41 ray diagram for convex mirror
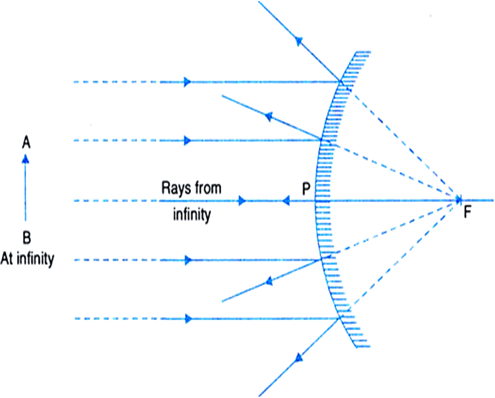
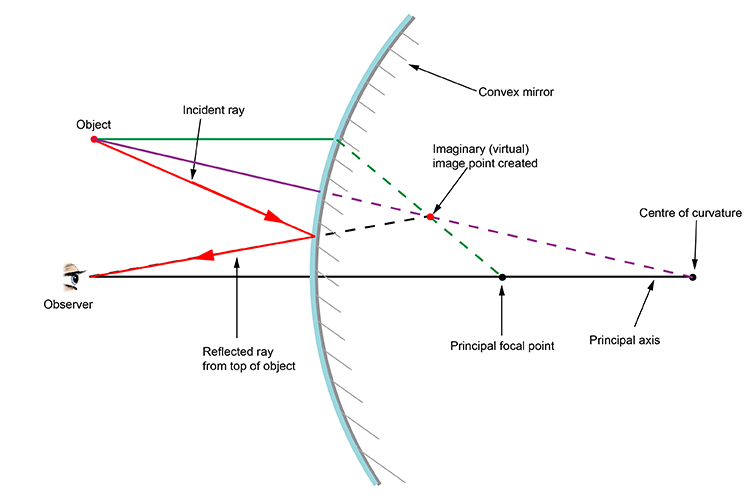
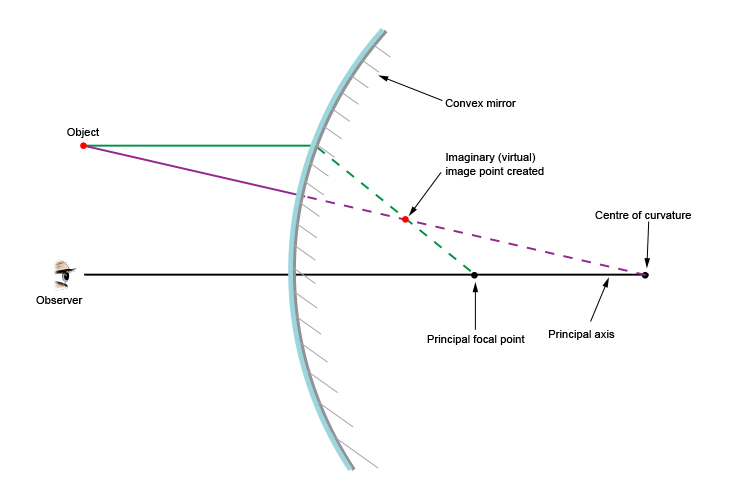
Apr 23, 2020 · Convex Mirror - Ray diagram. Last updated at April 23, 2020 by . For a Convex Mirror, The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirror So, there will only be 2 cases. They are Object is Placed at Infinity Object is Placed between Principal axis and Infinity A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection.
May 15, 2020 · Parts of Concave and Convex Mirror Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Mirrors Concave Mirror - Ray diagram Convex Mirror - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Mirrors Sign convention for Spherical Mirrors
Ray diagram for convex mirror
Shows how to draw ray diagrams and locate the image for concave mirrors. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscience.c... Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. In B, a convex mirror is used. Convex mirrors always produce upright, virtual images. In C, a plane mirror is used. Plane mirrors always produce upright, virtual images. In D, the object is located beyond the center of curvature of a concave mirror. At such an object location, the image would be real, inverted and reduced in size.
Ray diagram for convex mirror. A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram. Jul 07, 2020 · Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Applications of Concave Mirror In torchlight, headlamp, vehicle headlight, searchlight, and lighthouse, where a beam of light is converged to a certain point thus giving a better focus A ray diagram that shows the position and the magnification of the image formed by a concave mirror. The animation illustrates the ideas of magnification, and of real and virtual images. Click and drag the candle to move it along the optic axis. Click and drag its flame to change its size. Jul 07, 2020 · Convex Mirror Ray Diagram. Applications of Convex Mirrors. As side view mirrors in cars, buses, and trucks because the image formed is upright and small thus giving a wide field of view of the area toward the side of and behind the vehicle;
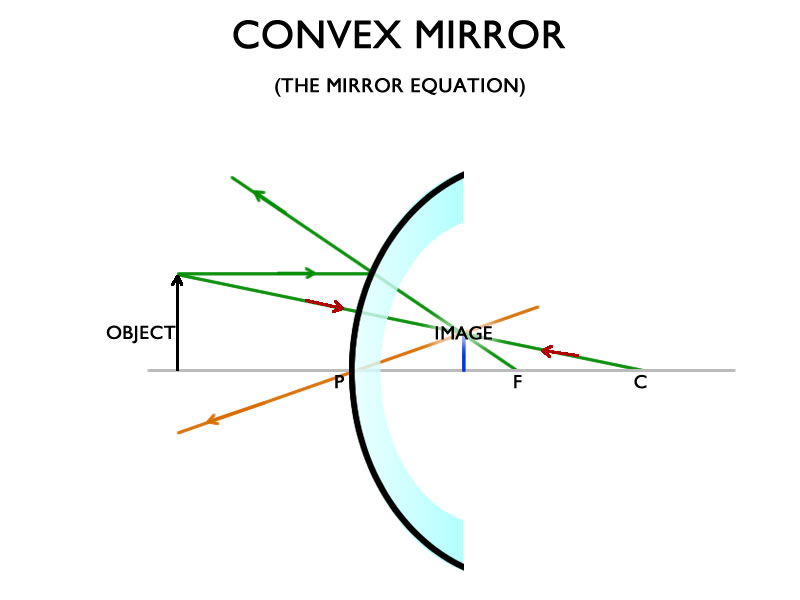
Dec 06, 2021 · The types of object placement in convex mirror are given below: a. When an object placed at infinity; b. When an object placed between the pole and infinity; Convex Mirror Diagram. The Convex mirror ray diagrams based on the image placement stated above is given below: Summary of Convex Mirror Ray Diagram While making ray diagrams, these two rules are important for students. The purpose of drawing ray diagrams is to find the location, size, direction, and type of image formed by a convex mirror. The steps involved in drawing ray diagrams are quite simple and easy to understand. Description of how to draw ray diagrams for convex mirrors for grade 10 science A ray diagram that shows the position and the magnification of the image formed by a convex mirror. The animation illustrates the ideas of magnification, of real and virtual images. Click and drag the candle along the optic axis. Click and drag its flame to change its size.
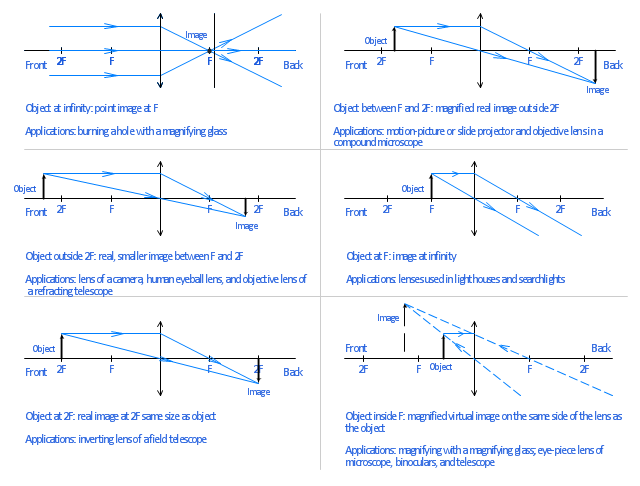
Step-by-Step Method for Drawing Ray Diagrams. The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the ... Ray Diagram for Convex and Concave Mirror. A mirror is a part of a smooth and highly polished reflecting surface. Most commonly used mirrors are plane mirrors. A spherical mirror is a part of a spherical reflecting surface. There are two types of spherical mirrors - convex mirror and concave mirror. Here are a number of highest rated Convex Mirror Image Formation pictures on internet. We identified it from reliable source. Its submitted by management in the best field. We take this nice of Convex Mirror Image Formation graphic could possibly be the most trending subject in imitation of we allocation it in google lead or facebook. Convex & concave mirror ray diagrams. Transcript. Let's explore the ray tracing technique to figure out the properties of images when things are kept in front of a concave or a convex mirror. Created by Mahesh Shenoy.
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images. The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn.
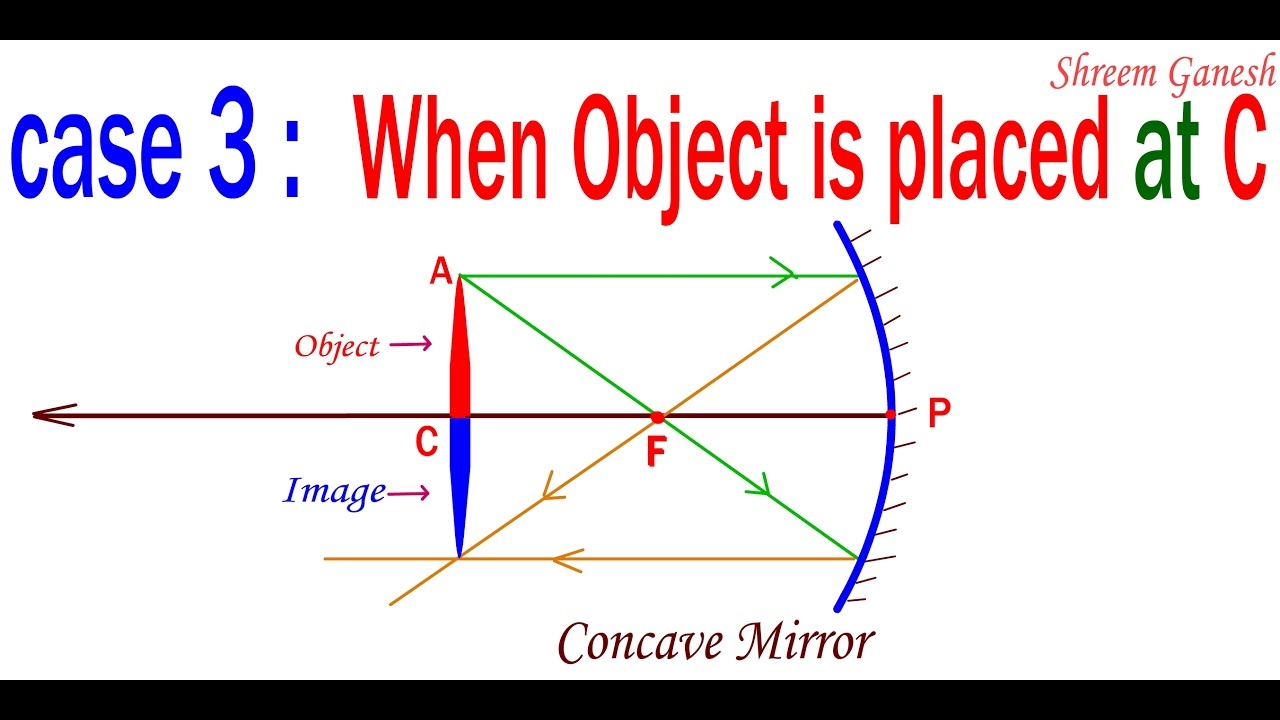
Dec 06, 2019 · Ray diagram : The minimum deviation Dm, the refracted ray inside the prism becomes parallel to its base, we have. Question 92. Use the mirror equation to show that (a) an object placed between / and 2/ of a concave mirror produces a real image beyond 2f. (b) a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object.
View mirror-ray-diagram-assign3.pdf from SOCI 101 at St. Elizabeth Catholic High School. SNC Mirror Ray Diagram Concave/Convex Assignment 4 Questions include table and Gizmo screen shot of each ray
How to Draw a Ray Diagram for a Convex Mirror. Step 1: Identify the distance of the object from the mirror (d), the center of curvature (c) of the mirror, and the focal length (f) which is equal ...
Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the distance from the mirror to the object is p.
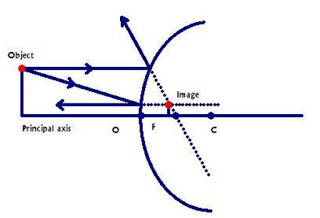
Convex Mirror Image. A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here.. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror.
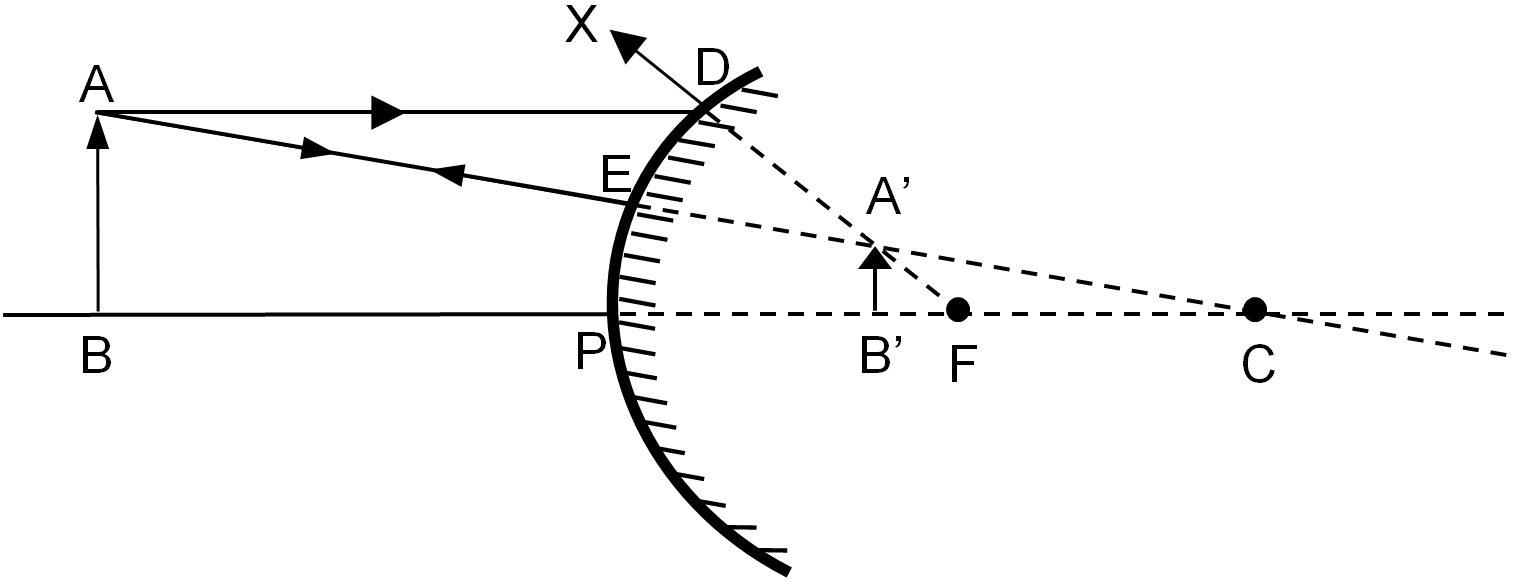
According to sign conventions, the incident rays are drawn from left of the mirror to the right as shown in the ray diagrams below. ii. As the rays incident on convex mirror appear to converge at a point on the positive side of the origin, the focal length of the convex mirror is positive. iii.
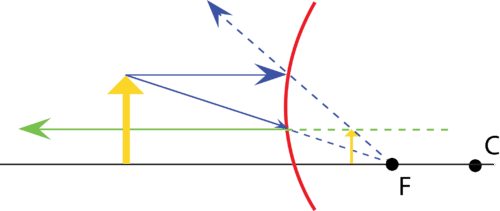
Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. The intersection of these two reflected rays gives the position of an image of the object. In case of a convex mirror any ...
A meridional ray or tangential ray is a ray that is confined to the plane containing the system's optical axis and the object point from which the ray originated. A skew ray is a ray that does not propagate in a plane that contains both the object point and the optical axis. Such rays do not cross the optical axis anywhere, and are not parallel ...
Oct 31, 2021 · Assume a concave mirror with focal length f = 5.0 cm. An object of height 2.80 cm is placed at a distance s = 12.6 cm from the mirror. On graph paper, draw a ray diagram to scale, including at least t
Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors Process of drawing ray diagrams is the same no matter where the object is located. 1. IR parallel to the principal axis, RR through the focal point upon reflection. 2. IR through the focal point F, RR parallel to the principal axis upon reflection. 3. IR through C, RR reflects through C. Convex mirrors always ...

Some nice early sunset tones hittingThe Big Beehive mountain as it looks down onto Mirror Lake (you can see why it got its name!) in Banff, Canada.
In each diagram use an arrow 10 cm tall pointing upwards as the object. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. Concave And Convex Mirrors Ray Diagram For Convex And Concave Mirror. Converging mirror ray diagram. The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located […]
Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors Ray 1: parallel to the axis then from F. Ray 2: Vertex. Ray 3: from C. • image is virtual, upright, and smaller than object Ray 4: towards F, then parallel. Concave mirrors: Shaving and makeup mirrors Solar cookers Satellite dishes (for EM waves)
Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed: (a) At 2F Method for drawing ray diagrams - Concave lens. A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens.
Ray diagram. 1 : The ray 1 or the light beam 1 that come to the convex mirror are drawn parallel to the principal axis and touch the upper end of the object, then reflected by the convex mirror where the beam of light reflects as if from the focal point (f).
Nov 18, 2021 · For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t
Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams. When the object is kept at infinity: As the parallel rays coming from the object converge at the principal focus, F of a concave mirror; after reflection through it. Therefore, when the object is at infinity the image will form at F. Object at Infinity.

Image from page 797 of "A Manual of botany : being an introduction to the study of the structure, physiology, and classification of plants " (1875)
This physics video tutorial provides the ray diagrams for a concave and convex mirror. It also contains a few examples and practice problems along with the ...
Convex Ray Diagram. Here are a number of highest rated Convex Ray Diagram pictures upon internet. We identified it from reliable source. Its submitted by dealing out in the best field. We agree to this nice of Convex Ray Diagram graphic could possibly be the most trending subject following we ration it in google benefit or facebook.
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Concave and Convex Mirrors. Concave and Convex Mirrors - GeoGebra Materials. Description. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror.
In B, a convex mirror is used. Convex mirrors always produce upright, virtual images. In C, a plane mirror is used. Plane mirrors always produce upright, virtual images. In D, the object is located beyond the center of curvature of a concave mirror. At such an object location, the image would be real, inverted and reduced in size.
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.
Shows how to draw ray diagrams and locate the image for concave mirrors. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscience.c...
























Comments
Post a Comment