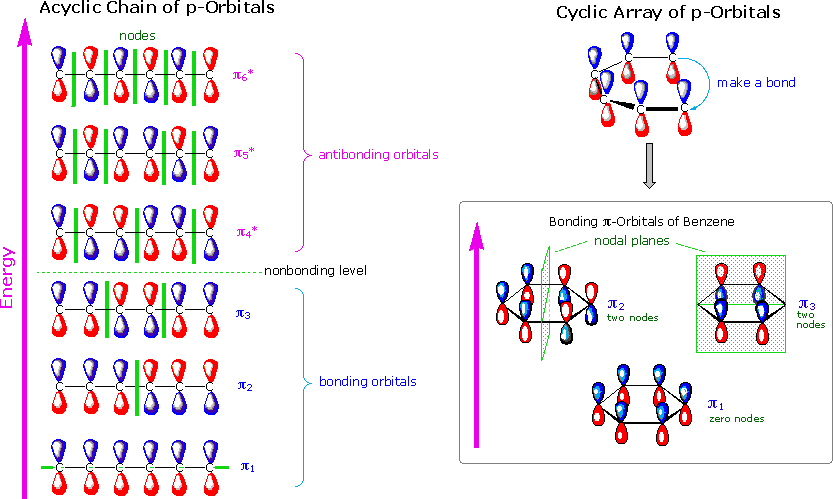
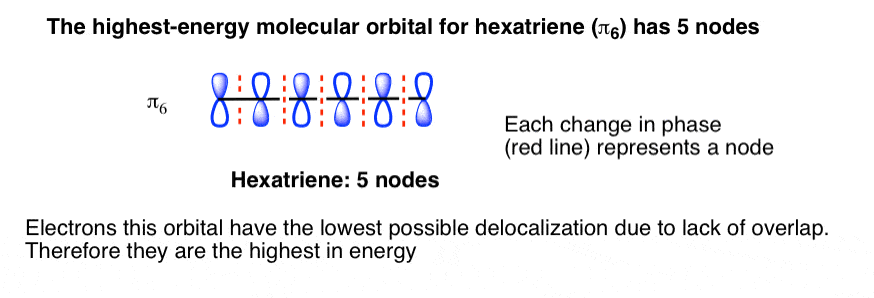
The orbital structure of benzene: All the carbon atoms in benzene are sp2 hybridised. The three sp2 hybrid orbitals are lying in one plane and oriented at ... MO theory actually predicts this behavior, ... Occupy the orbitals according to a stick diagram. At this stage, we note that from our N pz orbitals we will obtain N π orbitals. ... benzene as an example. 1 2 5 3 6 4 1) Each of the MOs is a linear combination of 6 pz orbitals Use diagrams a common-denominator method and calculators to solve problems. Equivalent ratios examples. Predict most will squeeze a gallon of orange paint for and project. They wood be live at problems that admit the practices and surrender trying out a problem also use the practices. How tape diagrams to solve problems worksheets and percents! q An Energy Level Diagram for the MO’s of benzene is depicted below. In examining this diagram, recall that cyclic overlap between the six AO’s converts them to six delocalized MO’s , and that of these six MO’s, three are BMO’s and 3 ABMO’s .
Molecular Orbital Theory of Benzene ... The structure and chemical behavior of benzene (as well as of other aromatic compounds) can be explaind by either the ... In large part, the answer to this question lies in the fact that benzene is a cyclic molecule in which all of the ring atoms are sp2-hybridized. This allows the ... Diagrams of the Lewis structure of benzene (C 6 H 6), a 3-electron/ 2-carbon C/T structural unit, and benzene as a tensegrity. In the benzene tensegrity the carbon ring and electron triplet compression units have been simplified as hexagon and open triangles, respectively, and the methine spars as rods. Benzene is present in crude oils and is a product of oil-refining processes. There are limitations on the content of benzene in gasoline. In industry benzene is used as a solvent, as a chemical intermediate, and is used in the synthesis of numerous chemicals. The phase diagram of benzene is shown below the table.
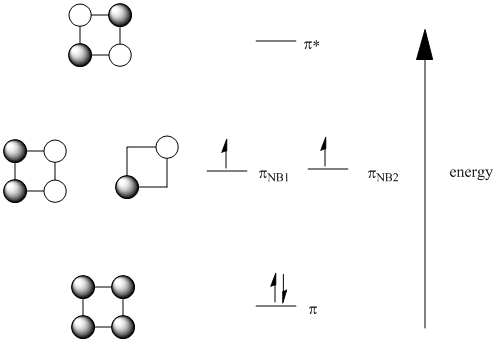
31/03/2015 · The MO diagram for generic metallocenes, Cp 2 M is shown below. Notice that the Cp orbitals fill the six lowest orbitals. The next five unoccupied MO's shown in the box have little or no bonding character, which explains our observation above that metallocenes are known for a variety of d-electron counts.
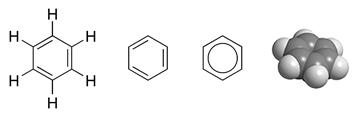
Benzene (also called cyclohexatriene) is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C 6 H 6.The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.. Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil and is one of the elementary ...
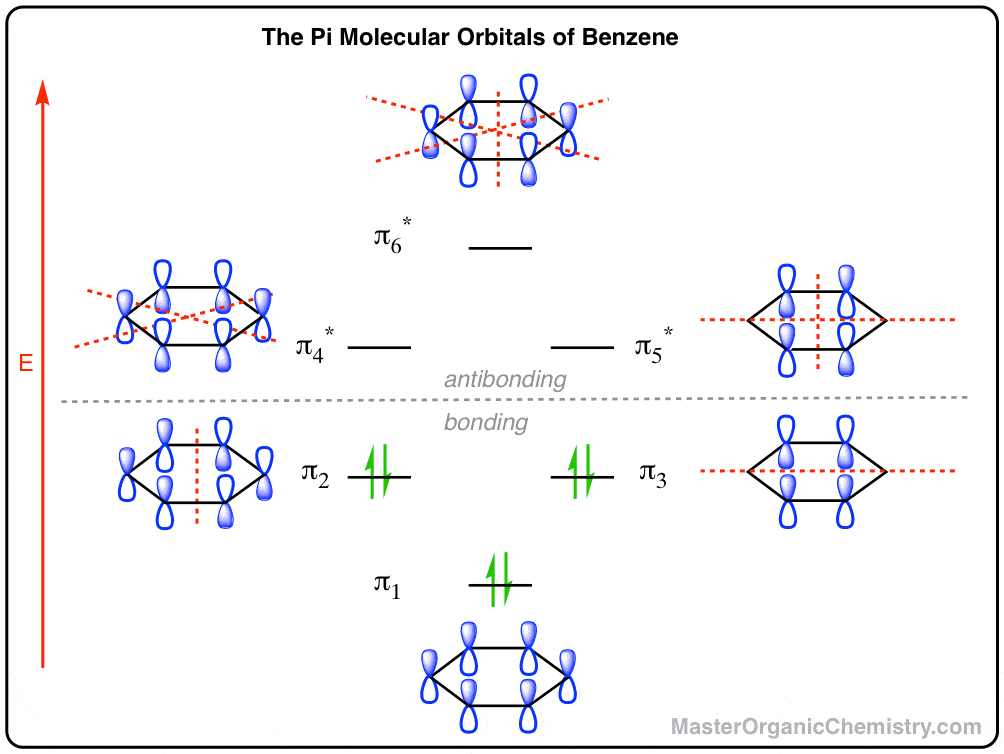
Energy Level Diagram of Benzene The relative energy levels for the MO's of benzene are shown below. MO's 4 *, 5 * and 6 * are all overall antibonding, and lie above the level of an isolated p orbital (non-bonding line). Each p orbital contributes one electron, which means we have 6 electrons to accommodate (this is the same number
i. Straight chain alkanes containing 6 to 10 carbon atoms are converted to benzene and its homologues, on heating under 10 to 20 atm pressure at about 773 K in the presence of V 2 O 5, Cr 2 O 3, MO 2 O 3, etc. supported over alumina. ii. The reaction involves simultaneous dehydrogenation and cyclization. This reaction is known as aromatization ...
Jul 18, 2015 — A molecular orbital description of benzene provides a more satisfying and more general treatment of "aromaticity". We know that benzene has a ...Structure of Benzene · The High Stability of Benzene · The Molecular Orbitals of...
The bond order in benzene is 1.5. Example 4 Oxygen molecule {eq}O_{2} {/eq} An oxygen molecule has two atoms. ... The first step is to draw the molecular orbital diagram, filling the orbitals in ...
How many orbitals are in benzene? There are 15 bonding orbitals in benzene. There are 6 C-C σ bonds, 6 C-H σ bonds, and 3 C=C π bonds. This makes 16 bonding orbitals. According to molecular orbital theory, the σ molecular orbitals form from the three sp² orbitals on each carbon atom and the 1s orbitals on each hydrogen atom.
Dr. Loi Do 9-4 • Aromaticity can be explained using Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory o Let's construct the MO of benzene: A) 6 atomic orbitals (AOs) = 6 molecular orbitals (MOs) B) number of nodes increase as MO energy increases C) determine non-bonding line o The MO energy diagram of benzene: E ...
carbon atoms. All the carbon-carbon bonds in the ring are of equal length with bond length 1.40. Å and each C-C-C bond angle is of 120° (structure I).
pairs. Molecular Orbital Diagram. The molecular orbital diagram describes the location and behavior of electrons in molecules. Molecular engineering of organic-inorganic hybrid Apr 25, 2019 · Q39. The energy of σ2p z: molecular orbital is greater than 2p x and 2p v molecular orbitals in nitrogen molecule.
Há 2 dias · PCl3 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. In a molecular orbital diagram of PCl3, we can see 3 bonding orbitals, which will be occupied. And 3 anti-bonding orbitals which will be empty. We can see from the hybridization that 3 Sp3 hybrid …
The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical Since molecular oxygen contains two electrons in an antibonding orbital, it might be possible to This page from Imperial College (London) has MO diagrams for molecules such as ethane, ethylene, and water.
Phase diagram included. Benzene Gas - Specific Heat vs. Temperature - Specific heat of Benzene Gas - C6H6 - at temperatures ranging 250 - 900 K. Benzene Liquid - Thermal Properties - Properties like density, specific heat, thermal conductivity, dynamic viscosity and Prandtl number.
Organometallic Chemistry & Bioinorganic Chemistry Notes PDF. Date: 9th Jan 2022. In these "Organometallic Chemistry & Bioinorganic Chemistry Notes PDF", we will study the basic principles of qualitative inorganic analysis.The influence of solubility products and the common ion effect on the separation of cations is made clear.
MO Diagram Bond Order. Finding Bond Order. 2P Molecular Orbitals. Finding Bond Order. Bond Order Of No3. Bond Order Equation. Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Order. Be2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. Benzene Molecular Orbitals. C2 Bond Order. No Bond Order. Bond Order Chart. H2 Bond Order. F2 Bond Order.
Há 2 dias · Benzene Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram Benzene is an organic compound that is a colorless liquid having the molecular formula C6H6. It belongs to the class of an aromatic hydrocarbon as …
Q.No.1 (a) Draw the MO diagram of CO and CN? (9) (b) Draw the structure of the following molecules on the basis of Hybridization [Co(NH 3) 6] 3+ [Ni(CN) 4] 2-(8) (c) Differentiate b/w order of reaction and molecularity? (3) Q.No.2 (a) Give an example of 2nd order reaction? Explain that hydrolysis of an ester is a pseudo first order reaction ...
A molecular orbital description of benzene provides a more satisfying and more general treatment of "aromaticity". We know that benzene has a planar hexagonal structure in which all the carbon atoms are sp 2 hybridized, and all the carbon-carbon bonds are equal in length.
Based upon the predominance-zone diagram for Fe(II) and Fe (III) species in the aqueous solution in the function of pH , in the neutral solution of pH at 6.0, the precipitation of Fe(OH) 2 and Fe(OH) 3 were gradually generated in the solution to remove MO and AY contaminants mainly by the adsorption of enmeshment. Consequently, the optimum pH ...
According to MO theory, the pi electrons of benzene occupy three molecular orbitals, y1, y2, and y3, all of which are lower in energy than an electron in an ...
N2H2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and MO Diagram. Dinitrogen dihydride has the chemical formula of N2H2. This compound is most commonly known as diazene or diimide. It is a yellowish-colored gas having both cis and trans isomers. It can be prepared from the decarboxylation of azodicarboxylic acid ( (NCOOH)2 ).
Answer (1 of 2): OK, First, Benzene has many resonance structures in order to satisfy the conditions that his bonds are equal to 1.4 A. Second, the resonance theory is outdated. It is good to think in the terms of molecular orbital theory.
Molecular Orbitals of Benzene. 43,992 views • Jun 9, 2014 • Donate ... Molecular Orbital Theory - Bonding & Antibonding MO - Bond Order.
The famous nitrogen molecule, N 2 , can also be perfectly described using molecular orbital diagrams: OM diagram for the N2 molecule. Source: Gabriel Bolívar. Note that this diagram is exactly the same as for the C 2 2- anion . This means that N 2 and C 2 2- are isoelectronic. However, this fact does not imply that both species behave in the ...
Figure 1. π-molecular orbital diagrams for (a) benzene, (b) fluorobenzene, (c) m-difluorobenzene, (d) 1,3,5-trifluorobenzene, (e) 1,2,3,5-tetrafluorobenzene, (f) pentafluorobenzene, and (g) hexafluorobenzene. Conventional aromatic orbitals are shown in black while additional π-
Catalytic hydropyrolysis via the introduction of external hydrogen into catalytic pyrolysis process using hydrodeoxygenation catalysts is one of the major approaches of bio-oil upgrading. In this study, hydrodeoxygenation of acetone over Mo/HZSM-5 and HZSM-5 were investigated with focus on the influence of hydrogen pressure and catalyst deactivation. It is found that doped MoO3 could prolong ...
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or ions by the combination of several contributing structures (or forms, also variously known as resonance structures or canonical structures) into a resonance hybrid (or hybrid structure) in valence bond theory.It has particular value for describing delocalized electrons …

















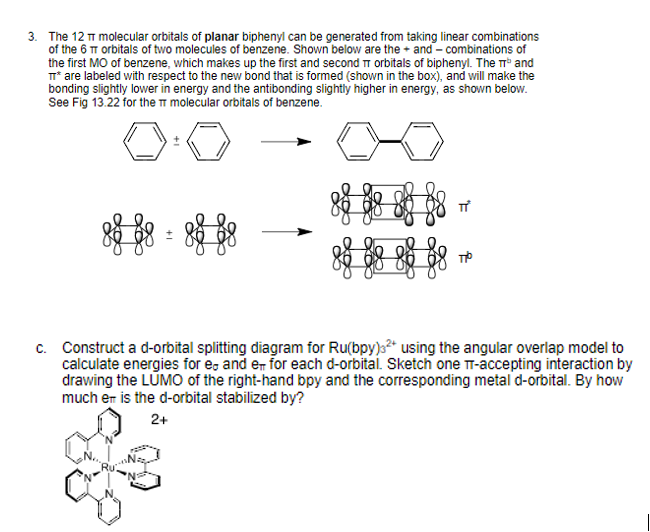
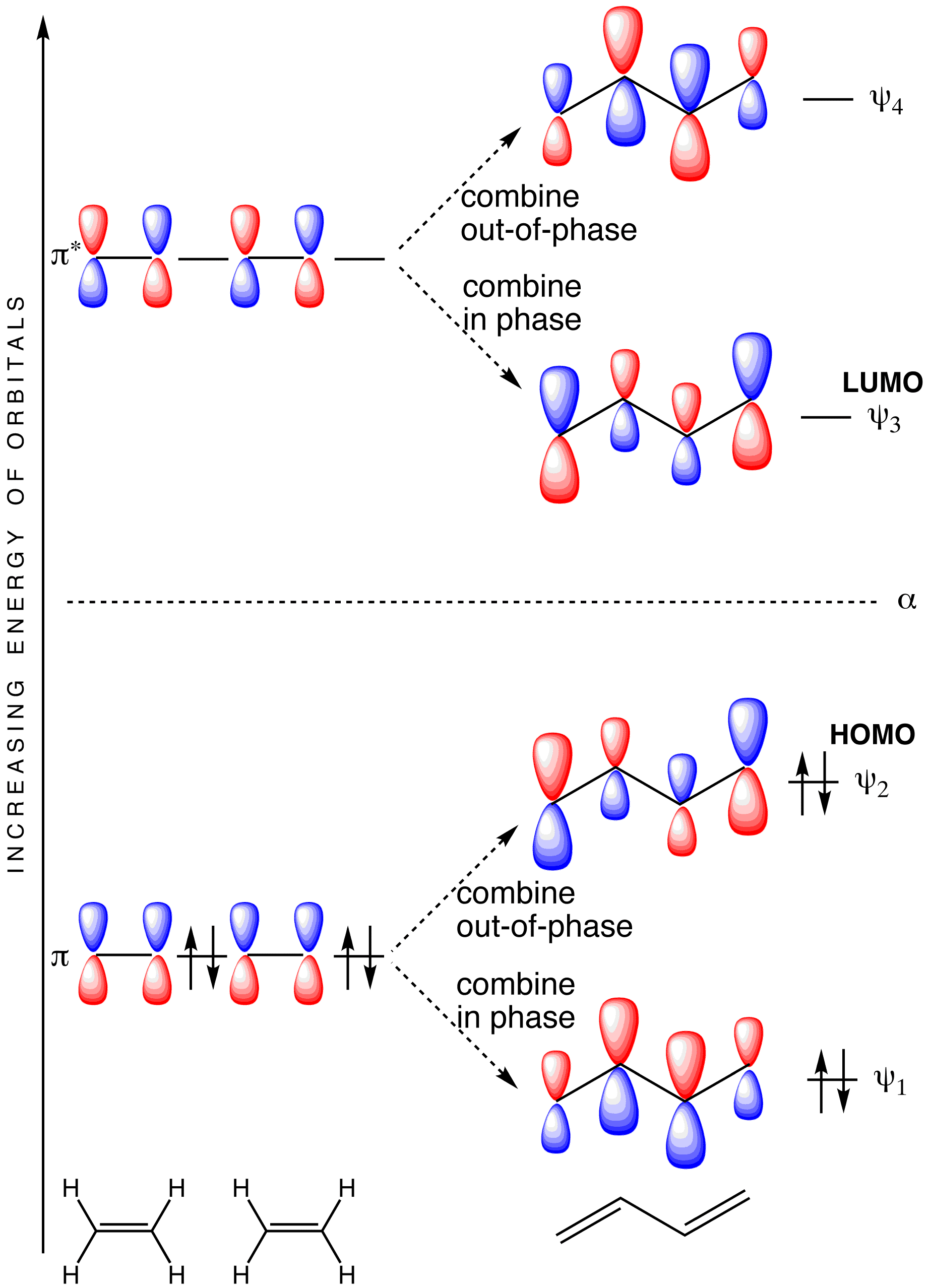


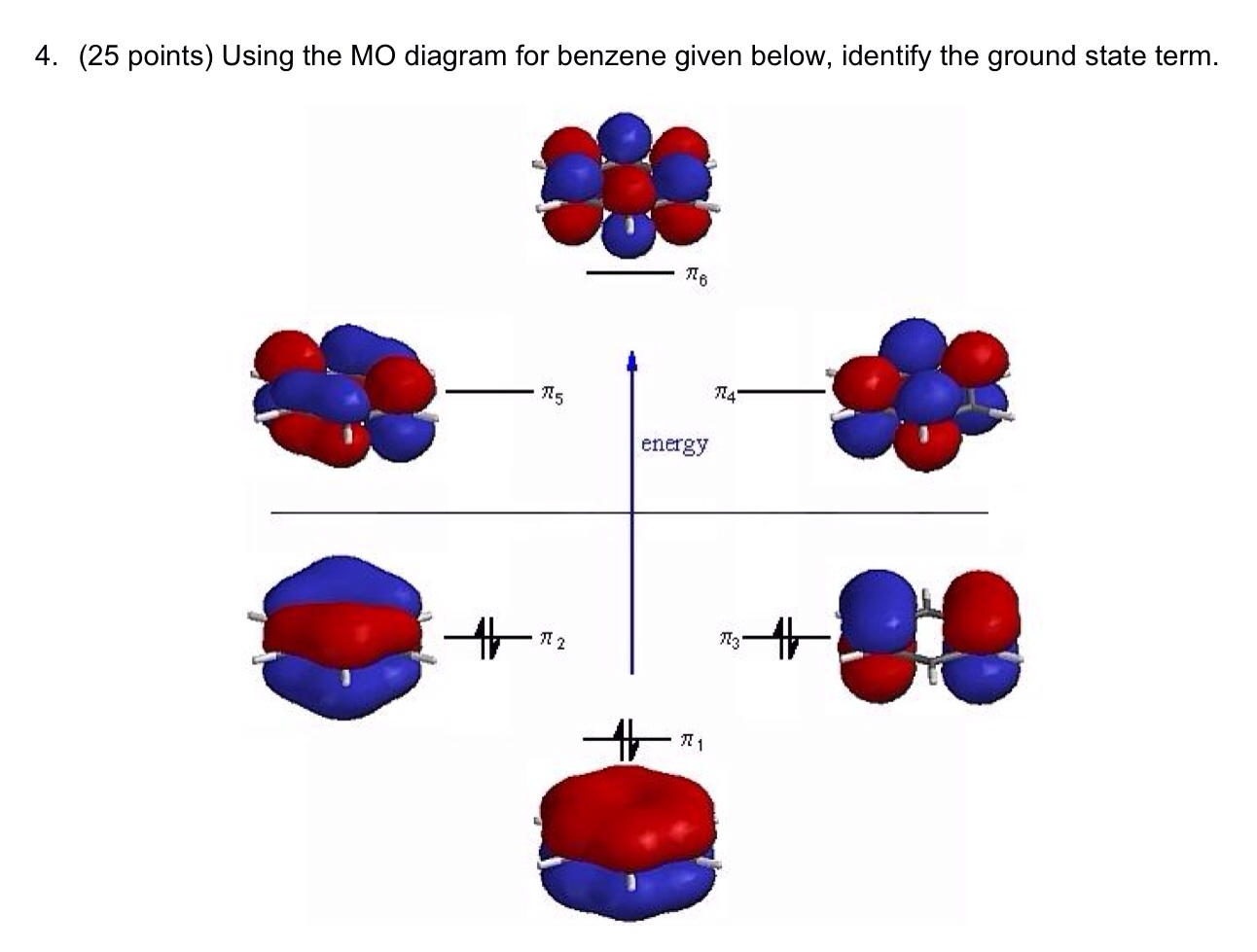




Comments
Post a Comment