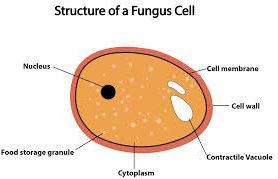
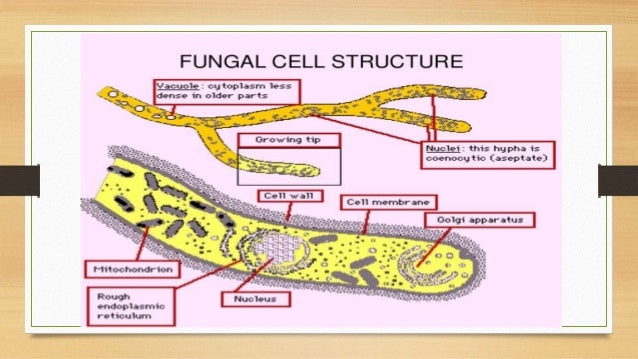
39 fungal cell diagram
Biology of Fungi Lecture 3: Fungal Structure and Function Page 2 of 5 Fungal Cell Wall u Functions Q Structural barrier Q Determines pattern of cell growth and is partly dependent upon: l Chemical composition l Assembly of the wall components Q Environmental interface of the fungus l Protects against osmotic lysis l Acts as a molecular sieve l Contains pigments for protection The fungal cell wall is made of glucans and chitin; while glucans are also found in plants and chitin in the exoskeleton of arthropods, fungi are the only organisms that combine these two structural molecules in their cell wall. Unlike those of plants and oomycetes, fungal cell walls do not contain cellulose.
We'll use the 2D cut-through cell diagrams you're used to to help explain where these structures are, what they look like and what they do. However, don't forget that cells exist in 3D and not only that, their structures move! Animal Cells. Animal cells have many different structures depending on their function.

Fungal cell diagram
Fungal cells have a cell wall made of chitin (remember that plant cell walls are made of cellulose). A yeast cell. Athlete's foot, caused by a fungus. Some fungi are pathogens, for example the ... Fungal cells are of two basic morphological types: true hyphae (multicellular filamentous fungi) or the yeasts (unicellular fungi), which make pseudohyphae. A ... Fungal cells are characterized by being elongated and tubular in shape, with rounded edges. They have a cell wall Like plant cells, fungal cells are surrounded by a rigid structure known as the cell wall, which helps protect the cell, give it support and a defined shape. This cell wall is made up of a carbohydrate called chitin. Make up hyphae
Fungal cell diagram. Raman Spectroscopy and Density Functional Theory Calculations of ?-Glucans and Chitins in Fungal Cell Walls The following 200 files are in this category, out of 846 total. (previous page) ( next page) 1ملف.png 330 × 379; 90 KB. 201601 Endoplasmic reticulum.png 400 × 400; 92 KB. 201710 Cells.png 1,000 × 1,000; 1.42 MB. 201710 SingleCell.svg 512 × 512; 1.34 MB. The fungal cell wall is located outside the plasma membrane and is the cell compartment that mediates all the relationships of the cell with the environment. It protects the contents of the cell, gives rigidity and defines the cellular structure. The cell wall is a skeleton with high plasticity that protects the cell from different stresses, among which osmotic changes stand out. 6,855 fungus cell stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See fungus cell stock video clips. of 69. structure of a fungus mycelium mushroom yeast cell structure plant animal cells eukaryotic structure lysosomal fungi cell multicellular organisms multicellular cell mushroom life cycle.
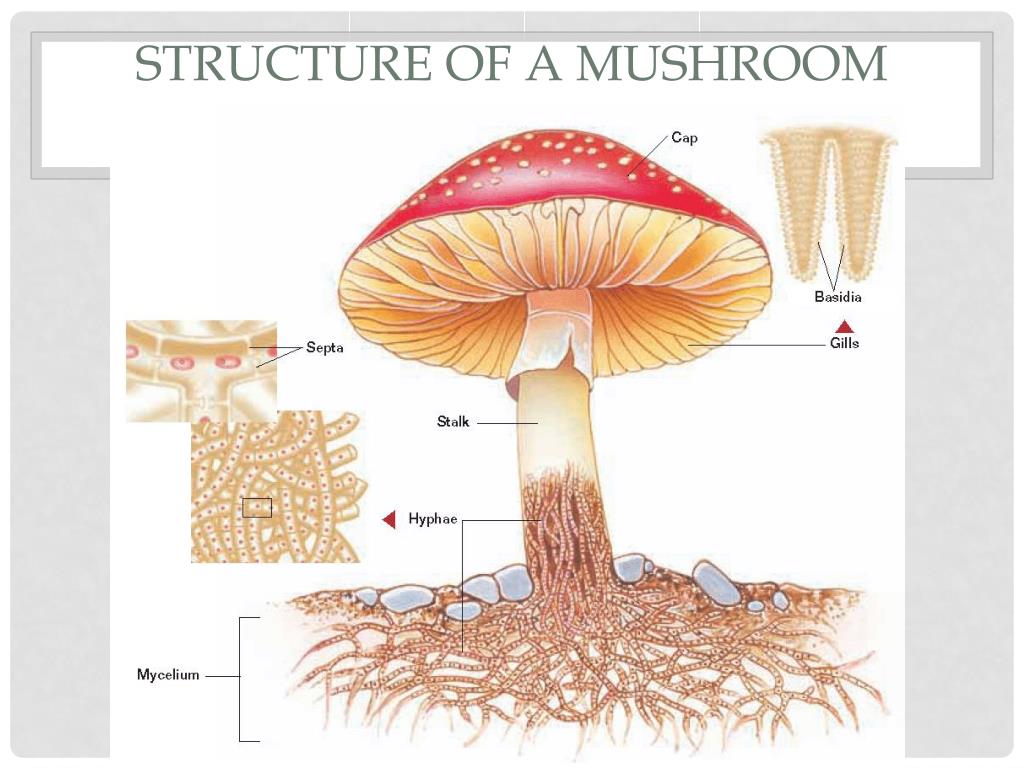
The science dealing with the study of fungi is called "Mycology".A thallus refers to the fungal cell body, which can be either unicellular (yeasts) or multicellular (moulds).. Some fungi show dimorphism between the two states by following both yeast and mould cell cycle and called "Dimorphic fungi". In this context, we will discuss the structure of fungi by looking into the diagram and ... 5. Bracket Fungi (Shelf Fungi): The basidiocarps or fructifications appear on tree trunks, logs, lumber, etc. just as brackets or shelves, e.g. Fomes applanatus (perennial), Polyporus sulphureus (annual). 6. Puffballs: The basidiocarp is a stalked rounded structure which on ripening sends out puffs of spores. Biosynthesis is a unique feature of the fungal cell wall. They possess a complicated cellular structure. The cells of fungus comprise the membrane-bound nucleus and the DNA that is wrapped around histone proteins. Chlorophyll is absent in fungal cells. Pigments are associated with the cell wall and vary from black, green and red. May 26, 2021. 0. 0. 0. Plants Animals Fungi Venn Diagram Venn Diagram Diagram Cell. Plant Cells Vs Animal Cells With Diagrams Plant And Animal Cells Animal Cell Plant Cell Diagram. Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes Venn Diagram Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes Prokaryotes Plant And Animal Cells.
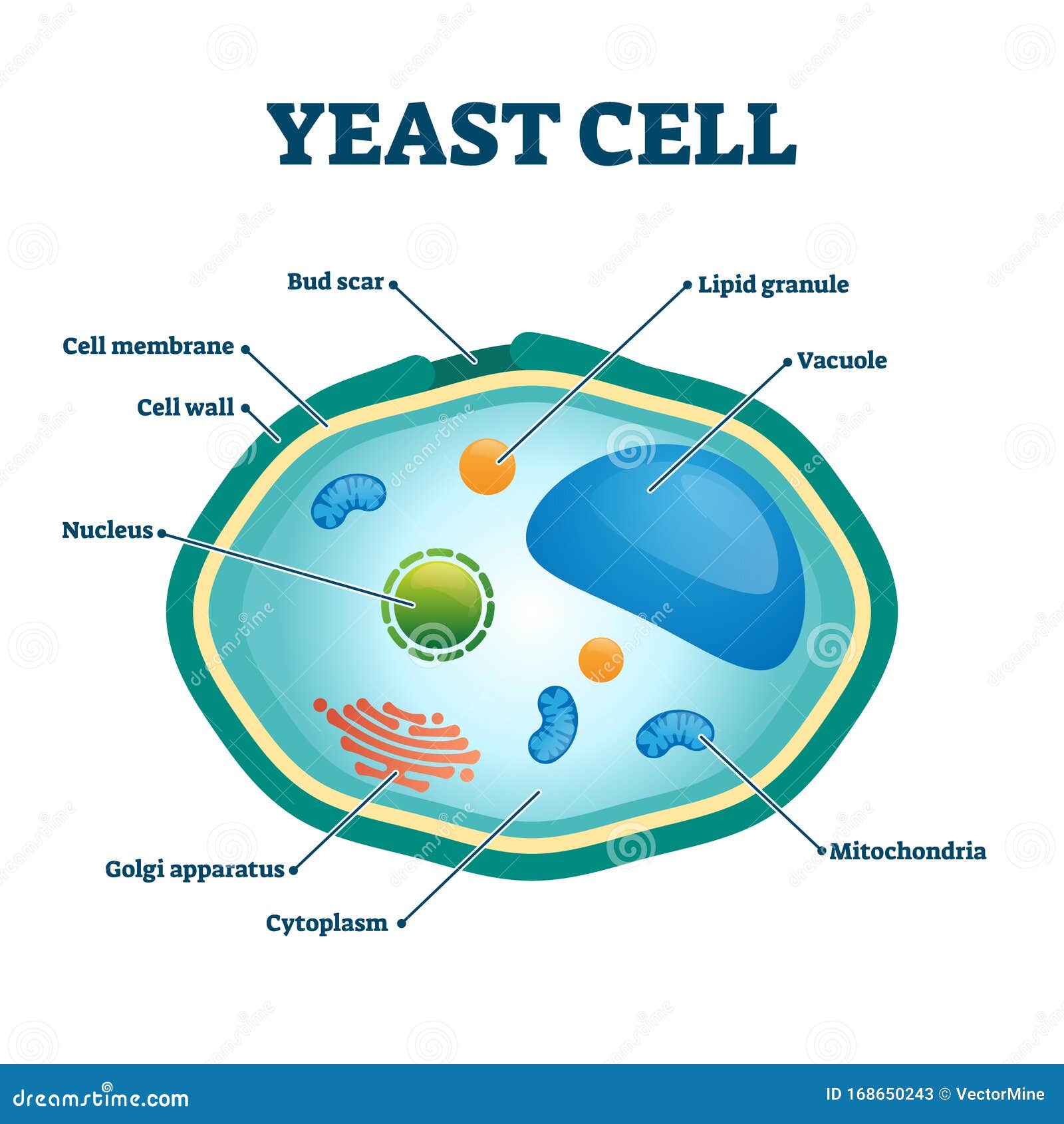
5 Mar 2021 — Most fungi are multicellular organisms. They display two distinct morphological stages: the vegetative and reproductive. The vegetative stage ... Plastids are involved in storage, photosynthesis. Larger vacuole keeps the cell turgid. Fungal cell- It has a cell wall made of chitin and other cell components are present. Mostly, fungal cells are multicellular except for the yeast cell which is a unicellular eukaryotic cell. Protozoa- These are unicellular eukaryotes. Like Amoeba, Paramoecium. Cell Walls. Not all species of fungi have cell walls, but in those that do, cell wall synthesis is an important factor in determining the final morphology of fungal elements. Thus, our knowledge of fungal morphogenesis has evolved in parallel with our understanding of fungal cell wall biosynthesis. Biology Chart. Vector illustration on. Fungal hyphae cells. Cross section of a Fungal hyphae cells septum; bud scar, mitochondrion; vacuole; nucleus; endoplasmic reticulum; lipid granule; membrane. Cross section of a yeast cell. Structure of fungal cell. Vector diagram for educational, biological, and science use.
Fungal cell structure • Yeasts (unicellular, budding) • Molds (hyphae, mycelia, spores) • Dimorphs (both) Pathogenesis Toxins: produced, but not relevant to human infections Disease from: Bulk of organisms Immune response to them or their byproducts. 2 Overview of fungal infections
The backbone of most of the fungal cell wall is made up of polysaccharides. The cell wall components can be divided into two groups on the basis of the chemical nature of the components such as the structural (fibrillar) polymers that consist predominantly of straight-chain molecules, providing structural rigidity, and the matrix components that cross-link the fibrils and that coat and embed the structural polymers.
Human pathogenic fungi produce three basic ‘cell’ types: hyphae, yeast cells, and spores. The organization and subcellular structure of these different cell types and their modes of growth and formation are reviewed. Growth and form is the consequence of how new cell surface is formed. This is generated by the delivery of vesicles to the surface which provides new membrane and the enzymes ...
Cell structure of Fungi. The cell wall of a fungal cell is made up of chitin (fungal cellulose, C22H54N4O21). In case of primitive fungi, the true cellulose with or without chitin can be found. Occasional Plasma-lemma appears, coiled ingrowths called lomasomes which lie below the cell wall.
Download scientific diagram | Fungal cell wall components. The fungal cell wall contains a cell membrane with various membrane proteins, a protective layer of chitin (yellow) as well as glucans ...
The molecular composition of the cell wall is critical for the biology and ecology of each fungal species. Fungal walls are composed of matrix components that are embedded and linked to scaffolds of fibrous load-bearing polysaccharides. Most of the major cell wall components of fungal pathogens are …
Septate hyphae (with septa) and aseptate hyphae (coenocytic or without septa). Fungal hyphae cells Cross section of a Fungal hyphae cells (septum; bud scar, mitochondrion; vacuole; nucleus; and growth tip and vesicles). Vector diagram for educational, biological, and science use fungal cell diagram stock illustrations.
A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle that is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. The most conspicuous compartment in most plant cells is a very large, fluid-filled vacuole. Large vacuoles are also found in three genera of filamentous sulfur bacteria, the Thioploca, Beggiatoa, and Thiomargarita.
Fungal cells A yeast is a unicellular fungus. The diagram below shows the ultrastructure of a typical yeast cell: Bacterial cells Bacterial cells have a more simple structure compared to animal,...
This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of the fungal cell. (a) The Cell Wall of the Fungal Cell: The composition of cell wall is variable among the different groups of fungi or between the different species of the same group. In the majority of fungi, the wall lacks cellulose but contains a form of chitin known as the fungus cellulose which is strictly not identical with insect chitin.
by NAR Gow · 2017 · Cited by 511 — In most fungal species the inner cell wall consists of a core of covalently attached branched β-(1,3) glucan with 3 to 4% interchain and chitin ...
Vector diagram for educational, biological, and science use fungal cell diagram stock illustrations. Fungal hyphae cells. Cross section of a Fungal hyphae cells (septum; bud scar, mitochondrion; vacuole; nucleus; and growth tip and vesicles). Vector diagram for educational, biological, and science use.
Fungal cell walls contain chitin, as opposed to the cellulose found in the cell walls of plants and many protists. Additionally, whereas animals have cholesterol in their cell membranes, fungal cell membranes have different sterols called ergosterols.
The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that is present only in eukaryotic cells. The vital function of a nucleus is to store DNA or hereditary information required for cell division, metabolism and growth. Nucleolus: It manufactures cell's protein-producing structures and ribosomes.
Illustration about Typical fungi cell. Fungal Hyphae. Structure fungi. Diagram illustrating the ultrastructure of a septate hypha. Illustration of herbs, fungal, edible - 49947916
Fungal cells are characterized by being elongated and tubular in shape, with rounded edges. They have a cell wall Like plant cells, fungal cells are surrounded by a rigid structure known as the cell wall, which helps protect the cell, give it support and a defined shape. This cell wall is made up of a carbohydrate called chitin. Make up hyphae
Fungal cells are of two basic morphological types: true hyphae (multicellular filamentous fungi) or the yeasts (unicellular fungi), which make pseudohyphae. A ...
Fungal cells have a cell wall made of chitin (remember that plant cell walls are made of cellulose). A yeast cell. Athlete's foot, caused by a fungus. Some fungi are pathogens, for example the ...








![Home [pneumonia-disease.weebly.com]](https://pneumonia-disease.weebly.com/uploads/5/3/5/1/53514965/258806342.png)














Comments
Post a Comment