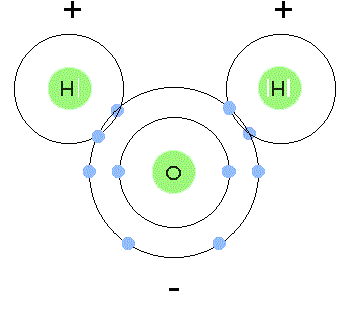
39 electron distribution diagram of water
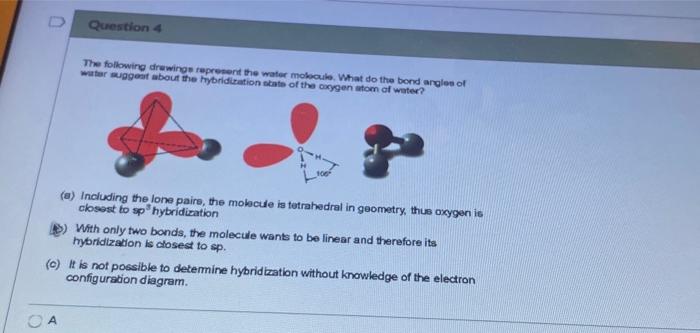
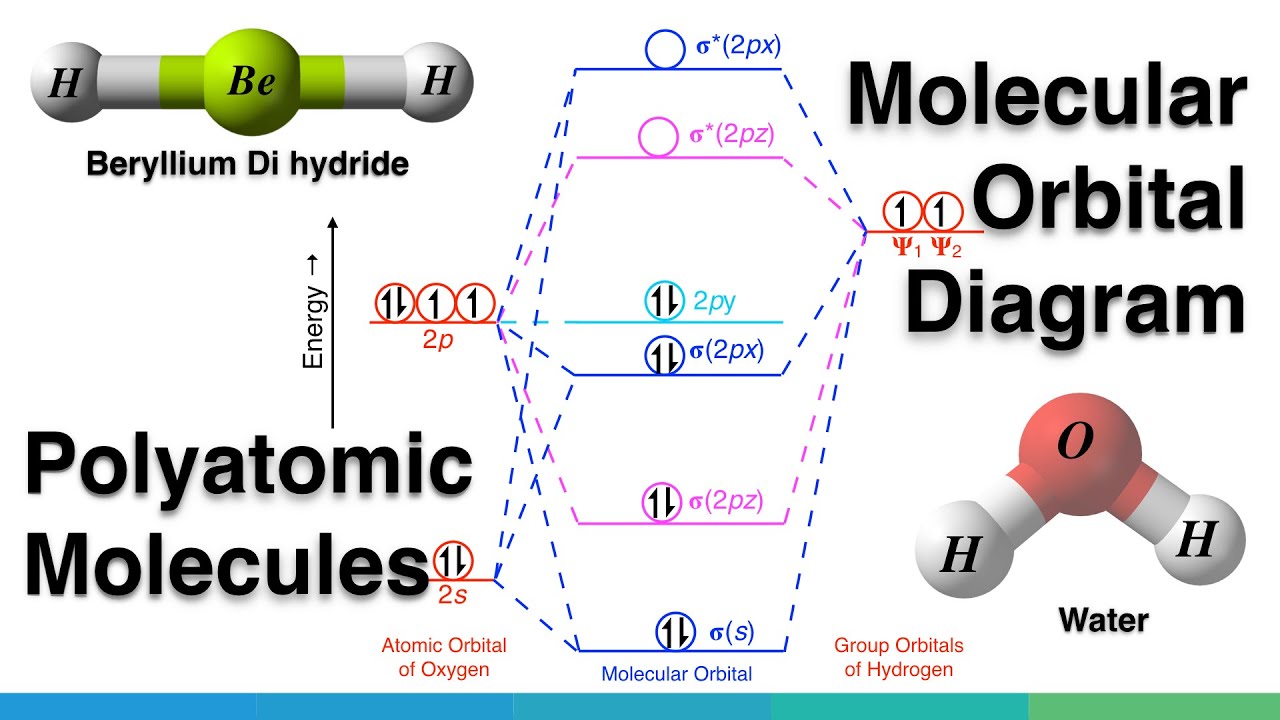
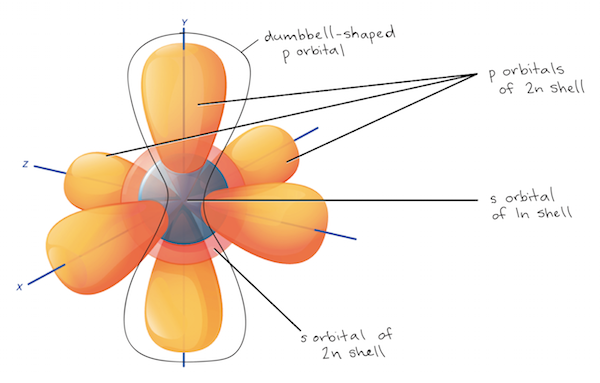
The Configuration of the Water Molecule. A molecule of water is composed of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. The one and only electron ring around the nucleus of each hydrogen atom has only one electron. The negative charge of the electron is balanced by the positive charge of one proton in the hydrogen nucleus. In this video we look at the electron geometry for Water (H2O). Because the water molecule has four electron domains (the two hydrogen atoms and the two lone...
@article{osti_5259143, title = {Structure of electron tracks in water. 2. Distribution of primary ionizations and excitations in water radiolysis. [accelerated electrons]}, author = {Pimblott, S M and Mozumder, A}, abstractNote = {A procedure for the calculation of entity-specific ionization and excitation probabilities for water radiolysis at low linear energy transfer (LET) has been developed.

Electron distribution diagram of water
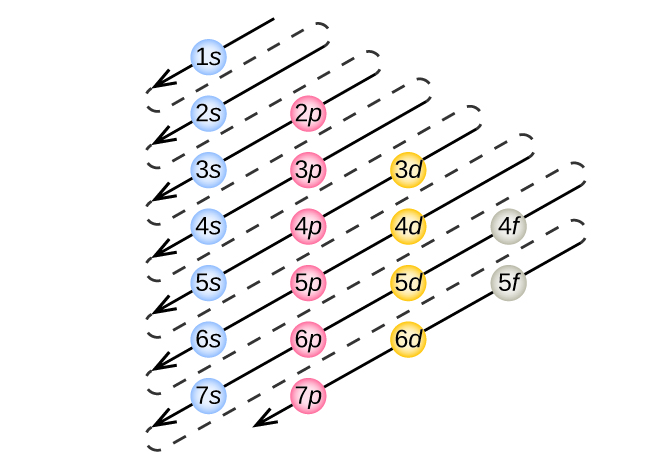
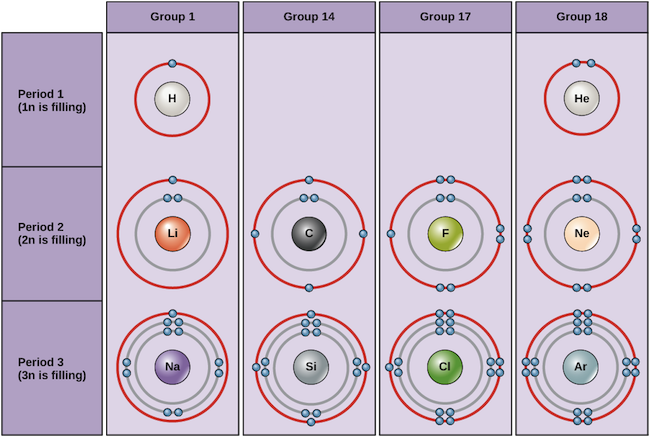
Electron distribution diagram of water which element is more electronegative. Why does electro-activity increase over a period? Consider sodium at the beginning of period 3 and chlorine at the end (ignoring noble gas, Argon). Think of sodium chloride as if it's covalently bonded. Both sodium and chlorine have their linked electrons at level 3. Jun 01, 2000 · The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Scientific and Technical Information Answer (1 of 3): Oxygen: 1s2, 2s2, 2p4 Hydrogen: 1s1 The bonds are polar-covalent.
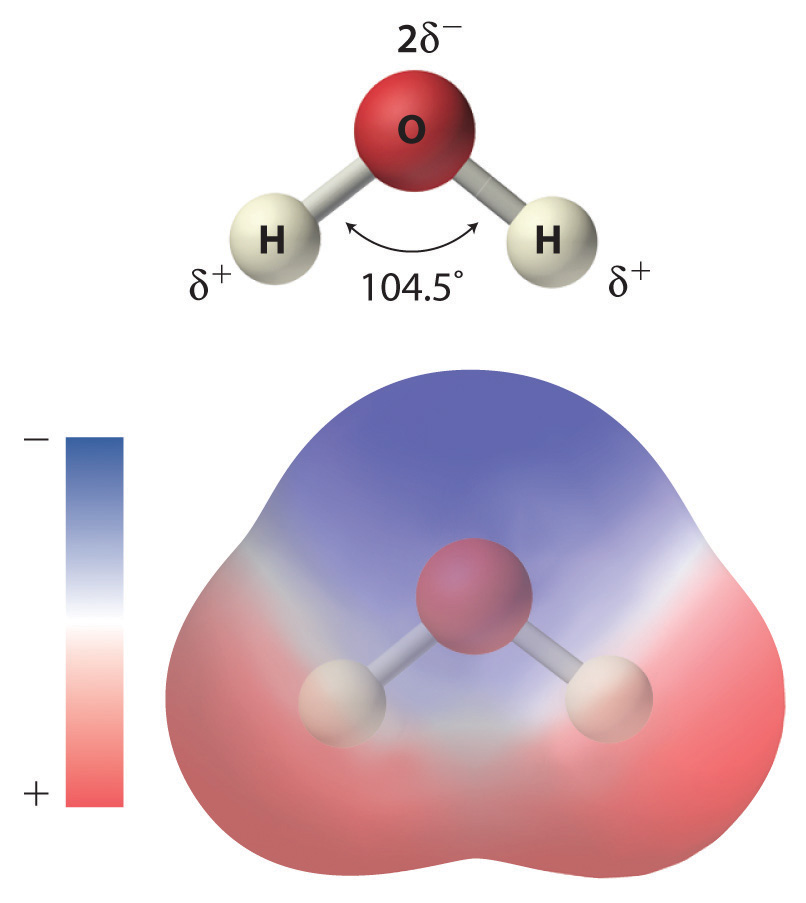
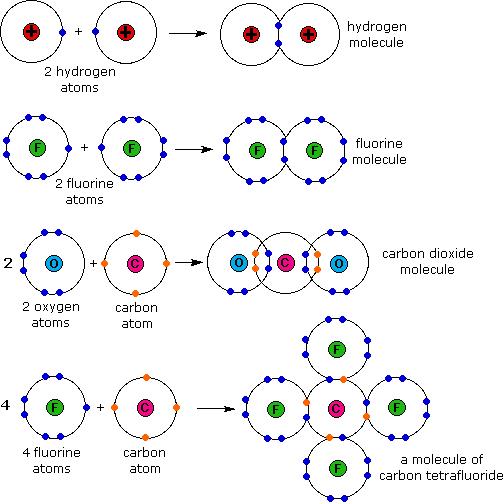
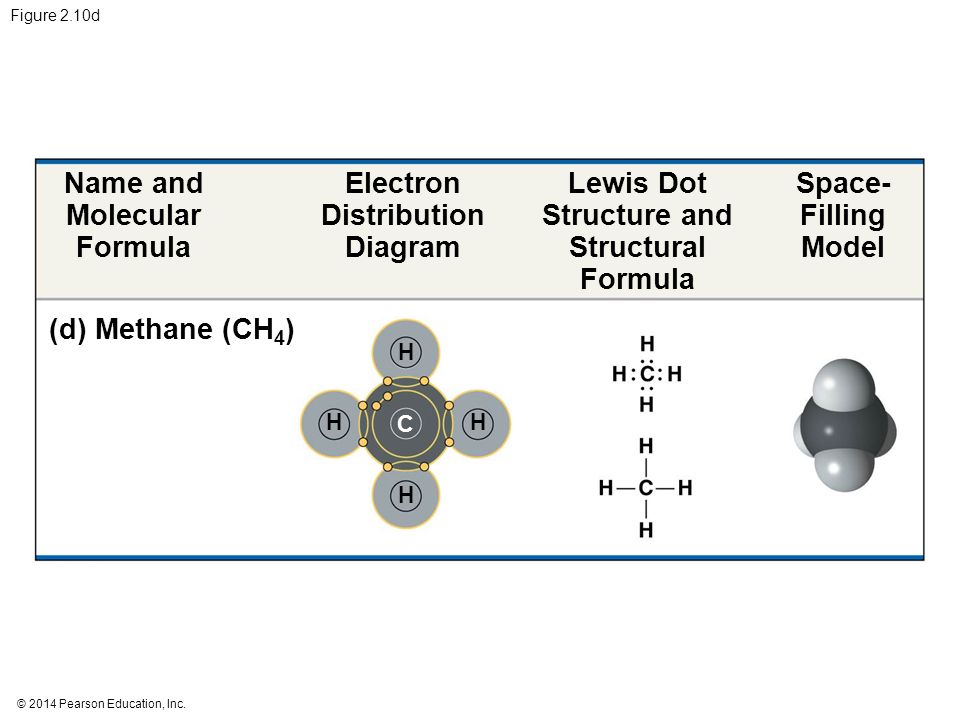
Electron distribution diagram of water. Draw the electron distribution diagram for water. Begin with 1 central water molecule. Show . the chemistry of each element within the central water molecule (all electron orbits, lone pair electrons, type of chemical bond, polarity/charge, and correct shape). What type of bond creates a water molecule? Shape of water molecule Lewis dot diagram O H 104.5o H space filling model. O-H bonds are polarized because of the difference in electronegativity between the O and H atoms. Hydrogen bonds This unequal electron distribution results in strong non-bonding interactions between water molecules - hydrogen bonds. Electron distribution diagram is also known as Lewis-dot structure. Lewis-dot structure : It shows the bonding between the atoms of a molecule and it also shows the unpaired electrons present in the molecule. In the Lewis-dot structure the valance electrons are shown by 'dot'. The given molecule is, CO_2CO2 b. electron in the first energy shell/electron in the third energy shell c. water/glucose 13. What determines the chemical behavior of an atom? 14. Sketch an electron distribution diagram for sodium: a. How many valence electrons does it have? _____ Circle the valence electron(s). b. How many protons does it have? _____ Section 3 . 15. Define ...
24 Dec 2015 — Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Sketch a water molecule showing oxygens electron shells and the covalently shared electrons. Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Why is water considered a polar molecule? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative. (This is a very important concept. Spend some time with this one!) Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Why is water considered a polar molecule? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative. (This is a very important concept. Spend some time with this one!) Diagram on Reading Guide Question 18 Draw the electron distribution diagram for water. Begin with 1 central water molecule. Show the chemistry of each element within the central water molecule (all electron orbits, lone pair electrons, type of chemical bond, polarity/charge, and correct shape). What type of bond creates a water molecule?
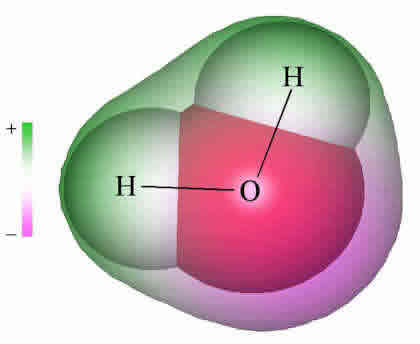
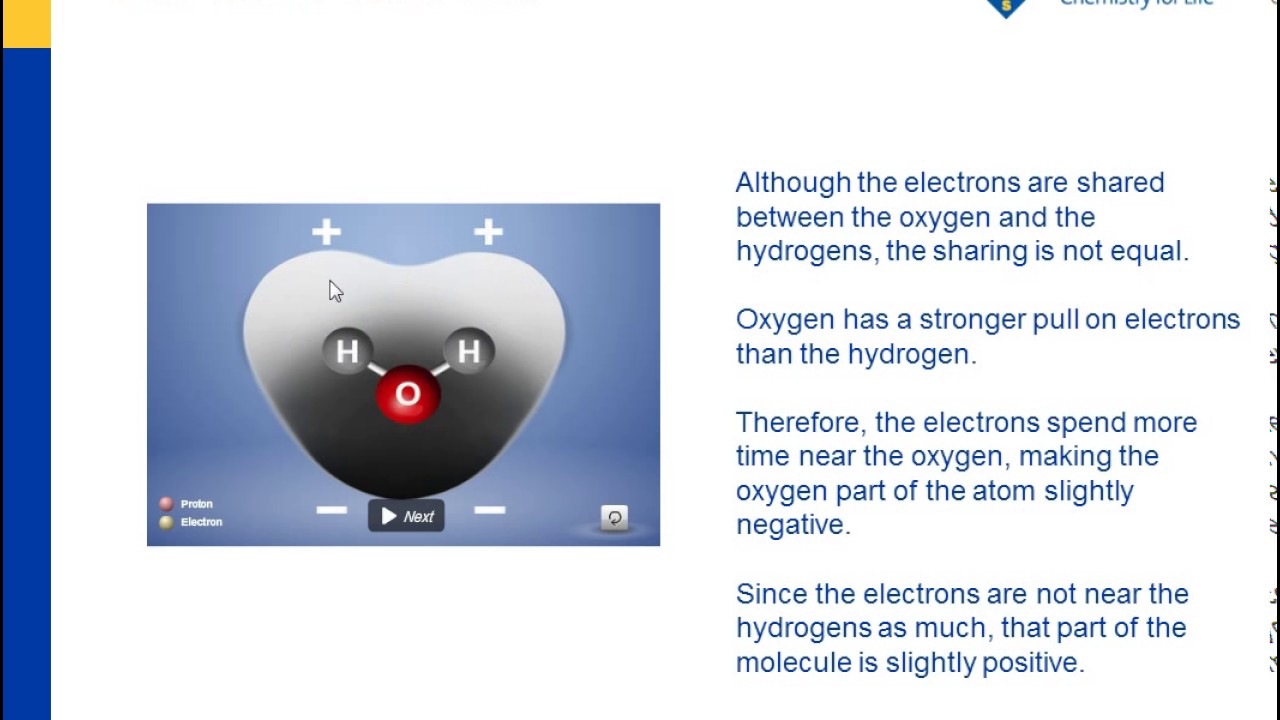
Water: Structure and Properties ... electron orbitals overlap. At larger distances two atoms ... than that of hydrogen the electron distribution is concentrated more around the former, i.e. water is electricallypolarized,havingapermanentdipolemoment of 6 10230Cm in the gas phase. The dipole moment is 18. Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Why is water considered a polar molecule? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative. (This is a very important concept. Spend some time with this one!) Electron distribution diagram of water which element is more electronegative Electrons are shared differently in ionic and covalent bonds. Covalent bonds can be non-polar or polar and react to electrostatic charges. Ionic bonds, like those in table salt (NaCl), are due to electrostatic attractive forces between their positive (Na+) and negative ... 22 Dec 2020 — Water has a partial unfavorable cost () near the oxygen atom due the unshared sets of electrons, as well as partial favorable charges () near ...
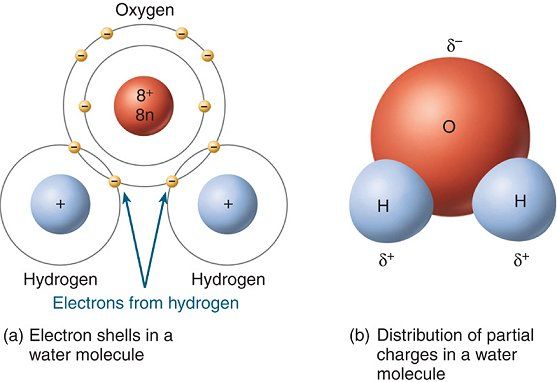
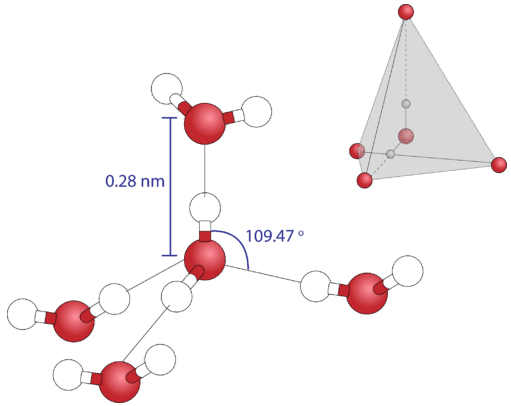
1: (a) Electronic distribution in water molecule: the tetrahedral structure of the molecular orbitals is shown, with the electrons involved in the covalent ...
Electron Distribution Table for my Bio 111 class. This site uses cookies to improve your experience and to help show content that is more relevant to your interests.
Draw the electron distribution diagram for water. Begin with 1 central water molecule. Show the chemistry of each element within the central water molecule (all electron orbits, lone pair electrons, type of chemical bond, polarity/charge, and correct shape). What type of bond creates a water molecule?
The x-ray structure factor of water measured under ambient conditions with synchrotron radiation is compared with those predicted on the basis of partial structure factors describing the nuclear positions obtained by neutron diffraction and of different assumptions for the electron distribution. The comparison indicates that a charge of approximately 0.5 e is transferred from each hydrogen ...
QUESTION 1 [26] The following questions are about the figure indicating water's versatility as a solvent. 1.1 (4) Give the electron distribution diagram for water. Identify and explain the chemical bonds between the different atoms of a water molecule. 1.2 (5) 1.3 Identify the chemical bonds that form between water molecules.
Draw the electron distribution diagram for water. Begin with 1 central water molecule. Show the chemistry of each element within the central water molecule (all electron orbits, lone pair electrons, type of chemical bond, polarity/charge, and correct shape).
Electron Configuration Diagrams | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchoolLearn the basics about Drawing electron configuration diagrams. Find out more ...
make an electron distribution diagram of water. Subject: Biology Price: Bought 3. Share With. make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Why is water considered a polar molecule? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative
Jan 09, 2022 · 39 make an electron distribution diagram of water. Solution for Draw the electron distribution diagram for water. Begin with 1 central water molecule. Show the chemistry of each element within the central ... Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Yahoo Answers has shut down as of May 4, 2021. Yahoo Answers was once a key part of Yahoo ...
The molecule of water. A molecule is an aggregation of atomic nuclei and electrons that is sufficiently stable to possess observable properties — and there are few molecules that are more stable and difficult to decompose than H 2 O. In water, each hydrogen nucleus is bound to the central oxygen atom by a pair of electrons that are shared between them; chemists call this shared electron pair ...
The distribution of electron density in a water molecule is very nearly spherical, and orientational correlation between molecules in the liquid is not "seen" by x rays. Structure and correlation ...
Electron distribution diagram of water which element is more electronegative. Why does electro-activity increase over a period? Consider sodium at the beginning of period 3 and chlorine at the end (ignoring noble gas, Argon). Think of sodium chloride as if it's covalently bonded. Both sodium and chlorine have their linked electrons at level 3.
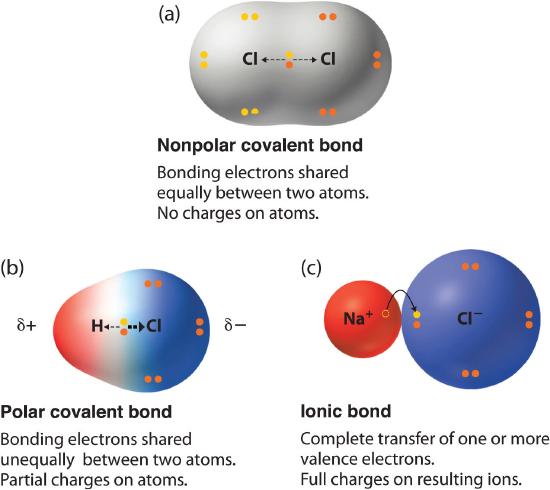
For example, the bond between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms of a water molecule is a polar covalent bond. 20. Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Why is water considered a polar molecule? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative. (This is a very important concept.
Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Why is water considered a polar molecule? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative. (This is a very important concept. Spend some time with this one!) - 3 - •• 0 : 19. Another bond type is the
Answer (1 of 3): Oxygen: 1s2, 2s2, 2p4 Hydrogen: 1s1 The bonds are polar-covalent.
Jun 01, 2000 · The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Scientific and Technical Information
Electron distribution diagram of water which element is more electronegative. Why does electro-activity increase over a period? Consider sodium at the beginning of period 3 and chlorine at the end (ignoring noble gas, Argon). Think of sodium chloride as if it's covalently bonded. Both sodium and chlorine have their linked electrons at level 3.












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/PolarConvalentBond-58a715be3df78c345b77b57d.jpg)



Comments
Post a Comment