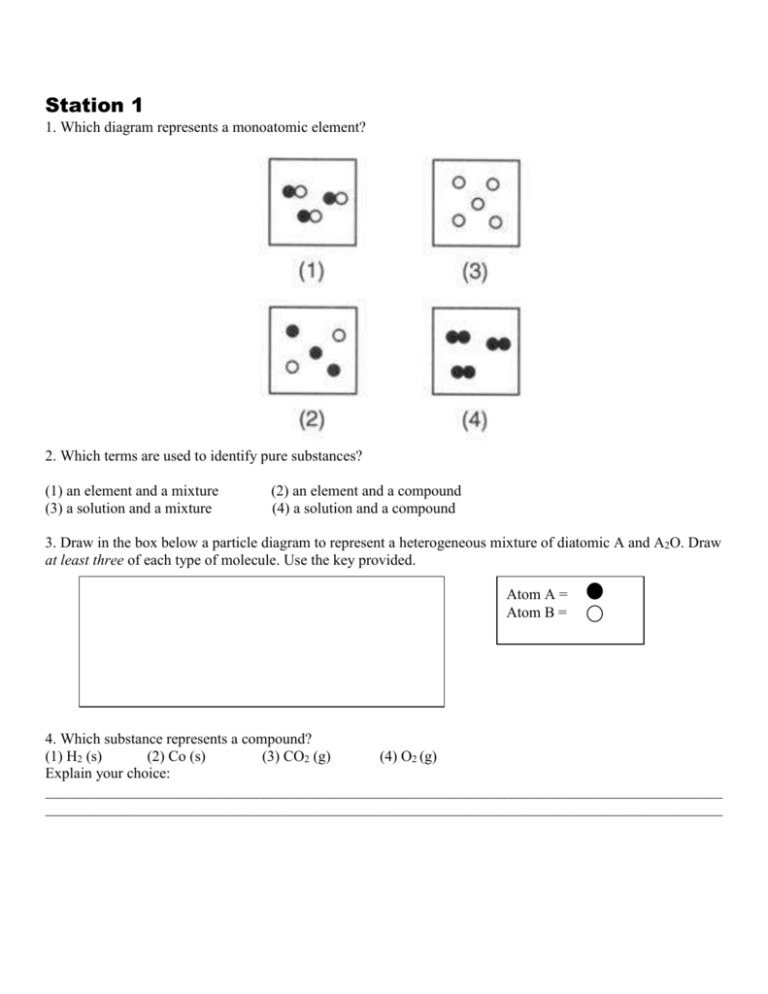
39 diagram of a mixture
The left-hand diagram is for the binary system of chloroform and carbon tetrachloride, two liquids that form nearly ideal mixtures. The solid phases are pure crystals, as in Fig. 13.1. The right-hand diagram is for the silver–copper system and involves solid phases that are solid solutions (substitutional alloys of variable composition). The area labeled s\(\aph\) is a solid solution that is ... Consider the first triangular diagram below, which shows all possible mixtures of methane, oxygen and nitrogen. Air is a mixture of about 21 volume percent oxygen, and 79 volume percent inerts (nitrogen). Any mixture of methane and air will therefore lie on the straight line between pure methane and pure air - this is shown as the blue air-line.
P-xy T-xy Diagrams. Definition: The P-xy and the T-xy are diagrams that represent the liquid and vapour equilibrium for a binary mixture. The component that is graphed is the most volatile one because is the one that will evaporate first during the distillation process. On the x-axis goes the mole fraction x,y (for liquid phase and vapour phase ...
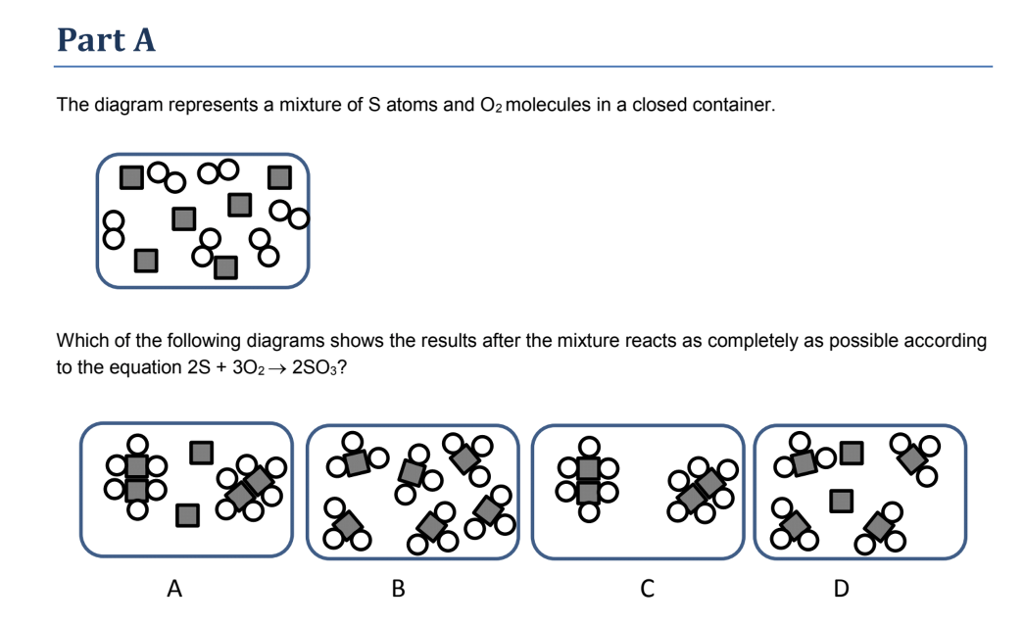
Diagram of a mixture
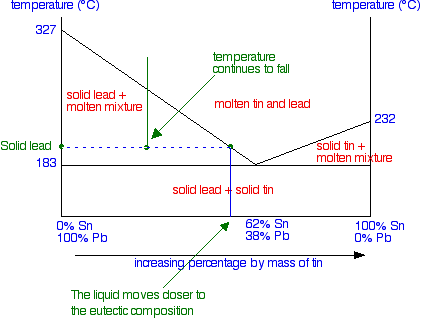
- Mixtures - more than one phase • Solubility Limit : Max concentration for which only a single phase solution occurs. Question: What is the solubility limit at 20°C? Answer: 65 wt% sugar . If Co < 65 wt% sugar: syrup If Co > 65 wt% sugar: syrup + sugar. 65 Sucrose/Water Phase Diagram Pure Sugar Temperature (°C) 0 20 40 60 80 100 The following diagrams show the molecules in two pure substances before mixing and the mixture of molecules afterwards. A particle diagram is a box in which coloured balls are draw to represent atoms or molecules. We Are Aware That All Life Stems From A Single Cell And That The Cell Is The Most Basic Unit […] Using the Phase Diagram. Suppose you have a mixture of 67% lead and 33% tin. That's the mixture from the first cooling curve plotted above. Suppose it is at a temperature of 300°C. That corresponds to a set of conditions in the area of the phase diagram labeled as molten tin and lead. Now consider what happens if you cool that mixture. Eventually the temperature will drop to a point where it ...
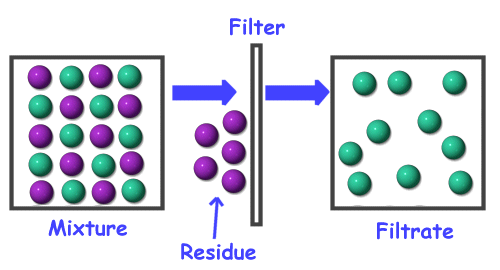
Diagram of a mixture. Figure 1: Interrelationship Diagram "Computer replacement project" is the card identifying the issue. The ideas that were brainstormed were a mixture of action steps, problems, desired results, and less-desirable effects to be handled. All these ideas went onto the diagram together. diagrams. •A particle diagram is a box in which coloured balls are draw to represent atoms or molecules. •These diagrams can represent elements and compounds, as well as their molecular composition by the types of balls and how they are connected. Element Compound Mixture of an Element and Compound Mixture of two compounds - two types of compounds present. _D_5. Mixture of a compound and an element. Part 4: Column A lists a substance. In Column B, list whether the substance is an element (E), a compound (C), a Heterogeneous Mixture (HM), or a Solution (S). (Remember a solution is a homogeneous mixture.) In Column C, list TWO physical Separating mixtures The individual substances in a mixture can be separated using different methods, depending on the type of mixture. These methods include filtration, evaporation, distillation ...
julie. Answered 5 months ago. A, because noble gases are monatomic which leaves us with A and D, but D is not a mixture since it only contains 1 kind of gas. Upvote · 4. A mixture contains more than one type of atom or molecule. The following diagrams show the molecules in two pure substances before mixing, and the mixture of molecules afterwards. Look at the diagrams closely, and label each of them as either a single substance, or a mixture. 1. _____ 2. _____ 3. _____ Elements, compounds and mixtures (2 ... SUBSTANCE MIXTURE One type of monatomic element One type of diatomic element. Mixture of monatomic elements Mixture of a binary compound and monatomic element. Mixture of 2 binary compounds Particle Diagrams One type of binary compound One type of ternary compound Applications of the PV diagram. The various processes seen above can be combined to create cycles found in most internal and external combustion engines. These diagrams are showing how pistons in engines (powered by fuel) or the various processes in a power plant, change the volume and pressure of a working fluid (ex. steam water for turbines, fuel-air mixture for engines) to create work.
The page explains what is meant by an ideal mixture and looks at how the phase diagram for such a mixture is built up and used. Important: If you haven't already read the page about saturated vapour pressure, you should follow this link before you go on. Use the BACK button on your browser to return to this page when you are ready. Ideal mixtures. An ideal mixture is one which obeys Raoult's ... 10.3.2020 · Eutectic point is a point where multiple phases meet. For the iron-carbon alloy diagram, the eutectic point is where the lines A1, A3 and ACM meet. The formation of these points is coincidental. At these points, eutectic reactions take place where a liquid phase freezes into a … For binary mixture phase diagram only two-component mixture, (e.g. A (more volatile) and B (less volatile)) are considered. There are two types of phase diagram: constant pressure and constant temperature. 5.1.3. Constant Pressure Phase Diagram The Figure 5.1 shows a constant pressure phase diagram for an ideal solution ... Air Lubricator diagram Construction and Operation Of Air Lubricator : The construction and operation of a typical force-feed type air lubricator are illustrated in Fig. Its operation is similar to the principle of simple carburetor used in the petrol engines to obtain an air-fuel mixture.
1.Which two particle diagrams represent mixtures of diatomic elements? A) mass B)density C) length D) volume 2.At STP, which physical property of aluminum always remains the same from sample to sample? A) CO2(aq) B) CO2(g) C) CO2( ) D)CO2(s) 3.Which sample of CO2 has a definite shape and a

The Diagrams Represent Some Elements Mixtures And Compounds Which Diagram Shows An Element A Pure Brainly In
dimensional diagram showing the properties of the mixture as a function of temperature, pressure, and composition. The lines in the above vapor pressure diagrams will appear on this three-dimensional diagram as surfaces, and the points, such as boiling points will be curved lines. (Because the boiling point changes with
Solved Sketch A Particle Diagram Representing A Mixture Of Hydrogen And Oxygen Gases Sketch A Particle Diagram For The Compound Formed When These Course Hero
Pure substance definition examples, compounds, mixtures diagram basics . gold, sugar, carbon, copper; aluminium, silver, boron, H 2 O, salt, diamond, etc. Matters vs Pure Substance vs Mixtures & Examples. Let's try to understand the state of matters first before understanding the types of matters or pure substance.
Pxy Diagram. The following diagram is the Pxy diagram for a benzene-toluene mixture at a constant temperature of 373K. They y-coordinates show the pressure of the mixture and the x-coordinates show the mole fraction of benzene in liquid and/or vapour phases. Higher pressure forces molecules to come closer together, which causes the molecules to ...
Temperature Entropy (T-s) Diagram. A T-s diagram is the type of diagram most frequently used to analyze energy transfer system cycles. This is because the work done by or on the system and the heat added to or removed from the system can be visualized on the T-s diagram.
What is a Mixture? Mixtures are the substances composed of two or more forms of matter. You can separate them by physical methods. Such examples include a mixture of salt and water, a mixture of sugar and water, different gases, air, etc. In any mixture, the various components do not form through any kind of chemical changes.
Welcome to our process flow diagram symbols list. Scroll down and use the table of contents on the left to navigate this page and see the different symbol types most commonly used by engineers. But first, let’s review the purpose and benefits of a PFD.
A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in Figure 2. Figure 2.
Learn to plot T-xy, P-xy and y-x diagram for a binary mixture using Aspen Plus. Objective:1. Learn how to plot Txy, Pxy, xy diagram of mixture2. Require inpu...
A heterogeneous mixture is a type of mixture that allows the components to be seen as two or more phases are present. A mixture is an example of water. Water is a homogeneous mixture of nitrogen, oxygen and smaller amounts of other compounds in the gaseous materials. Stay tuned with BYJU'S to learn more interesting topics in Chemistry.
mixture. The infinite slope at cA=0 and 1 means that it is very hard to remove final few impurities from a mixture. AM Donald 3 Phase Diagrams This is the situation if no molecular interactions to ... construct a phase diagram Πwhich contains all the essential physics.
Which particle diagram represents a mixture of three substances Answers: 3 Show answers ??? Another question on Chemistry. Chemistry, 21.06.2019 19:00. Apeak with a retention time of 407 s has a width at half-height (w1/2) of 7.6 s. a neighboring peak is eluted 17 s later with a w1/2 of 9.4 s. a compound that is known not to be retained was ...
We call the temperature at which a mixture begins to boil (when the first bubble of vapor forms) the bubble point temperature (or pressure) of the mixture. The bubble point as a function of composition is shown on a T xy diagram as the line forming the bottom of the phase envelope.
Describes how to use an interactive simulation that plots pressure versus temperature for a mixture of ethane and hexane. This simulation is located at: ht...

Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Mixtures Chemical Substance Molecule Matter Diagram Red Transparent Png
DIAGRAM IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING DIAGRAM IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING DIAGRAM IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING DIAGRAM Particle Diagram Activity Identify the diagrams as: a. Mixture, Element, Compound b. # of types of compounds or elements c. Homogenous or heterogenous SEPARATION DIAGRAMS MIXTURE SEPARATION - NO CHEMICAL CHANGE SALTWATER -----> WATER + SALT
The diagram was created in the 1960s by Kawakita Jiro and is also known as the KJ method. The purpose of an affinity diagram is to generate, organize, and consolidate information concerning a product, process, complex issue, or problem. Constructing an affinity diagram is a creative process that expresses ideas without quantifying them.
Mixtures. A mixture contains different substances that are not chemically joined to each other. For example, a packet of sweets may contain a mixture of different coloured sweets. The sweets are ...
The diagram is for a 50/50 mixture of the two liquids. That means that there are only half as many of each sort of molecule on the surface as in the pure liquids. If the proportion of each escaping stays the same, obviously only half as many will escape in any given time. If the red molecules still have the same tendency to escape as before, that must mean that the intermolecular forces ...
17.5.2021 · Today, bacteria are considered as one of the oldest forms of life on earth. Even though most bacteria make us ill, they have a long-term, mutual relationship with humans and are very much important for our survival. But before we elaborate on its uses, let us know the structure of bacteria, its classification, and the bacteria diagram in detail.

The Physics Classroom New At The Physics Classroom Classifications Of Matter For The Chemistry Teachers Among Us Here S One Of Our Newest Concept Builders From Our Chemistry Collection The Classification Of
Mixtures. A mixture is made from different substances that are not chemically joined.. For example, powdered iron and powdered sulfur mixed together makes a mixture of iron and sulfur. They can be ...
mixture. A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. compound. A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds. pure substance. A sample of matter, either a single element or a single compound, that has definite chemical and physical properties (one type of particle) element.
KS3 Science / Chemistry - Element/Compound/Mixture diagrams. Chemistry/Physics teacher. Resources include KS3 Science, AQA 9-1 Biology, Chemistry and Physics, A-Level Chemistry (AQA) and Physics (Edexcel) 14 diagrams that pupils can identify as elements, compounds or mixtures (and if mixtures, mixtures of what?).
Chapter 8 Phase Diagrams. (b) The interpretation of diagrams. Point a represents the vapor pressure of a mixture with liquid composition xA and b represents the composition of the vapor that is in equilibrium with the liquid at that pressure. Note that when two phases are in equilibrium, P = 2, so F' = 1.
The boiling point diagram shows how the equilibrium compositions of the components in a liquid mixture vary with temperature at a fixed pressure. Consider an example of a liquid mixture containing 2 components (A and B) - a binary mixture. This has the following boiling point diagram.
One type of phase diagram plots temperature against the relative concentrations of two substances in a binary mixture called a binary phase diagram, as shown at right.Such a mixture can be either a solid solution, eutectic or peritectic, among others.These two types of mixtures result in very different graphs.
phase diagram, the alloy will become fully solid at the eutectic temperature, shown as the eutectic isotherm on the phase diagram. Construction: The region below the eutectic isotherm, and outside the solid solution region, will be a solid mixture of alpha and beta, that is, a two phase region, and the diagram is labeled to reflect this.
Using the Phase Diagram. Suppose you have a mixture of 67% lead and 33% tin. That's the mixture from the first cooling curve plotted above. Suppose it is at a temperature of 300°C. That corresponds to a set of conditions in the area of the phase diagram labeled as molten tin and lead. Now consider what happens if you cool that mixture. Eventually the temperature will drop to a point where it ...
The following diagrams show the molecules in two pure substances before mixing and the mixture of molecules afterwards. A particle diagram is a box in which coloured balls are draw to represent atoms or molecules. We Are Aware That All Life Stems From A Single Cell And That The Cell Is The Most Basic Unit […]
- Mixtures - more than one phase • Solubility Limit : Max concentration for which only a single phase solution occurs. Question: What is the solubility limit at 20°C? Answer: 65 wt% sugar . If Co < 65 wt% sugar: syrup If Co > 65 wt% sugar: syrup + sugar. 65 Sucrose/Water Phase Diagram Pure Sugar Temperature (°C) 0 20 40 60 80 100

























Comments
Post a Comment