40 lactic acid fermentation diagram
Diagram of the pathway for heterolactic fermentation of ... Diagram of the pathway for heterolactic fermentation of fructose by lactic acid bacteria. Panel A: The end products of the pathway are lactic acid, acetic acid, ethanol and CO 2 . Energy (ATP) is ... Lactic Acid Fermentation: Definition, Products & Equation ... Lactic acid fermentation, a metabolic process, refers to when our muscle cells manage pyruvate during anaerobic respiration. Learn more about the definition of lactic acid fermentation, and ...
Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Worksheet YEAST & BACTERIA Lactic Acid Fermentation LACTIC ACID. ANIMALS/HUMANS 3. Name the three processes of aerobic . cellular respiration. How many ATP’s does each process produce, and what is the total ATP produced from one glucose? 3 Processes of Cellular Respiration: # ATP produced: GLYCOLYSIS 2 KREBS CYCLE . 2 ELECTRON TRANSPORT …
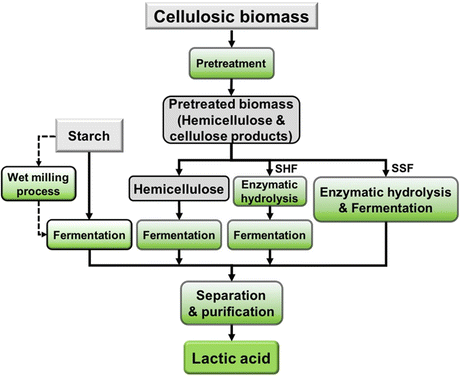
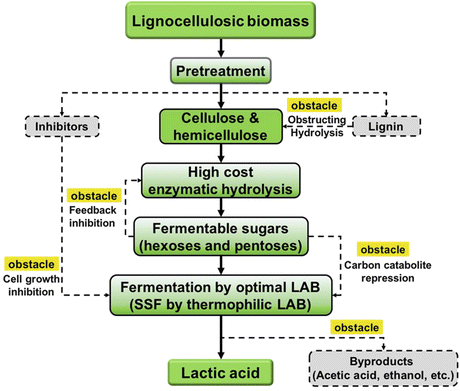
Lactic acid fermentation diagram
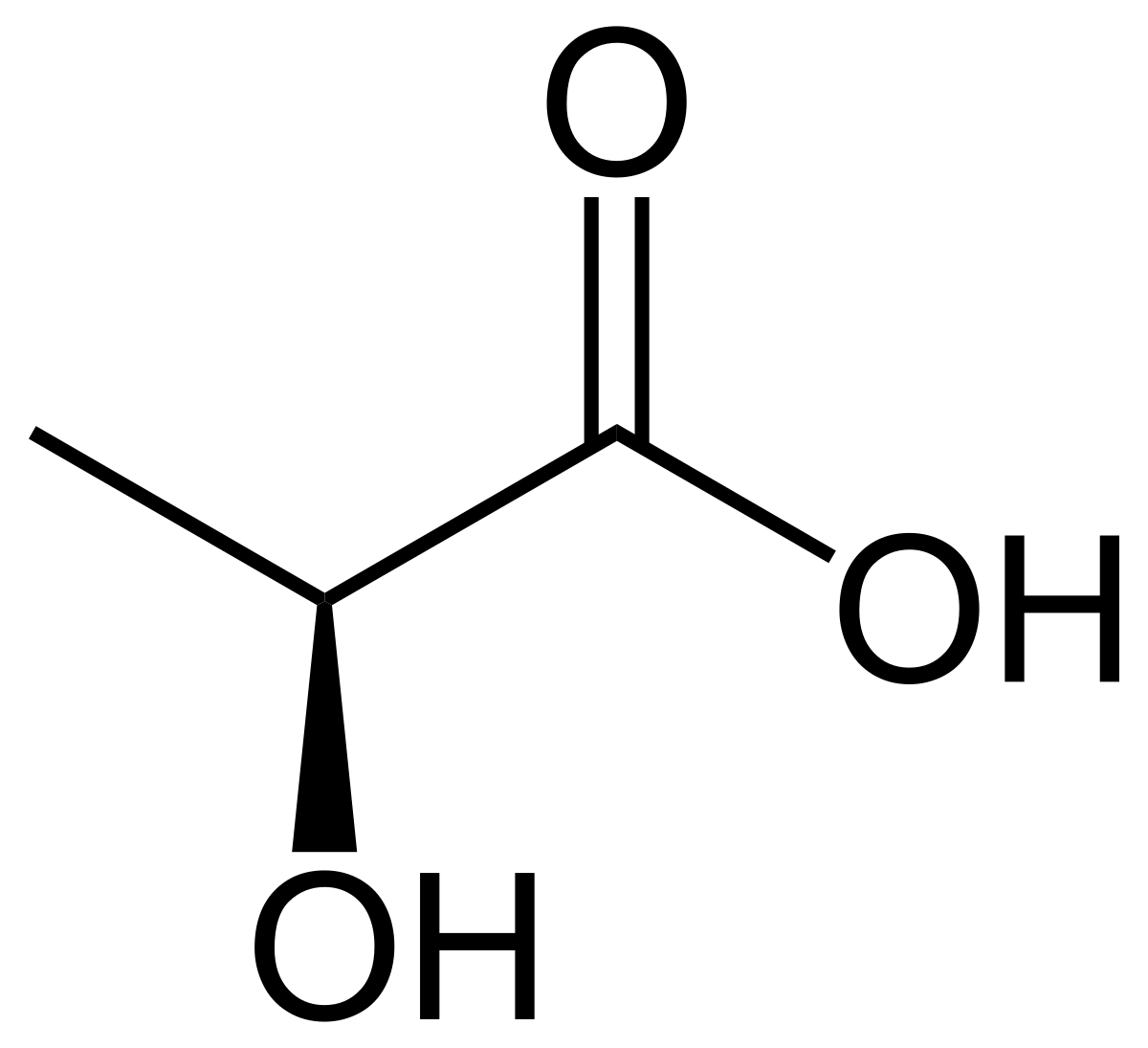
15.3: Lactic Acid Fermentation - Chemistry LibreTexts Lactic acid fermentation is the type of anaerobic respiration carried out by yogurt bacteria ( Lactobacillus and others) and by your own muscle cells when you work them hard and fast. Figure 15.3. 3: Lactic acid, C 3 H 6 O 3. Lactic acid fermentation converts the 3-carbon pyruvate to the 3-carbon lactic acid ( C 3 H 6 O 3) (see figure below ... Development of a sustainable process for the production of ... Lactic acid is a commonly occurring substance in nature, ranging from existence in micro-organisms to the human body. Traditionally, lactic acid has applications in industries such as food, chemicals, pharmaceuticals and textiles. In this work, a sustainable process for the production of polymer grade lactic acid (99 wt. % on dry basis) from crude lactic acid was simulated. What Is Fermentation? - Definition, Types, Anaerobic ... Types of Fermentation. There are three different types of fermentation: Lactic Acid Fermentation. In this, starch or sugar is converted into lactic acid by yeast strains and bacteria. During exercise, energy expenditure is faster than the oxygen supplied to the muscle cells. This results in the formation of lactic acid and painful muscles.
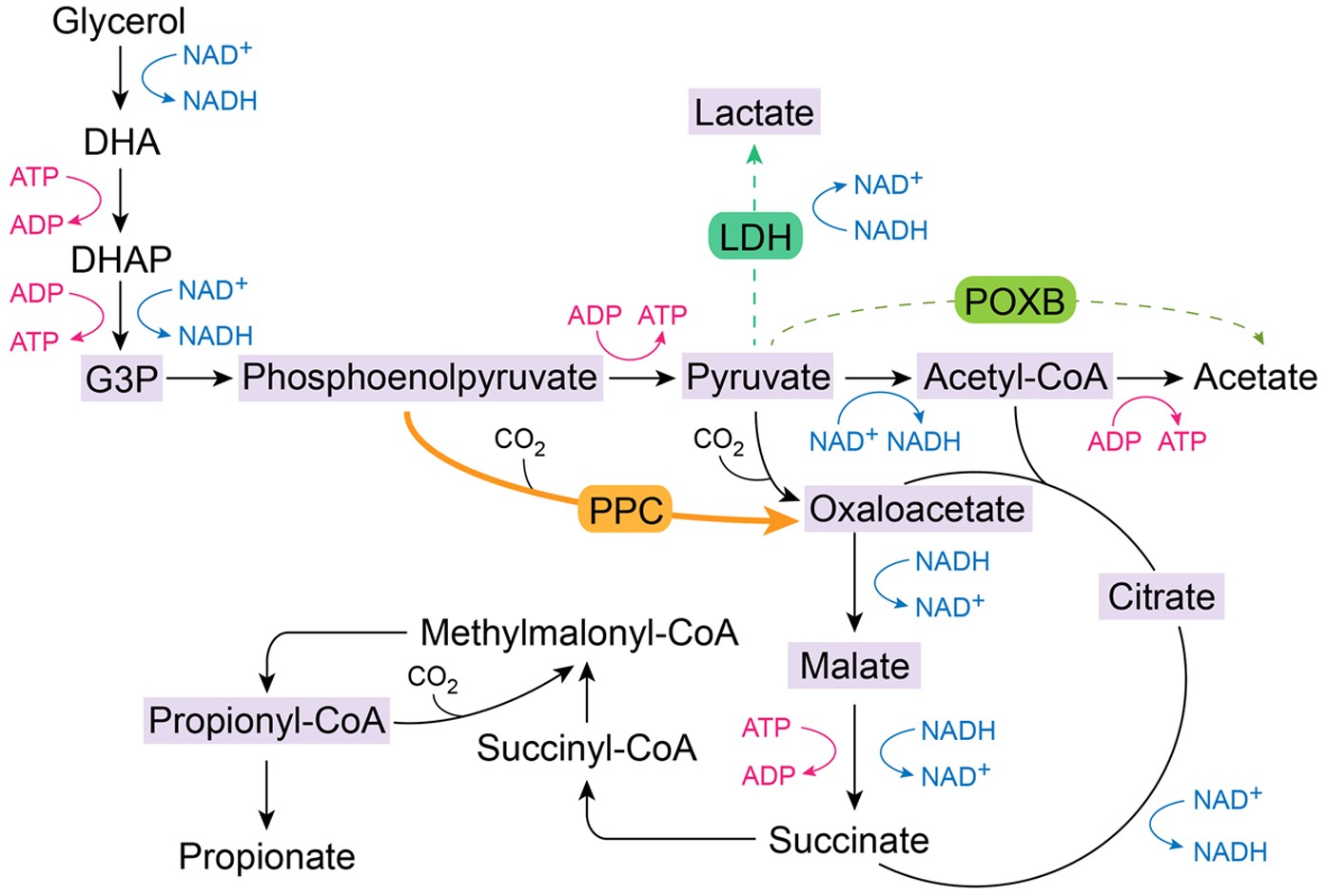
Lactic acid fermentation diagram. Fermentation in Yeast Lab Instructions.docx - Sugar ... There are 2 types of fermentation: 1. Lactic Acid 2. Alcohol Lactic acid fermentation converts pyruvate into lactic acid and cellular energy while alcohol fermentation converts pyruvate into alcohol and carbon dioxide (CO 2). In this lab we will explore fermentation respiration and its bi-product CO 2. › pmc › articlesThe Microbiology of Malting and Brewing Finally, there is a growing trend of American craft brews incorporating Brettanomyces spp. and lactic acid bacteria in the fermentation, maturation, or bottle re-fermentation process, and even a rare few purportedly conduct a fermentation entirely by Brettanomyces. Cellular Metabolism and Fermentation This lactic acid causes the muscle stiffness couch-potatoes feel after beginning exercise programs. The stiffness goes away after a few days since the cessation of strenuous activity allows aerobic conditions to return to the muscle, and the lactic acid can be converted into ATP via the normal aerobic respiration pathways. Fermentation of ... Conventional lactic acid (LA) fermentation versus modern ... Download scientific diagram | Conventional lactic acid (LA) fermentation versus modern LA fermentation process: conventional LA fermentation uses neutralizers, generating gypsum along with calcium ...
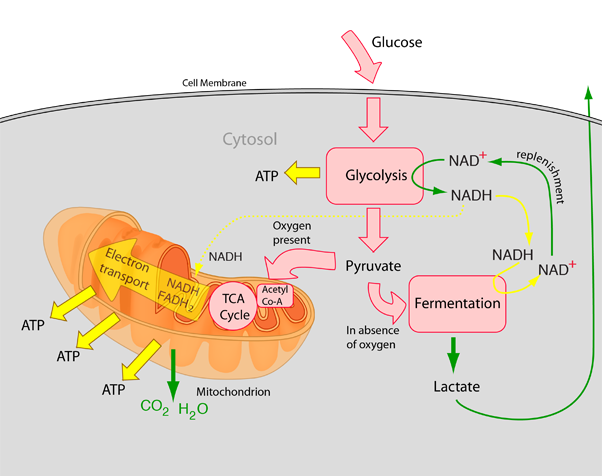
Lactic Acid - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Diagram for recovery of lactic acid from fermentation broth. For the production of food-grade lactic acid a fermentation medium with a higher-grade sugar source and low protein content is required. The calcium present in the broth is precipitated as calcium sulfate. The solution is then washed, filtered, and treated with activated carbon. Fermentation and anaerobic respiration | Cellular ... Fermentation is another anaerobic (non-oxygen-requiring) pathway for breaking down glucose, one that's performed by many types of organisms and cells. In fermentation, the only energy extraction pathway is glycolysis, with one or two extra reactions tacked on at the end. Fermentation and cellular respiration begin the same way, with glycolysis. Lactic acid separation and recovery from fermentation ... 2021-04-20 · Lactic acid has become one of the most important chemical substances used in various sectors. Its global market demand has significantly increased in recent years, with a CAGR of 18.7% from 2019 to 2025. Fermentation has been considered the preferred method for producing high-purity lactic acid in the industry over chemical synthesis. However, the … Venn Diagram: Alcohol vs. Lactic Acid Fermentation Create your own Venn Diagrams at ClassTools.net
Lactic acid and ethanol fermentation Lab Report Extract of sample "Lactic acid and ethanol fermentation". The presence of CO2, released as the waste product is responsible for its foam like expansion as it forms bubbles in the dough. Ethanol, on the other hand evaporates from the dough completely after the bread is fully baked (Kratz, 2005). Lactic Acid - University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Lactic acid is widely used in the food industry as an acidulant, preservative, precursor for stearoyl-2-lactylates. Perhaps its greatest industrial potential is for biodegradable polymers such as polylactic acid. Lactic acid can be produced by chemical synthesis or by fermentation. Our research program on lactic acid began in the early 1980s ... L (+) lactic acid fermentation and its product polymerization industry. The microorganisms being used for lactic acid fermentation, the raw materials reported, the various novel fermentation processes and its processing methods have been reviewed. The properties and applications of lactic acid, its derivatives and polymer have been discussed. The various routes to polymerization and the Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration - Diagrams ... Lactic Acid Fermentation in the Human Body; Lactic acid fermentation in the human body takes place when there is not enough oxygen intake. This happens during intense exercise and running. The glucose gets broken down into lactic acid and gets accumulated in the muscles. The reaction is as follows: C 6 H 12 O 6 → C 3 H 6 O 3 + energy ...
Process flow diagram fermentation aerobic example - Canada ... CHAPTER 7 PRODUCTS OF MIXED Flow diagram. Coffee cherry : Sort the cherries. In the production of tea, there is a process referred to as fermentation. Glycolysis- 10 steps explained steps by steps with diagram. Glycolysis is the metabolic process that serves as the foundation for both aerobic and anaerobic cellular.
Fermentation: Meaning, Mechanism and Energy Yield in ... In vertebrates, the lactic acid formed in muscles in anaerobic respiration is carried by the blood to the liver where it is used to resynthesize glucose. Thus, these animals save the chemical energy of glucose contained in lactic acid. Microorganisms, which use this type of fermentation, excrete lactic acid. They, thus, lose the energy of ...
HOMOLACTIC FERMENTATION PDF - PDF Connect Me Lactic acid fermentation - Wikipedia. A product prepared by lactic acid bacteria LAB fermentation of sugars present in the pieces of fruits and vegetables. Lactic acid fermentation is a metabolic process by which glucose and other fermebtation sugars also, disaccharides of six-carbon sugars, e.
› topics › agricultural-andOat Milk - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Fermentation affects the flavor, texture, and health effects of the product, as some lactic acid bacteria produce β-glucanases while others produce exopolysaccharides that increase viscosity and ropiness (Mårtensson et al 2001, 2003, 2005). Oats are perceived as a tasty cereal and traditionally carry a positive health image.
PDF Lactic Acid Fermentation, Muscle Contractions, and Other ... Lactic acid's relation to milk gives it its name; lact- being the latin word for milk. Its discovery in muscles occurred later, in the year 1808, by Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius[13]. Secondly, lactic acid is only produced through a process known as lactic fermentation[14]. Lactic fermentation occurs in many organisms,
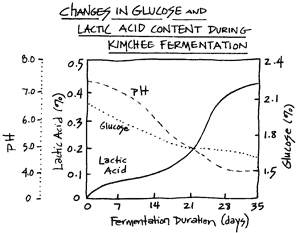
agricoop.nic.in › sites › defaultModel Project Report on Fruit & Vegetable Processing Unit Pickling is a process of preservation by fermentation. The fruits and vegetables are immersed in 5–10 per cent salt solution (brine) leading to lactic acid fermentation. Salt prevents growth of undesirable organisms and allow lactic acid bacteria to grow. The natural sugars present in fruits and vegetables are converted to lactic acid at 25°C.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › EnzymeEnzyme - Wikipedia 1) CO 2 + H 2 O ← Carbonic anhydrase H 2 CO 3 {\displaystyle {\ce {CO2{}+H2O<-[{\text{Carbonic anhydrase}}]H2CO3}}} (in lungs ; low CO 2 concentration) (2) The rate of a reaction is dependent on the activation energy needed to form the transition state which then decays into products. Enzymes increase reaction rates by lowering the energy of the transition state. First, binding forms a low ...
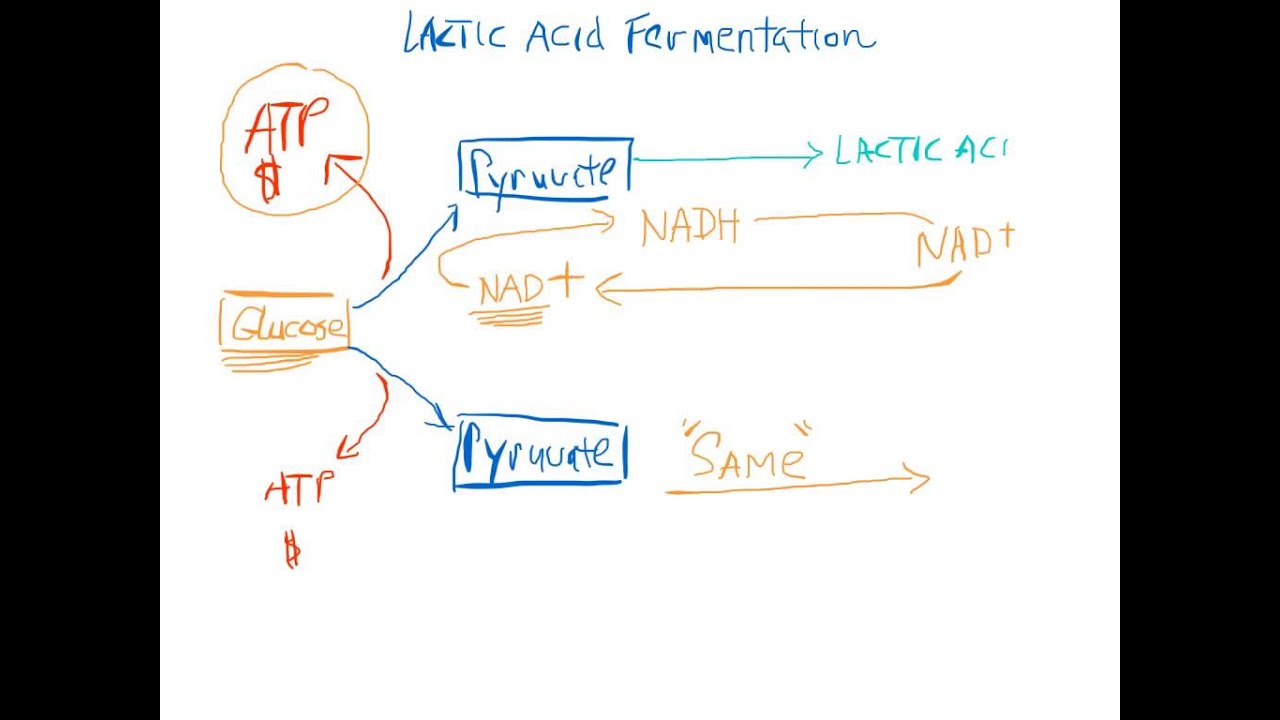
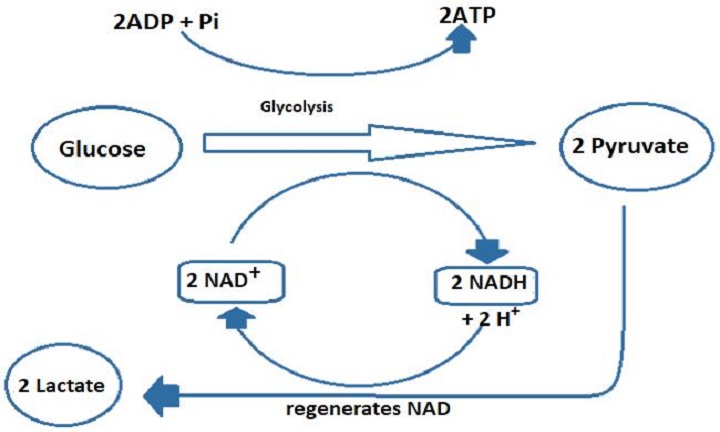
Cell Processes: Fermentation - Texas Gateway The following diagram shows a summary of lactic acid fermentation. Humans undergo lactic acid fermentation when the body needs a lot of energy in a hurry. When you are sprinting full speed, your cells will only have enough ATP stored in them to last a few seconds. Once the stored ATP is used, your muscles will start producing ATP through lactic ...
PDF Conceptual Design and Scale Up of Lactic Acid Production ... Overall process schematic for purification of lactic acid from fermentation-derived magnesium lactate is displayed in Figure 1. This process is divided into two major parts: the first part is esterification of lactic acid with ethanol in the RD column, and the second part is hydrolysis of the produced ethyl lactate back into its ...
Fermentation: Process, Examples, Reaction, Diagram 2022-01-19 · Lactic acid is produced during a high-intensity activity when oxygen supply becomes limited. Invertebrates produce succinate and alanine as a result of fermentation. Fermentative bacteria are necessary for the formation of methane, as well as hydrogen, carbon dioxide, formate, acetate, and carboxylic acids. The carbon dioxide and acetate are then …
Lactic acid fermentation process scheme, labeled vector ... Lactic acid fermentation process scheme, labeled vector illustration diagram. 1. Editable Vector .AI file. 2. Editable Vector .EPS-10 file. 3. High-resolution JPG image. Use for everything except reselling item itself. Description: Lactic acid fermentation process scheme, labeled vector illustration diagram.
DOC The Working Cell Part II Worksheet Study the diagram below. Label the processes using the following terms: Oxidative Respiration, Lactic Acid Fermentation, Glycolysis, Alcoholic Fermentation, Krebs cycle and ETC. 3. Write the number of ATP molecules produced by each process listed below. Then add up these numbers to get the total number of ATP molecules produced when one glucose ...
Lactic acid fermentation - Wikipedia Lactic acid fermentation is a metabolic process by which glucose or other six-carbon sugars (also, disaccharides of six-carbon sugars, e.g. sucrose or lactose) are converted into cellular energy and the metabolite lactate, which is lactic acid in solution.It is an anaerobic fermentation reaction that occurs in some bacteria and animal cells, such as muscle cells.
Difference Between Lactic Acid and Alcoholic Fermentation ... The main difference between lactic acid and alcoholic fermentation is that lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid molecules from pyruvate whereas alcoholic fermentation produces ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. Alcoholic fermentation of yeast is used in the food industry to produce wine and beer.
Separation and purification technologies for lactic acid ... Lactic acid is an important platform chemical with a wide range of applications. Production of lactic acid by fermentation is advantageous because renewable and low cost raw materials can be used as substrates. After fermentation, the broth needs to be purified to obtain pure lactic acid for further uses.
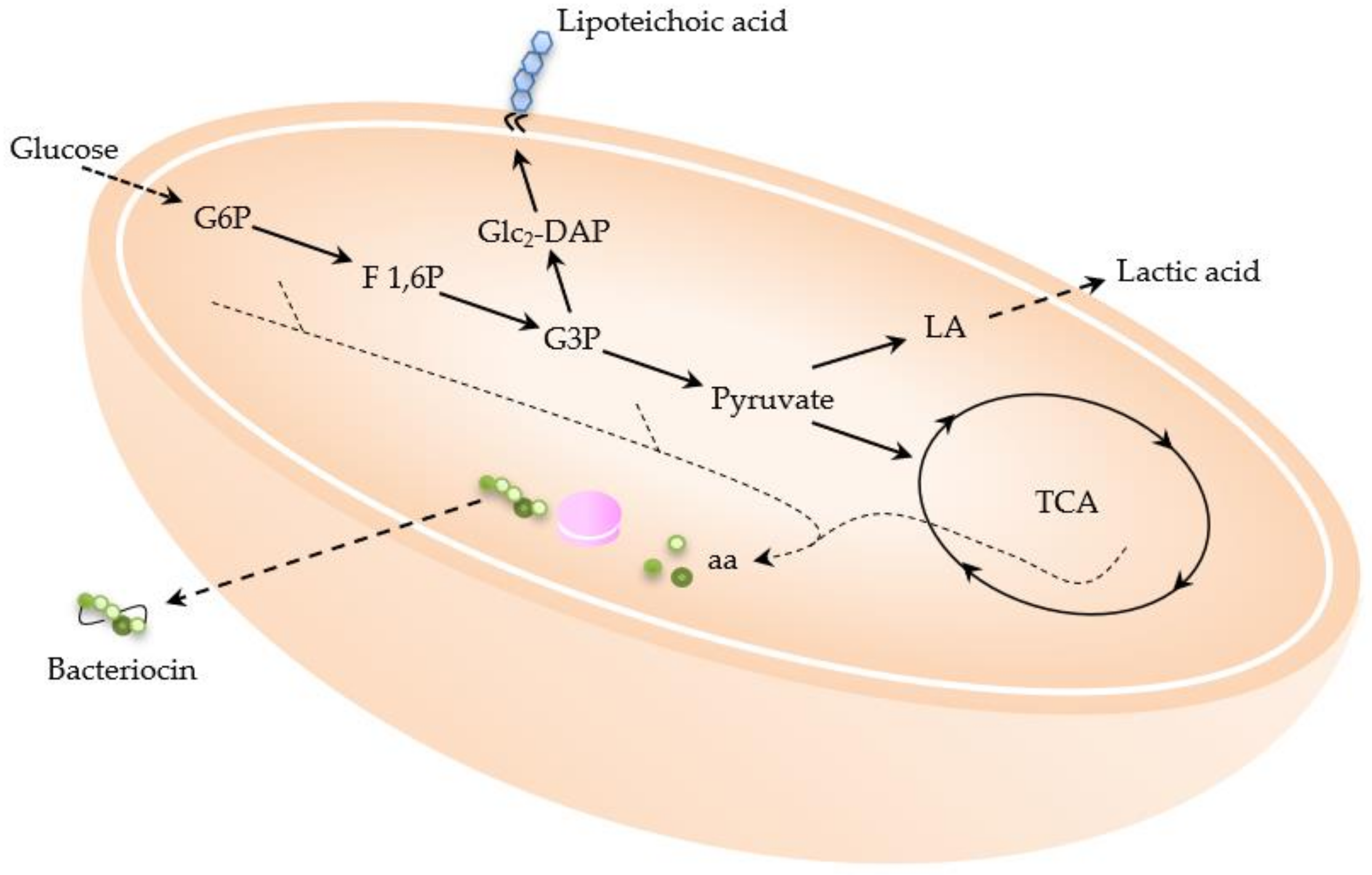
Lactobacillus - Wikipedia This diagram shows the biosynthesis of bioactive compounds ... Lactic acid lowers the vaginal pH to around 4.5 or less, hampering the survival of other bacteria, and H 2 O 2 reestablishes the normal bacterial microbiota and normal vaginal pH. In children, lactobacilli such as Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus (previously L. rhamnosus) are associated with a reduction of …
Lactic Acid Fermentation Equation & Process | What is ... The lactic acid fermentation occurs in certain animal cells and bacterial organisms. In animal cells, aerobic respiration is generally preferred - this process doesn't involve lactic acid ...
PDF ISD 2135 Maple River Schools / Homepage Lactic acid fermentation is used to produce foods such as cheese, yogurt, pickles, and kimchi. The diagram below shows the two types of fermentation. Follow the directions. 1. Label the process that shows alcoholic fermentation. 2. Label the process that shows lactic acid fermentation. Glycolysis 2 NADH Glucose 2 coz 2 Pyruvic Acid 2 2 2 Acid 2 ...
What Is Fermentation? - Definition, Types, Anaerobic ... Types of Fermentation. There are three different types of fermentation: Lactic Acid Fermentation. In this, starch or sugar is converted into lactic acid by yeast strains and bacteria. During exercise, energy expenditure is faster than the oxygen supplied to the muscle cells. This results in the formation of lactic acid and painful muscles.
Development of a sustainable process for the production of ... Lactic acid is a commonly occurring substance in nature, ranging from existence in micro-organisms to the human body. Traditionally, lactic acid has applications in industries such as food, chemicals, pharmaceuticals and textiles. In this work, a sustainable process for the production of polymer grade lactic acid (99 wt. % on dry basis) from crude lactic acid was simulated.
15.3: Lactic Acid Fermentation - Chemistry LibreTexts Lactic acid fermentation is the type of anaerobic respiration carried out by yogurt bacteria ( Lactobacillus and others) and by your own muscle cells when you work them hard and fast. Figure 15.3. 3: Lactic acid, C 3 H 6 O 3. Lactic acid fermentation converts the 3-carbon pyruvate to the 3-carbon lactic acid ( C 3 H 6 O 3) (see figure below ...















![Nota & Latihan Biology KSSM Form 4 Bab 7.3 - WeAcademia [2021]](https://weacademia-bucket-production.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/biology_form4_7_8_8e32094e89.PNG)




Comments
Post a Comment