43 calcium homeostasis diagram
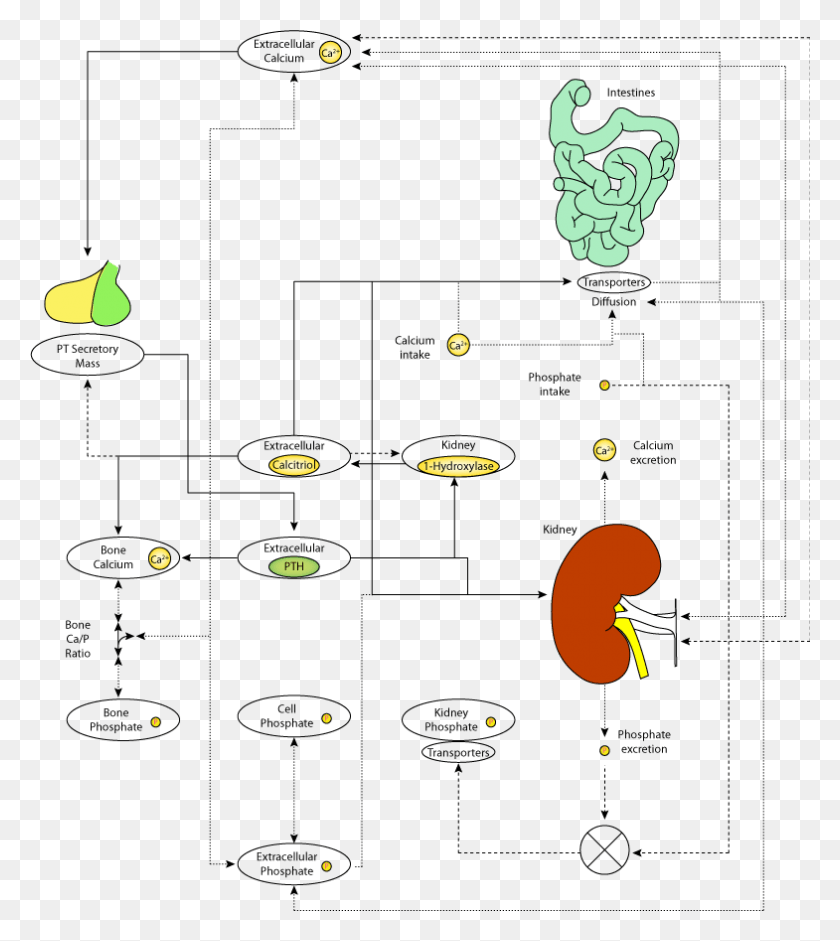
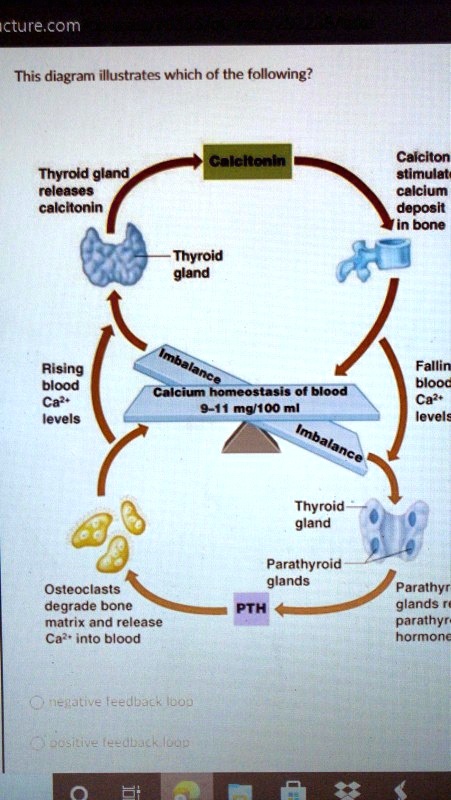
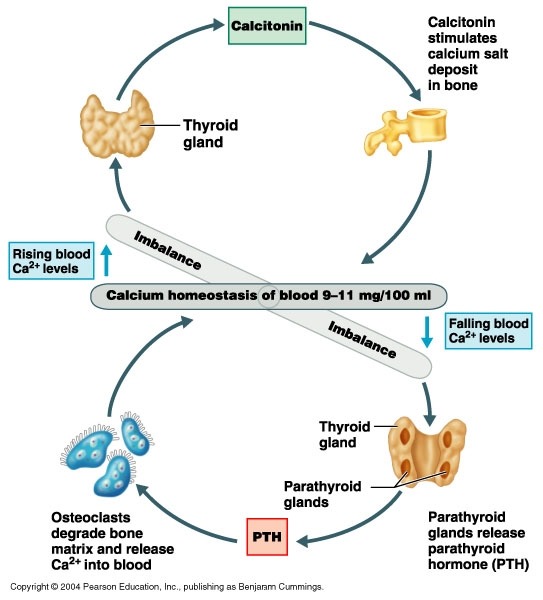
Kidney and Calcium Homeostasis - PubMed Central (PMC) Total body calcium in the adult human is about 1-2 kg and 99% of total calcium exists in bone. Even though only less than 1% of body calcium is in the extracellular space, maintaining the extracellular calcium concentration within a narrow range (8.5-10.5 mg/dL) is very important for calcium homeostasis. This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis What process is ... This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis. What process is represented by "E"? Select one: a. PTH promotes calcium release into blood by osteoclast. b. Calcium is removed from blood by osteoblasts. c. Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption.
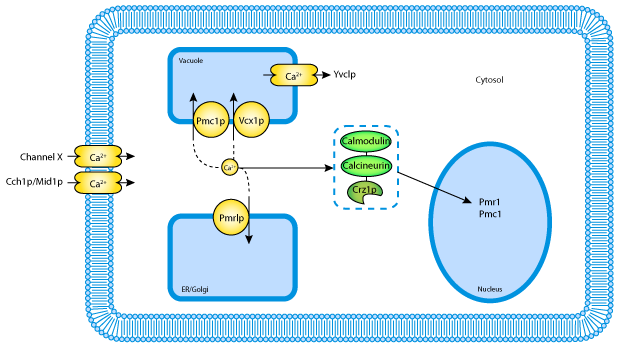
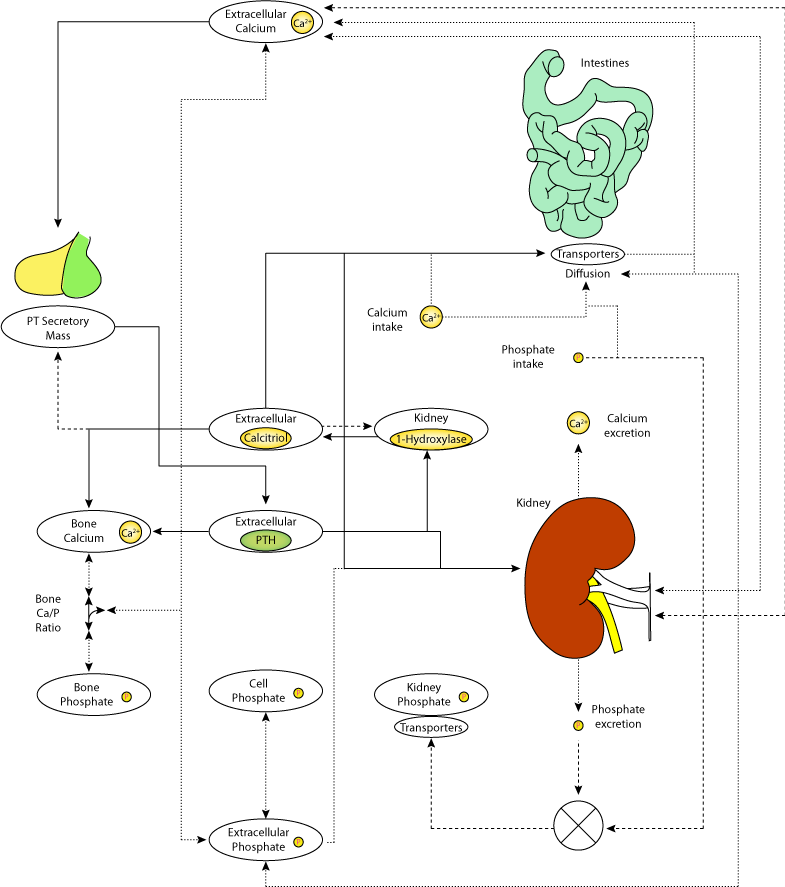
Calcium Homeostasis Pathway Suite Calcium Homeostasis Pathway Suite Calcium (Ca2+) permeates almost every aspect of cellular function. The provision of the Ca2+ signal and its timely removal is mediated by a vast array of channels, pumps and exchangers, also controlling a concentration gradient of four orders of magnitude between the extracellular environment and the cytoplasmic concentration in resting cells.
Calcium homeostasis diagram
Calcium Homeostasis - Structure and Function 3 ... Structure and Function 3: Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Musculoskeletal Systems (VMS1005) Calcium Homeostasis. Lear ning Objectives: 1) Know the main sour ces of calcium and phosphate in the body ! 2) Describe the r ole of the parathyr oid gland in calcium homeostasis ! 3) Briefly describe the mechanism for V itamin D metabolism ! Calcium Homeostasis Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Calcium Homeostasis. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Cryo-EM structure of the calcium homeostasis modulator 1 ... Calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) is a voltage-gated ATP release channel that plays an important role in neural gustatory signaling and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Here, we present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of full-length Ca 2+-free CALHM1 from Danio rerio at an overall resolution of 3.1 Å. Our structure ...
Calcium homeostasis diagram. Parathyroid Physiology: Calcium Homeostasis, Disorders of ... Calcium homeostasis is a complex process involving the following 4 key components: serum calcium, serum phosphate, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3, and parathyroid hormone (PTH). More than 99% of the total body calcium is stored in bone in the form of phosphate and hydroxide salts, predominantly as hydroxyapatite. Calcium Homeostasis - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Calcium homeostasis is also related to oral calcium intake, vitamin D prescription, parathyroid hormone levels, and phosphate levels. Whereas the normal serum ionized calcium level varies from 1.15 to 1.29 mmol/L, the calcium concentration of dialysate (in which all of the calcium is ionized) usually ranges from 1.25 to 1.79 mmol/L. Cryo-EM structure of the calcium homeostasis modulator 1 ... Calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) is a voltage-gated ATP release channel that plays an important role in neural gustatory signaling and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Here, we present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of full-length Ca2+-free CALHM1 from Danio rerio at an overall resolution of 3.1 Å. This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis. What process is ... general-biology. Homeostasis is when the body is static or unchanging. asked Aug 13, 2021 in Anatomy & Physiology by happyhealthy. anatomy-and-physiology. This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis. What process is represented by "B"? asked Sep 26, 2016 in Anatomy & Physiology by BrilliantBrayn. anatomy-and-physiology.
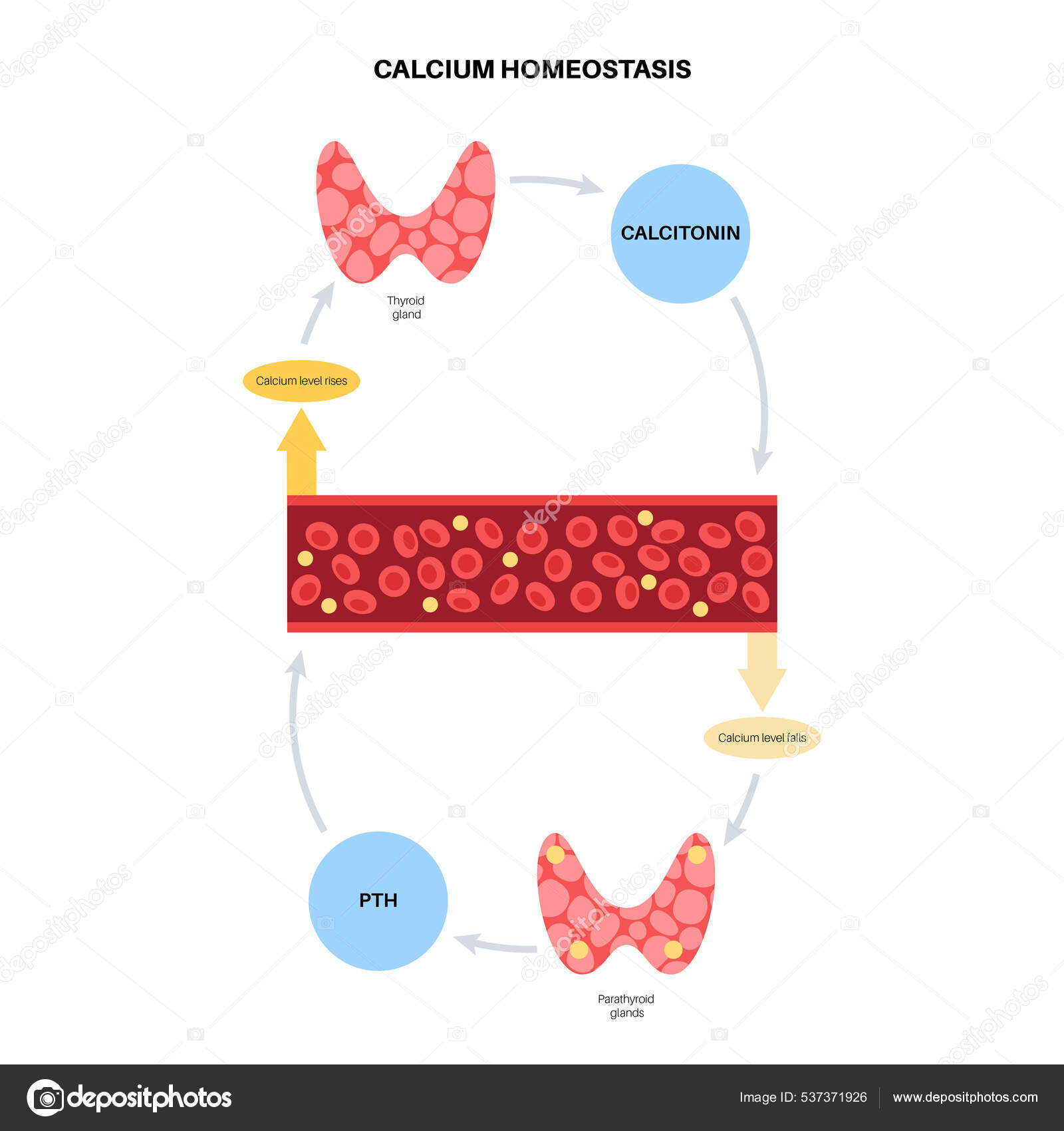
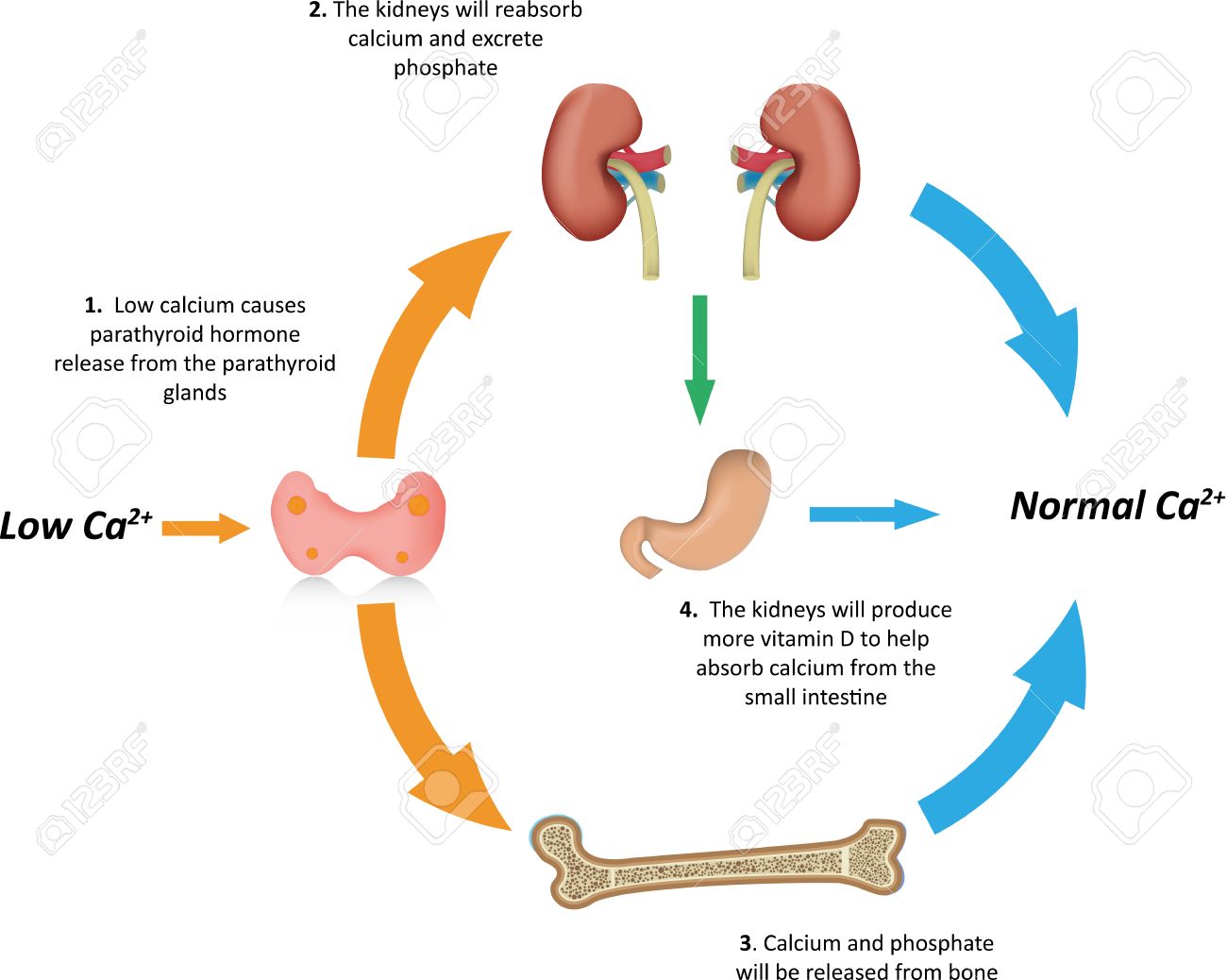
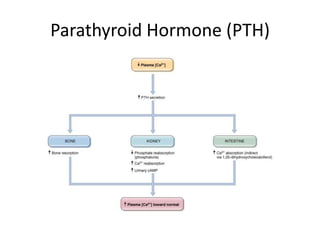
Calcium metabolism in birds - PubMed Calcium is one of the most important plasma constituents in mammals and birds. It provides structural strength and support (bones and eggshell) and plays vital roles in many of the biochemical reactions in the body. The control of calcium metabolism in birds is highly efficient and closely regulated … Calcium Homeostasis - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Calcium homeostasis refers to the maintenance of a constant concentration of calcium ions in the extracellular fluid. It includes all of the processes that contribute to maintaining calcium at its "set point." Because plasma [Ca 2+] rapidly equilibrates with the extracellular fluid, ECF [Ca 2+] is kept constant by keeping the plasma [Ca 2+] constant. Calcium and Phosphate Hormonal Regulation Notes: Diagrams ... CALCIUM & PHOSPHATE HOMEOSTASIS Blood calcium level regulation Normal total blood calcium: 8.5-10mg/dl Parathyroid hormone: ↑ calcium level Vitamin D: ↑ calcium level Calcitonin: ↓ calcium level Extracellular calcium Diffusible: can cross cell membranes Free-ionized calcium (Ca2+): involved in cellular processes → neuronal action ... What is Calcium Homeostasis? (with pictures) Calcium homeostasis is maintained by the actions of two hormones; parathyroid hormone and calcitonin. Parathyroid hormone is made in the parathyroid glands in response to low levels of calcium in the cells or blood. It stimulates the release of calcium from the bones into the blood, where it can be used by the cells.
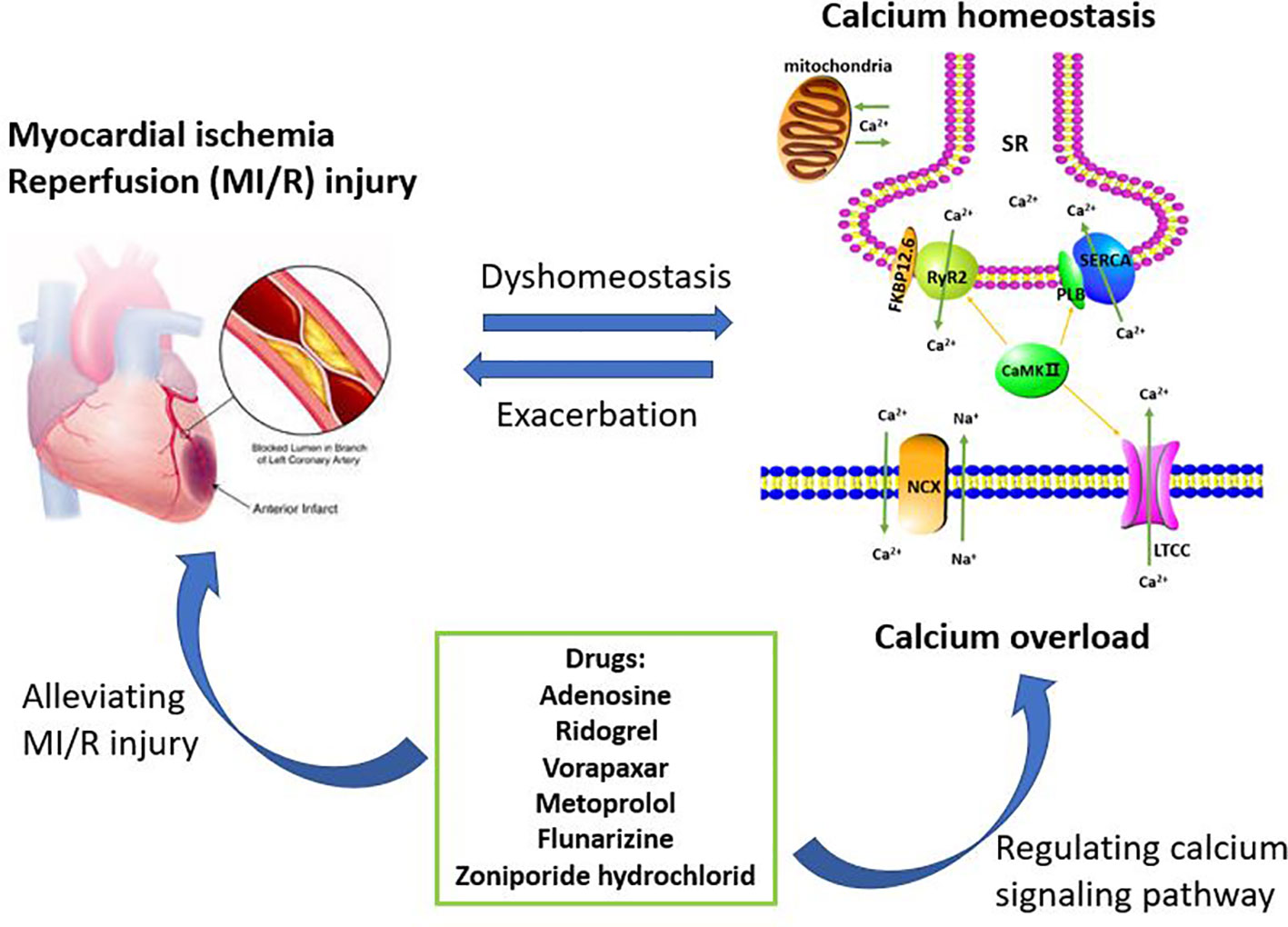
This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis What process is ... This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis. What process is represented by "D"? Answer PTH promotes calcium release into blood by osteoclast. Calcium is removed from blood by osteoblasts. Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption. Calcium is lost in urine. PTH promotes calcium reabsorption from urine. Role of calcium homeostasis in Alzheimer's disease | NDT Importantly, calcium homeostasis disorders ultimately lead to cellular pathology in AD, including apoptosis, Aβ deposition, hyperphosphorylation of tau, and abnormal synaptic plasticity. Some therapeutic drugs based on calcium homeostasis have indeed achieved positive effects, such as reducing the risk of dementia in hypertensive patients. Cryo-EM structures of calcium homeostasis modulator ... Calcium homeostasis modulator (CALHM) family proteins are Ca 2+-regulated adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-release channels involved in neural functions including neurotransmission in gustation.Here, we present the cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structures of killifish CALHM1, human CALHM2, and Caenorhabditis elegans CLHM-1 at resolutions of 2.66, 3.4, and 3.6 Å, respectively. CALCIUM HOMEOSTASIS Diagram | Quizlet CALCIUM HOMEOSTASIS study guide by amccorm6 includes 7 questions covering vocabulary, terms and more. Quizlet flashcards, activities and games help you improve your grades.
This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis. What process is ... This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis. What process is represented by "A"? asked Sep 26, 2016 in Anatomy & Physiology by Lulul. A. Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption. B. PTH promotes calcium release into blood by osteoclast. C. Calcium is lost in urine.
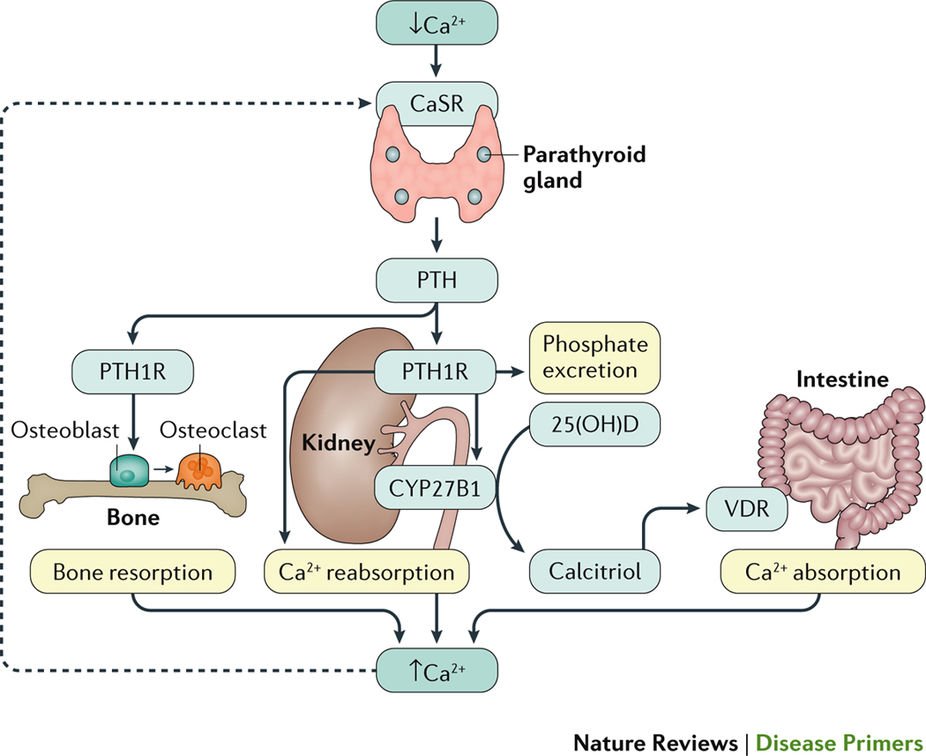
Calcium Regulation - Vitamin D - PTH - TeachMePhysiology Calcium is the fifth most abundant element in the body. Calcium is vital for several biological processes including neurotransmission, muscle contraction, hormone secretion and blood coagulation. In this article, we will review calcium regulation throughout the body, and consider some clinical relevance.
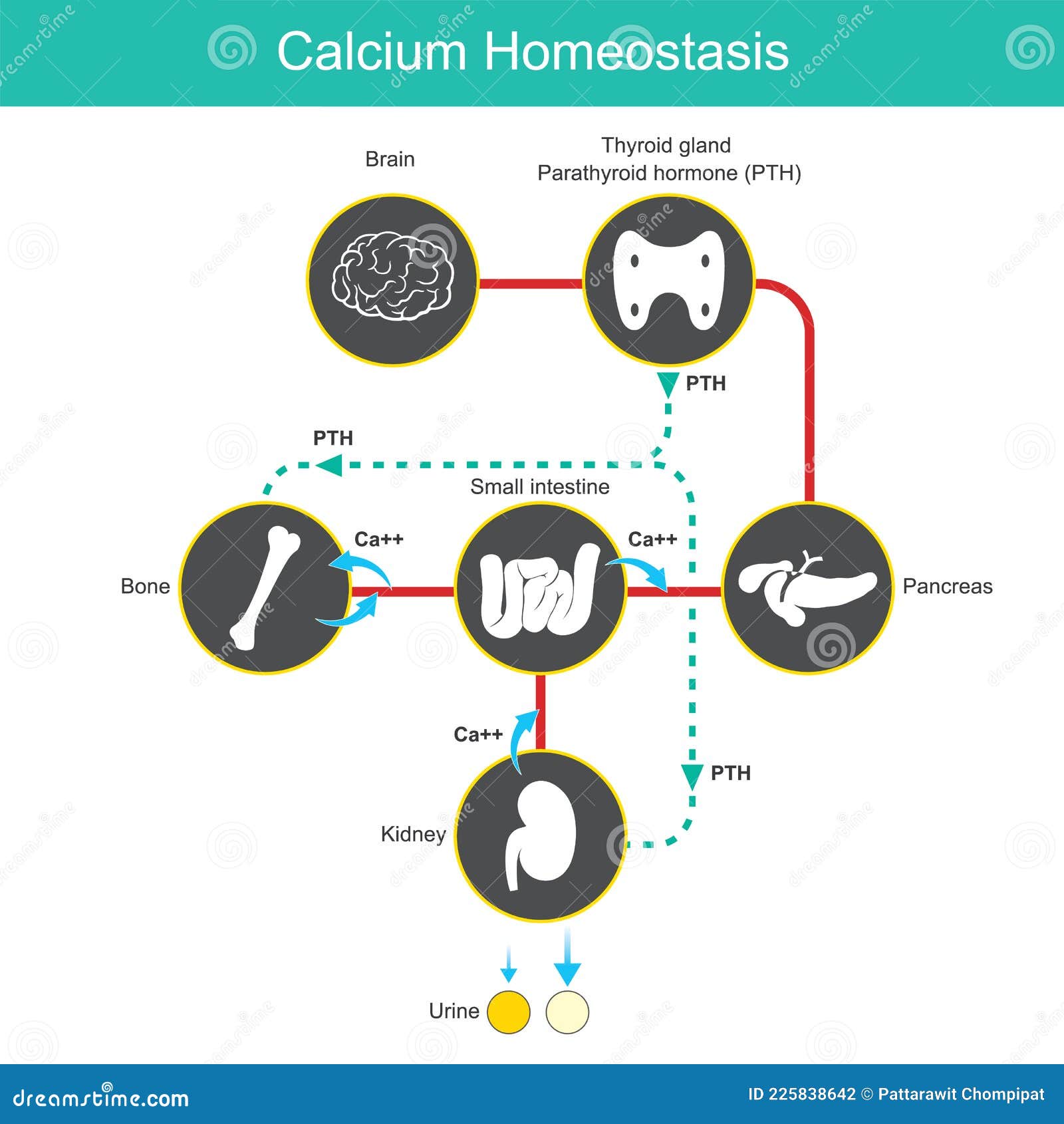
Calcium homeostasis. diagram for learning calcium levels ... Calcium homeostasis. diagram for learning calcium levels in blood human. vector illustration. - download this royalty free Vector in seconds. No membership needed.
TRP channels in calcium homeostasis: from hormonal control ... TRP channels in calcium homeostasis: from hormonal control to structure-function relationship of TRPV5 and TRPV6 Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017 Jun;1864(6):883-893. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.11.027. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Authors Mark K C van Goor 1 ...
Solved 8) This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis. What ... A) Calcium is removed from blood by osteoblasts. B) PTH promotes calcium reabsorption from urine. C) PTH promotes calcium release into blood by osteoclast. D) Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption. E) Calcium is lost in urine. 9) This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis. What; Question: 8) This is a diagram of calcium homeostasis. What process ...
Calcium Homeostasis and Selected Causes of Hypercalcemia ... Download scientific diagram | Calcium Homeostasis and Selected Causes of Hypercalcemia in Pediatric Patients. The serum calcium level is determined mainly by the interplay of three dynamic ...
6.7 Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal ... Calcium homeostasis, i.e., maintaining a blood calcium level of about 10 mg/dL, is critical for normal body functions. Hypocalcemia can result in problems with blood coagulation, muscle contraction, nerve functioning, and bone strength. Hypercalcemia can result in lethargy, sluggish reflexes, constipation and loss of appetite, confusion, and coma.
Calcium Homeostasis · Part One Calcium Homeostasis. Describe the function, distribution, regulation and physiological importance of sodium, chloride, potassium, magnesium, calcium and phosphate ions . Describe the control of plasma calcium. Calcium is a bivalent cation. Almost all (99%) of calcium is located in bone, with the remainder in plasma and soft tissues.
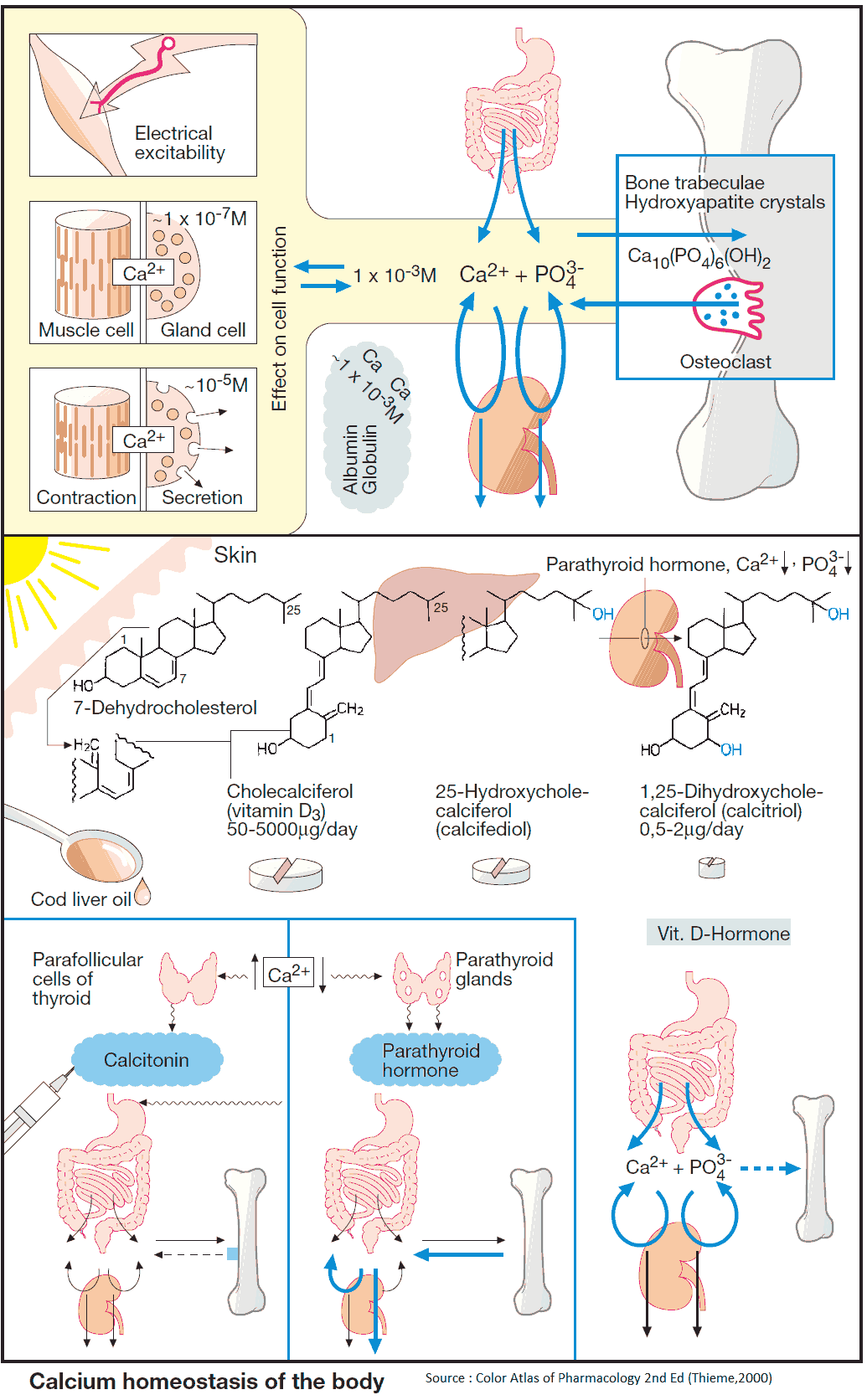
Schematic diagram of synthesis of vitamin D and regulation ... Schematic diagram of synthesis of vitamin D and regulation of calcium homeostasis. Vitamin D is majorly synthesized in the skin during exposure to UV radiation and less absorbed from the diet. 25 ...
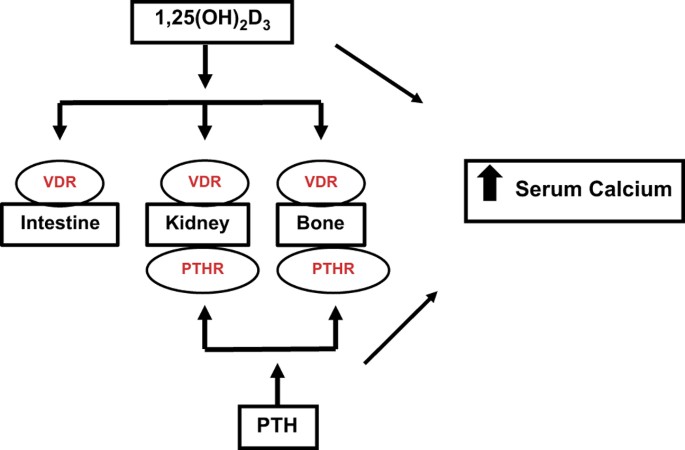
Schematic diagram of calcium homeostasis. | Fluid and ... Calcium homeostasis is a complex process involving the following 4 key components: serum calcium, serum phosphate, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3, and parathyroid hormone (PTH). More than 99% of the total body calcium is stored in bone in the form of phosphate and hydroxide salts, predominantly as hydroxyapatite.
Calcium homeostasis and osteoporosis | McMaster ... Figure 1: Calcium homeostasis is a process controlled by chiefly by hormones vitamin D and PTH. Vitamin D enters circulation via synthesis in the skin or intestinal absorption and is subsequently converted to its active form, 1,25 (OH) 2 D via separate hydroxylation processes in the liver and kidneys. Both 25 (OH)D and 1,25 (OH) 2 D are ...
Cryo-EM structure of the calcium homeostasis modulator 1 ... Calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) is a voltage-gated ATP release channel that plays an important role in neural gustatory signaling and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Here, we present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of full-length Ca 2+-free CALHM1 from Danio rerio at an overall resolution of 3.1 Å. Our structure ...
Calcium Homeostasis Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Calcium Homeostasis. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Calcium Homeostasis - Structure and Function 3 ... Structure and Function 3: Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Musculoskeletal Systems (VMS1005) Calcium Homeostasis. Lear ning Objectives: 1) Know the main sour ces of calcium and phosphate in the body ! 2) Describe the r ole of the parathyr oid gland in calcium homeostasis ! 3) Briefly describe the mechanism for V itamin D metabolism !


















![PDF] Vitamin D, calcium homeostasis and aging | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/c544c3fd576c686da2aeb6efa36371fe7c4f89d6/2-Figure1-1.png)





Comments
Post a Comment